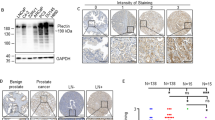
Abstract
Extracellular proteases are recognized as critical factors in the progression of a number of carcinomas, including prostate cancer. Matrix metalloproteases (MMP) are important in processes of tumor growth, invasion and dissemination, but other classes of proteases, such as serine and cysteine proteases, also contribute. We utilized the TRAMP model for prostate cancer to elucidate proteases involved in prostate cancer progression. General proteomic analysis was performed on normal murine prostate, early TRAMP tumors and advanced TRAMP tumors, as well as normal and involved lymph nodes. Zymography and antigenic analyses revealed increased expression of mainly pro-MMP in early TRAMP tumors but substantial elaboration of activated MMP only in late TRAMP tumors. Progressive increase in cysteine, serine and certain membrane-bound proteases from normal to early to advanced prostate tumors, was also seen. Our results implicate pericellular proteases as initiators of major proteolytic cascades during tumor progression and suggest targets for maximal therapeutic effect.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim SJ et al. Prognostic impact of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (PA), PA inhibitor type-1, and tissue-type PA antigen levels in node-negative breast cancer: a prospective study on multicenter basis. Clin Cancer Res 1998; 4: 177–182.
Powell WC et al. Expression of the metalloproteinase matrilysin in DU-145 cells increases their invasive potential in severe combined immunodeficient mice. Cancer Res 1993; 53: 417–422.
Shalinsky DR et al. Broad antitumor and antiangiogenic activities of AG3340, a potent and selective MMP inhibitor undergoing advanced oncology clinical trials. Ann NY Acad Sci 1999; 878: 236–270.
Van Veldhuizen PJ, Sadasivan R, Cherian R, Wyatt A . Urokinase-type plasminogen activator expression in human prostate carcinomas. Am J Med Sci 1996; 312: 8–11.
Bubley GJ et al. Eligibility and response guidelines for phase II clinical trials in androgen-independent prostate cancer: recommendations from the Prostate-Specific Antigen Working Group. J Clin Oncol 1999; 17: 3461–3467.
Doherty A et al. Correlation of the osteoblastic phenotype with prostate-specific antigen expression in metastatic prostate cancer: implications for paracrine growth. J Pathol 1999; 188: 278–281.
Rittenhouse HG, Finlay JA, Mikolajczyk SD, Partin AW . Human kallikrein 2 (hK2) and prostate-specific antigen (PSA): two closely related, but distinct, kallikreins in the prostate. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 1998; 35: 275–368.
Lin B et al. Prostate-localized and androgen-regulated expression of the membrane-bound serine protease TMPRSS2. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 4180–4184.
Takeuchi T, Shuman MA, Craik CS . Reverse biochemistry: use of macromolecular protease inhibitors to dissect complex biological processes and identify a membrane-type serine protease in epithelial cancer and normal tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 11054–11061.
Miyake H et al. Elevation of serum levels of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its receptor is associated with disease progression and prognosis in patients with prostate cancer. Prostate 1999; 39: 123–129.
Crowley CW et al. Prevention of metastasis by inhibition of the urokinase receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993; 90: 5021–5025.
Wan XS et al. Treatment with soybean-derived Bowman Birk inhibitor increases serum prostate-specific antigen concentration while suppressing growth of human prostate cancer xenografts in nude mice. Prostate 1999; 41: 243–252.
Shepherd FA et al. Randomized double-blind pacebo-controlled trial of marimastat in patients with small cell lung cancer (SCLC) following response to first-line chemotherapy: an NCIC-CTG and EORTC study. Am Soc Clin Oncol 2001; 20: 4a.
Greenberg NM et al. Prostate cancer in a transgenic mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92: 3439–3443.
Takeuchi T et al. Cellular localization of membrane-type serine protease 1 and identification of protease-activated receptor-2 and single-chain urokinase-type plasminogen activator as substrates. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 26333–26342.
Furuya M et al. Clarification of the active gelatinolytic sites in human ovarian neoplasms using in situ zymography. Hum Pathol 2001; 32: 163–168.
Kristensen P, Eriksen J, Blasi F, Dano K . Two alternatively spliced mouse urokinase receptor mRNAs with different histological localization in the gastrointestinal tract. J Cell Biol 1991; 115: 1763–1771.
Unkeless JC et al. An enzymatic function associated with transformation of fibroblasts by oncogenic viruses. I. Chick embryo fibroblast cultures transformed by avian RNA tumor viruses. J Exp Med 1973; 137: 85–111.
Gururajan R, Grenet J, Lahti JM, Kidd VJ . Isolation and characterization of two novel metalloproteinase genes linked to the Cdc2L locus on human chromosome 1p36.3. Genomics 1998; 52: 101–106.
Sternlicht MD et al. The stromal proteinase MMP3/stromelysin-1 promotes mammary carcinogenesis. Cell 1999; 98: 137–146.
Upadhyay J et al. Membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) and MMP-2 immunolocalization in human prostate: change in cellular localization associated with high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Clin Cancer Res 1999; 5: 4105–4110.
Murphy G, Gavrilovic J . Proteolysis and cell migration: creating a path? Curr Opin Cell Biol 1999; 11: 614–621.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs Zena Werb and Mark Sternlicht for anti-MMP-2 and MMP-9 antibodies, Drs Charles Craik and Toshi Takeuchi for antibody to MT-SP1, and Dr Lynn Matrisian for the gift of anti-MMP-7 antibody. This publication was made possible by funds received from the Cancer Research Fund, under Interagency Agreement #97–12013 (University of California, Davis contract #98–00924V) with the Department of Health Services, Cancer Research Section, and from NIH/NHLBI P01 CA72006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bok, R., Hansell, E., Nguyen, T. et al. Patterns of protease production during prostate cancer progression: proteomic evidence for cascades in a transgenic model. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 6, 272–280 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.pcan.4500676
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.pcan.4500676
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Proteomic profiling of the tumor microenvironment: recent insights and the search for biomarkers
Genome Medicine (2014)
-
Localized matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 activity in the rat ventral prostate during the first week of postnatal development
Histochemistry and Cell Biology (2008)
-
The promise of genetically engineered mice for cancer prevention studies
Nature Reviews Cancer (2005)