Abstract
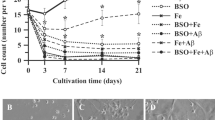
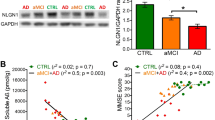
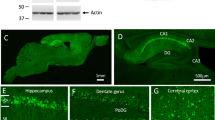
Current evidence supports the notion that β-amyloid deposits or Aβ intermediates may be responsible for the pathogenesis in Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients. In the present work, we have assessed the neuroprotective effect of the chronic intraperitoneal administration of a five-amino-acid β-sheet breaker peptide (iAβ5p) on the rat behavioral deficit induced by the intrahippocampal Aβ-fibrils injection. At 1 month after the injection, animals showed a partial reduction of the amyloid deposits formed and a decreased astrocytic response around the injection site. More importantly, we report that following the iAβ5p treatment, hippocampal-dependent spatial learning paradigms, including the standard Morris water maze and a working memory analysis, showed a significant prevention from impairments induced by Aβ deposits in the dorsal hippocampus. Thus, it is possible that a noninvasive treatment such as the one presented here with β-sheet breaker peptides may be used as a potential therapy for AD patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Walsh DM, Klyubin I, Fadeeva JV, Cullen WK, Anwyl R, Wolfe MS et al. Naturally secreted oligomers of amyloid β protein potently inhibit hippocampal long-term potentiation in vivo. Nature 2002; 416: 535–539.
Hardy JL, Selkoe DJ . The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 2002; 297: 353–356.
Pike CJ, Burdick D, Walencewicz AJ, Glabe CG, Cotman CW . Neurodegeneration induced by beta-amyloid peptides in vitro: the role of peptide assembly state. J Neurosci 1993; 13: 1676–1687.
Schenk D, Barbour R, Dunn W, Gordon G, Grajeda H, Guido T et al. Immunization with amyloid-β attenuates Alzheimer-disease-like pathology in the PDAPP mouse. Nature 1999; 400: 173–177.
Janus C, Pearson J, McLaurin J, Mathews PM, Jiang Y, Schmidt SD et al. Aβ peptide immunization reduces behavioural impairment and plaques in a model of Alzheimer's disease. Nature 2000; 408: 979–982.
Morgan D, Diamond DM, Gottschall PE, Ugen KE, Dickey C, Hardy J et al. Aβ peptide vaccination prevents memory loss in an animal model of Alzheimer's disease. Nature 2000; 408: 982–985.
DeMattos RB, Bales KR, Cummins DJ, Dodart JC, Paul SM, Holtzman DM . Peripheral anti-Aβ antibody alters CNS and plasma Aβ clearance and decreases brain Aβ burden in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 8850–8855.
Bard F, Cannon C, Barbour R, Burke RL, Games D, Grajeda H et al. Peripherally administered antibodies against amyloid β-peptide enter the central nervous system and reduce pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Nat Med 2002; 6: 916–919.
Check E . Nerve inflammation halts trial for Alzheimer's drug. Nature 2002; 415: 462.
Bishop GM, Robinson SR, Smith MA, Perry G, Atwood CS . Call for Elan to publish Alzheimer's trial details. Nature 2002; 416: 677.
Pfeifer M, Boncristiano S, Bondolfi L, Stalder A, Deller T, Staunfenbiel M et al. Cerebral hemorrhage after passive anti-Aβ immunotherapy. Science 2002; 298: 1379.
Bronfman FC, Garrido J, Alvarez A, Morgan C, Inestrosa NC . Laminin inhibits amyloid-beta-peptide fibrillation. Neurosci Lett 1996; 218: 201–203.
Morgan C, Bugueno MP, Garrido J, Inestrosa NC . Laminin affects polymerization, depolymerization and neurotoxicity of Abeta peptide. Peptides 2002; 23: 1229–1240.
Pappolla M, Bozner P, Soto C, Shao H, Robakis NK, Zagorski M et al. Inhibition of Alzheimer beta-fibrillogenesis by melatonin. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 7185–7188.
Ono K, Hasegawa K, Yoshiike Y, Takashima A, Yamada M, Naiki H . Nordihydroguaiaretic acid potently breaks down pre-formed Alzheimer's beta-amyloid fibrils in vitro. J Neurochem 2002; 81: 434–440.
Ono K, Yoshiike Y, Takashima A, Hasegawa K, Naiki H, Yamada M . Potent anti-amyloidogenic and fibril-destabilizing effects of polyphenols in vitro: implications for the prevention and therapeutics of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem 2003; 87: 172–181.
Solomon B, Koppel R, Frankel D, Hanan-Aharon E . Disaggregation of Alzheimer beta-amyloid by site-directed mAb. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 4109–4112.
Fraser PE, Nguyen JT, McLachlan DR, Abraham CR, Kirschner DA . Alpha 1-antichymotrypsin binding to Alzheimer A beta peptides is sequence specific and induces fibril disaggregation in vitro. J Neurochem 1993; 61: 298–305.
Kim JE, Lee M . Fullerene inhibits beta-amyloid peptide aggregation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003; 303: 576–579.
Luo Y, Smith JV, Paramasivam V, Burdick A, Curry KJ, Buford JP, Khan I, Netzer WJ, Xu H, Butko P . Inhibition of amyloid-beta aggregation and caspase-3 activation by the Ginkgo biloba extract EGb761. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 12197–12202, Epub 2002 Sep 04.
Kiuchi Y, Isobe Y, Fukushima K . Type IV collagen prevents amyloid beta-protein fibril formation. Life Sci 2002; 70: 1555–1564.
Gordon DJ, Sciarretta KL, Meredith SC . Inhibition of beta-amyloid(40) fibrillogenesis and disassembly of beta-amyloid(40) fibrils by short beta-amyloid congeners containing N-methyl amino acids at alternate residues. Biochemistry 2001; 40: 8237–8245.
Tjernberg LO, Naslund J, Lindqvist F, Johansson J, Karlstrom AR, Thyberg J, Terenius L, Nordstedt C . Arrest of beta-amyloid fibril formation by a pentapeptide ligand. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 8545–8548.
Soto C, Sigurdsson EM, Morelli L, Kumar RA, Castano EM, Frangione B . Beta-sheet breaker peptides inhibit fibrillogenesis in a rat brain model of amyloidosis: implications for Alzheimer's therapy. Nat Med 1998; 4: 822–826.
Nakagami Y, Nishimura S, Murasugi T, Kaneko I, Meguro M, Marumoto S, Kogen H, Koyama K, Oda T . A novel beta-sheet breaker, RS-0406, reverses amyloid beta-induced cytotoxicity and impairment of long-term potentiation in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 2002; 137: 676–682.
Soto C, Kindy MS, Baumann M, Frangione B . Inhibition of Alzheimer's amyloidosis by peptides that prevent β-sheet conformation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1996; 226: 672–680.
Soto C . Plaque busters: strategies to inhibit amyloid formation in Alzheimer's disease. Mol Med Today 1999; 5: 343–350.
Poduslo JF, Curran GL, Kumar A, Frangione B, Soto C . Beta-sheet breaker peptide inhibitor of Alzheimer's amyloidogenesis with increased blood-brain barrier permeability and resistance to proteolytic degradation in plasma. J Neurobiol 1999; 39: 371–382.
Permanne B, Adessi C, Saborio GP, Fraga S, Frossard MJ, Van Dorpe J et al. Reduction of amyloid load and cerebral damage in a transgenic mousemodel of Alzheimer's disease by treatment with a β-sheet breaker peptide. FASEB J 2002; 16: 860–862.
Morris RGM . Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Meth 1984; 11: 47–60.
De Ferrari GV, Chacón MA, Barría MI, Garrido JL, Godoy JA, Olivares G et al. Activation of Wnt signaling rescues neurodegeneration and behavioral impairments induced by β-amyloid fibrils. Mol Psychiatry 2003; 8: 195–208.
Frick KM, Baxter MG, Markowska AL, Olton DS, Price DL . Age-related spatial reference and working memory deficits assessed in the water maze. Neurobiol Aging 1995; 16: 149–160.
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986). The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic Press: New York.
Elghetany MT, Saleem A . Methods for staining amyloid in tissues: a review. Stain Technol 1988; 63: 201–212.
Puchtler H, Sweat F, Levine M . On the binding of Congo Red by amyloid. J Histochem Cytochem 1961; 10: 355–364.
Inestrosa N, De Ferrari G, Garrido J, Alvarez A, Olivares G, Barría M et al. Wnt signaling involvement in β-amyloid-dependent neurodegeneration. Neurochem Int 2002; 41: 341–344.
Münch G, Robinson SR . Potential neurotoxic inflammatory responses to Aβ vaccination in humans. J Neural Transm 2002; 109: 1081–1087.
Imbimbo BP . Toxicity of β-amyloid vaccination in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol 2002; 51: 794.
McLaurin J, Cecal R, Kierstead ME, Tian X, Phinney AL, Manea M et al. Therapeutically effective antibodies against amyloid-β peptide target amyloid-β residues 4–0 and inhibit cytotoxicity and fibrillogenesis. Nat Med 2002; 8: 1263–1269.
Dodart JC, Bales KR, Gannon KS, Greene SJ, DeMattos RB, Mathis C et al. Immunization reverses memory deficits without reducing brain Aβ burden in Alzheimer's disease model. Nat Neurosci 2002; 5: 452–457.
Soto C, Brañes MC, Alvarez J, Inestrosa NC . Structural determinants of the Alzheimer's amyloid β-peptide. J Neurochem 1994; 63: 1191–1198.
Sigurdsson EM, Permanne B, Soto C, Wisniewski T, Frangione B . In vivo reversal of amyloid-β lesions in rat brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2000; 59: 11–17.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Alicia Minniti for her help with the manuscript. FONDAP-Biomedicine Grant No. 13980001. Support of the Millennium Institute of Fundamental and Applied Biology (MIFAB) is also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chacón, M., Barría, M., Soto, C. et al. β-sheet breaker peptide prevents Aβ-induced spatial memory impairments with partial reduction of amyloid deposits. Mol Psychiatry 9, 953–961 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001516
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001516
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Blockade of Type 2A Protein Phosphatase Signaling Attenuates Complement C1q-Mediated Microglial Phagocytosis of Glutamatergic Synapses Induced by Amyloid Fibrils
Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
Amyloid Fibril–Induced Astrocytic Glutamate Transporter Disruption Contributes to Complement C1q-Mediated Microglial Pruning of Glutamatergic Synapses
Molecular Neurobiology (2020)
-
Activation of mGluR1 Mediates C1q-Dependent Microglial Phagocytosis of Glutamatergic Synapses in Alzheimer’s Rodent Models
Molecular Neurobiology (2019)
-
Investigation of thymol effect on learning and memory impairment induced by intrahippocampal injection of amyloid beta peptide in high fat diet- fed rats
Metabolic Brain Disease (2017)
-
Intranasal H102 Peptide-Loaded Liposomes for Brain Delivery to Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
Pharmaceutical Research (2015)