Abstract
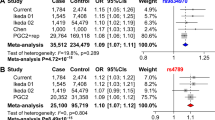
Previous studies have suggested that genetic variations in the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene may be associated with several neuropsychiatric diseases including bipolar disorder. The present study examined a microsatellite polymorphism located approximately 1.0 kb upstream of the translation initiation site of the BDNF gene for novel sequence variations, association with bipolar disorder, and effects on transcriptional activity. Detailed sequencing analysis revealed that this polymorphism is not a simple dinucleotide repeat, but it is highly polymorphic with a complex structure containing three types of dinucleotide repeats, insertion/deletion, and nucleotide substitutions that gives rise to a total of 23 novel allelic variants. We obtained evidence supporting the association between this polymorphic region (designated as BDNF-linked complex polymorphic region (BDNF-LCPR)) and bipolar disorder. One of the major alleles (‘A1’ allele) was significantly more common in patients than in controls (odds ratio 2.8, 95% confidential interval 1.5–5.3, P=0.001). Furthermore, a luciferase reporter gene assay in rat primary cultured neurons suggests that this risk allele (A1) has a lower-transcription activity, compared to the other alleles. Our results suggest that the BDNF-LCPR is a functional variation that confers susceptibility to bipolar disorder and affects transcriptional activity of the BDNF gene.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Maisonpierre PC, Belluscio L, Friedman B, Alderson RF, Wiegand SJ, Furth ME et al. NT-3, BDNF, and NGF in the developing rat nervous system: parallel as well as reciprocal patterns of expression. Neuron 1990; 5: 501–509.
Thoenen H . Neurotrophins and neuronal plasticity. Science 1995; 270: 593–598.
Duman RS . Synaptic plasticity and mood disorders. Mol Psychiatry 2002; 7(Suppl 1): S29–S34.
Knable MB, Barci BM, Webster MJ, Meador-Woodruff J, Torrey EF . Molecular abnormalities of the hippocampus in severe psychiatric illness: postmortem findings from the Stanley Neuropathology Consortium. Mol Psychiatry 2004; 9: 609–620.
Nibuya M, Morinobu S, Duman RS . Regulation of BDNF and trkB mRNA in rat brain by chronic electroconvulsive seizure and antidepressant drug treatments. J Neurosci 1995; 15: 7539–7547.
Hashimoto R, Takei N, Shimazu K, Christ L, Lu B, Chuang DM . Lithium induces brain-derived neurotrophic factor and activates TrkB in rodent cortical neurons: an essential step for neuroprotection against glutamate excitotoxicity. Neuropharmacology 2002; 43: 1173–1179.
Green E, Craddock N . Brain-derived neurotrophic factor as a potential risk locus for bipolar disorder: evidence, limitations, and implications. Curr Psychiatry Rep 2003; 5: 469–476.
Neves-Pereira M, Mundo E, Muglia P, King N, Macciardi F, Kennedy JL . The brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene confers susceptibility to bipolar disorder: evidence from a family-based association study. Am J Hum Genet 2002; 71: 651–655.
Sklar P, Gabriel SB, McInnis MG, Bennett P, Lim YM, Tsan G et al. Family-based association study of 76 candidate genes in bipolar disorder: BDNF is a potential risk locus. Mol Psychiatry 2002; 7: 579–593.
Geller B, Badner JA, Tillman R, Christian SL, Bolhofner K, Cook Jr EH . Linkage disequilibrium of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism in children with a prepubertal and early adolescent bipolar disorder phenotype. Am J Psychiatry 2004; 161: 1698–1700.
Oswald P, Del-Favero J, Massat I, Souery D, Claes S, Van Broeckhoven C et al. Non-replication of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) association in bipolar affective disorder: a Belgian patient-control study. Am J Med Genet 2004; 129B: 34–35.
Skibinska M, Hauser J, Czerski PM, Leszczynska-Rodziewicz A, Kosmowska M, Kapelski P et al. Association analysis of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene Val66Met polymorphism in schizophrenia and bipolar affective disorder. World J Biol Psychiatry 2004; 5: 215–220.
Neves-Pereira M, Cheung JK, Pasdar A, Zhang F, Breen G, Yates P et al. BDNF gene is a risk factor for schizophrenia in a Scottish population. Mol Psychiatry 2005; 10: 208–212.
Hong CJ, Huo SJ, Yen FC, Tung CL, Pan GM, Tsai SJ . Association study of a brain-derived neurotrophic-factor genetic polymorphism and mood disorders, age of onset and suicidal behavior. Neuropsychobiology 2003; 48: 186–189.
Nakata K, Ujike H, Sakai A, Uchida N, Nomura A, Imamura T et al. Association study of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene with bipolar disorder. Neurosci Lett 2003; 337: 17–20.
Kunugi H, Iijima Y, Tatsumi M, Yoshida M, Hashimoto R, Kato T et al. No association between the Val66Met polymorphism of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene and bipolar disorder in a Japanese population: a multicenter study. Biol Psychiatry 2004; 56: 376–378.
Pröschel M, Saunders A, Roses AD, Muller CR . Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the human gene for the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Hum Mol Genet 1992; 1: 353.
Strauss J, Barr CL, George CJ, King N, Shaikh S, Devlin B et al. Association study of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in adults with a history of childhood onset mood disorder. Am J Med Genet 2004; 131B: 16–19.
Krebs MO, Guillin O, Bourdell MC, Schwartz JC, Olie JP, Poirier MF et al. Brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene variants association with age at onset and therapeutic response in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 2000; 5: 558–562.
Muglia P, Vicente AM, Verga M, King N, Macciardi F, Kennedy JL . Association between the BDNF gene and schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 2003; 8: 146–147.
Comings DE . Polygenic inheritance and micro/minisatellites. Mol Psychiatry 1998; 3: 21–31.
American Psychiatric Association. American Psychiatric Association: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Association: Washington DC, 1994.
Numakawa T, Yamagishi S, Adachi N, Matsumoto T, Yokomaku D, Yamada M et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor-induced potentiation of Ca(2+) oscillations in developing cortical neurons. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 6520–6529.
Tadokoro K, Hashimoto R, Tatsumi M, Kamijima K, Kunugi H . Analysis of enhancer activity of a dinucleotide repeat polymorphism in the neurotrophin-3 gene and its association with bipolar disorder. Neuropsychobiology 2004; 50: 206–210.
Aoyama M, Asai K, Shishikura T, Kawamoto T, Miyachi T, Yokoi T et al. Human neuroblastomas with unfavorable biologies express high levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA and a variety of its variants. Cancer Lett 2001; 164: 51–60.
Garzon D, Yu G, Fahnestock M . A new brain-derived neurotrophic factor transcript and decrease in brain-derived neurotrophic factor transcripts 1, 2 and 3 in Alzheimer's disease parietal cortex. J Neurochem 2002; 82: 1058–1064.
Koizumi H, Hashimoto K, Shimizu E, Iyo M, Mashimo Y, Hata A . Further analysis of microsatellite marker in the BDNF gene. Am J Med Genet 2005; 135: 103.
Egan MF, Kojima M, Callicott JH, Goldberg TE, Kolachana BS, Bertolino A et al. The BDNF val66met polymorphism affects activity-dependent secretion of BDNF and human memory and hippocampal function. Cell 2003; 112: 257–269.
Dempster E, Toulopoulou T, McDonald C, Bramon E, Walshe M, Filbey F et al. Association between BDNF val66 met genotype and episodic memory. Am J Med Genet 2005; 134: 73–75.
Sweeney JA, Kmiec JA, Kupfer DJ . Neuropsychologic impairments in bipolar and unipolar mood disorders on the CANTAB neurocognitive battery. Biol Psychiatry 2000; 48:674–684.
Deckersbach T, Savage CR, Reilly-Harrington N, Clark L, Sachs G, Rauch SL . Episodic memory impairment in bipolar disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder: the role of memory strategies. Bipolar Disord 2004; 6: 233–244.
Sasaki T, Dai XY, Kuwata S, Fukuda R, Kunugi H, Hattori M et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene and schizophrenia in Japanese subjects. Am J Med Genet 1997; 74: 443–444.
Hawi Z, Straub RE, O'Neill A, Kendler KS, Walsh D, Gill M . No linkage or linkage disequilibrium between brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) dinucleotide repeat polymorphism and schizophrenia in Irish families. Psychiatry Res 1998; 81: 111–116.
Wassink TH, Nelson JJ, Crowe RR, Andreasen NC . Heritability of BDNF alleles and their effect on brain morphology in schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet 1999; 88: 724–728.
Virgos C, Martorell L, Valero J, Figuera L, Civeira F, Joven J et al. Association study of schizophrenia with polymorphisms at six candidate genes. Schizophr Res 2001; 49: 65–71.
Acknowledgements
We thank Shizuno T and Okada K for their technical assistance in laboratory. This study was supported by the Health and Labor Sciences Research Grants (Research on Psychiatric and Neurological Diseases and Mental Health), the Japan Health Sciences Foundation (Research on Health Sciences focusing on Drug innovation) and Mitsubishi Pharma Research Foundation (HK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website (http://www.nature.com/mp).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okada, T., Hashimoto, R., Numakawa, T. et al. A complex polymorphic region in the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene confers susceptibility to bipolar disorder and affects transcriptional activity. Mol Psychiatry 11, 695–703 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001822
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001822
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Mutation in Smek2 regulating hepatic glucose metabolism causes hypersarcosinemia and hyperhomocysteinemia in rats
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Forebrain-specific ablation of phospholipase Cγ1 causes manic-like behavior
Molecular Psychiatry (2017)
-
SorCS2 is required for BDNF-dependent plasticity in the hippocampus
Molecular Psychiatry (2016)
-
Molecular and genetic basis of depression
Journal of Genetics (2014)
-
BDNF Val66Met Impairs Fluoxetine-Induced Enhancement of Adult Hippocampus Plasticity
Neuropsychopharmacology (2012)