Abstract
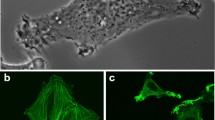
The role of myosin phosphorylation by myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) in regulating the invasiveness of metastatic cancer cells was investigated using the Dunning rat prostatic adenocarcinoma cell line, Mat Ly Lu, and in vitro invasion assay. Treatment with MLCK inhibitors resulted in marked reduction of invasiveness, which was principally due to impaired cellular motility, whereas the ability to survive and proliferate, to adhere to matrix, and to secrete gelatinases were minimally affected.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meyer T, Hart IR . Mechanisms of tumor metastasis. Eur J Cancer 1998; 34: 214–221.
Spudich JA . In persuit of myosin function. Cell Regul 1989; 1: 1–11.
Somlyo AP, Somlyo AV . Signal transduction by G-proteins. Rho-kinase and protein phosphatase to smooth muscle and non-muscle myosin II. J Physiol 2000; 522: 177–185.
Tan JL, Ravid S, Spudich JA . Control of nonmuscle myosins by phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem 1992; 61: 721–759.
Quax PHA et al. Plasminogen activator and matrix metalloproteinase production and extracellular matrix degradation by rat prostate cancer cells in vitro: correlation with metastatic behaviour in vivo. Prostate 1997; 32: 196–204.
Gillespie GY et al. Glioma migration can be blocked by nontoxic inhibitors of myosin II. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 2076–2082.
Klemke RL et al. Regulation of cell motility by mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Cell Biol 1997; 137: 481–492.
Yoshioka K et al. Small GTP-binding protein Rho stimulates the actomyosin system, leading to invasion of tumor cells. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 5146–5154.
Itoh K et al. An essential part for Rho-associated kinase in the transcellular invasion of tumor cells. Nat Med 1999; 5: 221–225.
Nguyen DHD et al. Myosin light chain kinase functions downstream of Ras/ERK to promote migration of urokinase-type plasminogen activator-stimulated cells in an integrin-selective manner. J Cell Biol 1999; 146: 149–164.
Cooper CR et al. Adhesion and invasion potential of rat prostatic cancer cells: correlation with metastatic potential. Invasion Metast 1993; 13: 178–184.
Saitoh J et al. Selective inhibition of catalytic activity of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem 1987; 262: 7796–7801.
Amano M et al. Phosphorylation and activation of myosin by Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase). J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 20246–20249.
Bresnick AR . Molecular mechanisms of nonmuscle myosin-II regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1999; 11: 26–33.
Eyk JE et al. Different molecular mechanisms for Rho family GTPase-dependent. Ca2+-independent contraction of smooth muscle. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 23433–23439.
Komatsu S et al. Identification of MAPKAPK homolog (MAPAPK-4) as a myosin II regulatory light chain kinase in sea urchin egg extracts. Arch Biochem Biophys 1997; 343: 55–62.
Isemura M et al. Myosin light chain kinase inhibitors ML-7 and ML-9 inhibit mouse lung carcinoma cell attachment to the fibronectin substratum. Cell Biol Int Rep 1991; 15: 965–972.
Brenner W et al. Differential inhibition of renal cancer cell invasion mediated by fibronectin, collagen IV and laminin. Cancer Lett 2000; 155: 199–205.
Boxberger H-J, Paweletz N . Influences of various substrata on morphology, motility and invasiveness of rat tumour cells. II. Studies on the highly metastatic variants BSp 73 ASML. Anticancer Res 1990; 10: 1265–1274.
Mohler JL, Levy F, Sharief Y . Metastatic potential and substrate dependence of cell motility and attachment in the Dunning R-3327 rat prostatic adenocarcinoma model. Cancer Res 1991; 51: 6580–6585.
Niki I et al. Presence and possible involvement of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases in insulin release from the rat pancreatic β cell. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1993; 191: 255–261.
Choi OH, Adelstein RS, Beaven MA . Secretion from rat basophilic RBL-2H3 cells is associated with diphosphorylation of myosin light chains by myosin light chain kinase as well as phosphorylation by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 536–541.
Hecht G, Koutsouris A . Myosin regulation of NKCC1: effects on cAMP-mediated CL− secretion in intestinal epithelial. Am J Physiol 1999; 277(Part 1): 441–447.
Belotti D et al. Paclitaxel (Taxol(R)) inhibits motility of paclitaxel-resistant human ovarian carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 1996; 2: 1725–1730.
Terzis AJA et al. Proliferation, migration and invasion of human glioma cells exposed to antifolate drugs. Int J Cancer 1993; 54: 112–118.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by a grant from Mahidol University and by The Thailand Research Fund to RT. The authors wish to thank Dr K Pienta for his generous gift of the Dunning cell lines and Dr P Wilairat for his critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tohtong, R., Phattarasakul, K., Jiraviriyakul, A. et al. Dependence of metastatic cancer cell invasion on MLCK-catalyzed phosphorylation of myosin regulatory light chain. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 6, 212–216 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.pcan.4500663
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.pcan.4500663
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Targeting the cytoskeleton against metastatic dissemination
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2021)
-
Marine alkaloid monanchoxymycalin C: a new specific activator of JNK1/2 kinase with anticancer properties
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Blockade of ROCK inhibits migration of human primary keratinocytes and malignant epithelial skin cells by regulating actomyosin contractility
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Comparative proteomics analysis of oral cancer cell lines: identification of cancer associated proteins
Proteome Science (2014)
-
Loss of PTEN induces microtentacles through PI3K-independent activation of cofilin
Oncogene (2013)