Abstract
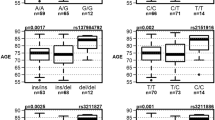
Cholesterol and 24S-hydroxycholesterol are involved in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Increased serum cholesterol concentrations have been detected in patients with AD. 24S-Hydroxycholesterol is the primary cholesterol elimination product of the brain and possesses neurotoxic properties in vitro. The enzyme catalyzing the conversion of cholesterol to 24S-hydroxycholesterol, cholesterol 24S-hydroxylase (CYP46), is mainly expressed in neurons. Concentrations of 24S-hydroxycholesterol in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and serum differ significantly between AD patients and non-demented subjects. To test the hypothesis if polymorphisms in the CYP46 gene might influence the function of the respective enzyme and thus cholesterol metabolism in the human brain, we screened for polymorphisms in 114 AD patients and 144 healthy controls. Two intronic single nucleotide polymorphisms were observed and their allelic distribution was investigated. In our study sample, carriers of the C allele of the IVS3+43C → T polymorphism were more prevalent in the group of AD patients than in healthy controls, while another IVS2-150A → G polymorphism did not show a significant association with AD. The CC genotype of the IVS3+43C → T polymorphism was associated with an increased 24S-hydroxycholesterol/cholesterol ratio in the CSF of AD patients. Our results indicate that the CYP46 gene locus may predispose to AD by increasing the 24S-hydroxycholesterol/cholesterol ratio in the brain.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Strittmatter WJ, Saunders AM, Schmechel D, Pericak-Vance M, Enghild J, Salvesen GS, Roses AD . Apolipoprotein E: high-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993; 90: 1977–1981
Notkola IL, Sulkava R, Pekkanen J, Erkinjuntti T, Ehnholm C, Kivinen P et al. Serum total cholesterol, apolipoprotein E ε4 allele, and Alzheimer's disease Neuroepidemiology 1998; 17: 14–20
Dupuy AM, Mas E, Ritchie K, Descomps B, Badiou S, Cristol JP, Touchon J . The relationship between apolipoprotein E4 and lipid metabolism is impaired in Alzheimer's disease Gerontology 2001; 47: 213–218
Kivipelto M, Helkala EL, Laakso MP, Hanninen T, Hallikainen M, Alhainen K et al. Midlife vascular risk factors and Alzheimer's disease in later life: longitudinal, population based study BMJ 2001; 322: 1447–1451
Wolozin B, Kellman W, Ruosseau P, Celesia GG, Siegel G . Decreased prevalence of Alzheimer disease associated with 3-hydroxy-3-methyglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors Arch Neurol 2000; 57: 1439–1443
Jick H, Zornberg GL, Jick SS, Seshadri S, Drachman DA . Statins and the risk of dementia Lancet 2000; 356: 1627–1631
Simons M, Keller P, De Strooper B, Beyreuther K, Dotti CG, Simons K . Cholesterol depletion inhibits the generation of β-amyloid in hippocampal neurons Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 6460–6464
Fassbender K, Simons M, Bergmann C, Stroick M, Lütjohann D, Keller P et al. Simvastatin strongly reduces levels of Alzheimer's disease beta-amyloid peptides Abeta 42 and Abeta 40 in vitro and in vivo Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 5856–5861
Jurevics H, Morell P . Cholesterol for synthesis of myelin is made locally, not imported into the brain J Neurochem 1995; 64: 895–901
Goodrum JF . Cholesterol from degenerating nerve myelin becomes associated with lipoproteins containing apolipoprotein E J Neurochem 1991; 56: 2082–2086
Björkhem I, Lütjohann D, Breuer O, Sakinis A, Wennmalm A . Importance of a novel oxidative mechanism for elimination of brain cholesterol J Biol Chem 1997; 48: 30178–30184
DiFrisco S, De Ruggieri P . Isolation of cerebrosterol from human brain Bull Soc Ital Biol Sper 1953; 29: 1351–1352
Björkhem I, Lütjohann D, Diczfalusy U, Stahle L, Ahlborg G, Wahren J . Cholesterol homeostasis in human brain: turnover of 24S-hydroperoxycholesterol and evidence for a cerebral origin of most of this oxysterol in the circulation J Lipid Res 1998; 39: 1594–1600
Kölsch H, Lütjohann D, Tulke A, Björkhem I, Rao ML . The neurotoxic effect of 24-hydroxycholesterol on SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells Brain Res 1999; 818: 171–175
Kölsch H, Ludwig M, Lütjohann D, Rao ML . Neurotoxicity of 24-hydroxycholesterol, an important cholesterol elimination product of the brain, may be prevented by vitamin E and estradiol-17β J Neural Transm 2001; 108: 475–488
Lütjohann D, Papassotiropoulos A, Björkhem I, Locatelli A, Bagli M, Oehring RD et al. Plasma 24-S-hydroxy-cholesterol (cerebrosterol) is increased in Alzheimer and vascular demented patients J Lipid Res 1999; 41: 195–198
Papassotiropoulos A, Lütjohann D, Bagli M, Locatelli S, Jessen F, Buschfort R et al. 24S-Hydroxycholesterol in cerebrospinal fluid is elevated in early stages of dementia Psychiatr Res 2002; 36: 27–32
Papassotiropoulos A, Lütjohann D, Bagli M, Locatelli S, Jessen F, Rao ML et al. Plasma 24S-hydroxycholesterol: a peripheral indicator of neuronal degeneration and potential state marker for Alzheimer's disease Neureport 2000; 2: 1–4
Lund EG, Guileyardo JM, Russell DW . cDNA cloning of cholesterol 24-hydroxylase, a mediator of cholesterol homeostasis in the brain Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 7238–7243
Garpenstrand H, Ekblom J, Forslund K, Rylander G, Oreland L . Platelet monoamine oxidase activity is related to MAOB intron 13 genotype J Neural Transm 2000; 107: 523–530
Krainer A, Maniatis T . RNA splicing IRL Press: Oxford 1988; pp 131–206
Bretillon L, Siden A, Wahlund LO, Lütjohann D, Minthon L, Crisby M et al. Plasma levels of 24S-hydroxycholesterol in patients with neurological diseases Neurosci Lett 2000; 293: 87–90
Lovell MA, Markesbery WR . Ratio of 8-hydroxyguanine in intact DNA to free 8-hydroxyguanine is increased in Alzheimer disease ventricular cerebrospinal fluid Arch Neurol 2001; 58: 392–396
Ramassamy C, Averill D, Beffert U, Bastianetto S, Theroux L, Lussier-Cacan S et al. Oxidative damage and protection by antioxidants in the frontal cortex of Alzheimer's disease is related to the apolipoprotein E genotype Free Radic Biol Med 1999; 27: 544–553
Anderson KM, Seed T, Ou D, Harris JE . Free radicals and reactive oxygen species in programmed cell death Med Hypotheses 1999; 52: 451–463
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR . ‘Mini-mental state’. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician J Psychiatr Res 1975; 12: 189–198
Hixson JE, Vernier DT . Restriction isotyping of human apolipoprotein E by gene amplification and cleavage with HhaI J Lipid Res 1990; 31: 545–548
Dzeletovic S, Breuer O, Lund E, Diczfalusy U . Determination of cholesterol oxidation products in human plasma by isotope dilution-mass spectrometry Anal Biochem 1995; 225: 73–80
Acknowledgements
We thank Sandra Schmitz, Anja Kerksiek and Christian Ehl for technical assistance. This study was supported by grants of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (HE2318/1–1, 1–2), of the Alzheimer Association (IIRG98–142) and of the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (01EC9402).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kölsch, H., Lütjohann, D., Ludwig, M. et al. Polymorphism in the cholesterol 24S-hydroxylase gene is associated with Alzheimer's disease. Mol Psychiatry 7, 899–902 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001109
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001109
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Preclinical characterization of [18F]T-008, a novel PET imaging radioligand for cholesterol 24-hydroxylase
European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (2022)
-
Association of cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) promoter polymorphism (rs3808607) and cholesterol 24S-hydroxylase (CYP46A1) intron 2 polymorphism (rs754203) with serum lipids, vitamin D levels, and multiple sclerosis risk in the Turkish population
Neurological Sciences (2022)
-
Atherosclerosis and Alzheimer - diseases with a common cause? Inflammation, oxysterols, vasculature
BMC Geriatrics (2014)
-
Role of Cholesterol in APP Metabolism and Its Significance in Alzheimer’s Disease Pathogenesis
Molecular Neurobiology (2013)
-
CYP46A1 T/C polymorphism associated with the APOEε4 allele increases the risk of Alzheimer’s disease
Journal of Neurology (2013)