Abstract
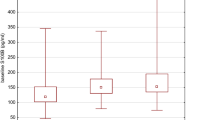
S100B, a calcium-binding protein produced by astroglial cells, is a marker of astroglial cellular integrity. It has been shown to be increased in acute brain damage and neurodegeneration. A recent study showed increased S100B levels in medicated acutely psychotic patients with schizophrenia. The study presented here included 26 drug-free patients with acute schizophrenia and 26 matched healthy controls. S100B blood concentrations were determined using a quantitative immunoassay upon admission and after 6 weeks of neuroleptic treatment. The PANSS was used to investigate psychopathology. Unmedicated schizophrenic patients showed significantly increased S100B levels compared to matched healthy controls. After 6 weeks of treatment, 11 patients showed normal S100B levels while in 15 patients the levels remained increased. These patients showed significantly higher PANSS negative scores upon admission and after 6 weeks of treatment. Schizophrenic patients display a loss of astroglial integrity which is not caused by neuroleptic medication. Continuously increased S100B levels are associated with negative symptomatology.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeLisi LE . Defining the course of brain structural change and plasticity in schizophrenia Psychiatry Res 1999 92: 1–9
McGlashan TH, Hoffman RE . Schizophrenia as a disorder of developmentally reduced synaptic connectivity Arch Gen Psychiatry 2000 57: 637–648
Heizman CW, Cox JA . New perspectives on S100 proteins: a multi-functional Ca2+, Zn2+ and Cu2+ binding protein family BioMetals 1998 11: 383–397
Beaudeux JL, Dequen L, Foglietti MJ . Pathophysiologic aspects of S-100beta protein: a new biological marker of brain pathology Ann Biol Clin 1999 57: 261–272
Griffin WST, Stanley LC, Ling C, White L, MacLeod V, Perrot LJ et al. Brain interleukin 1 and S-100 immunoreactivity are elevated in Down syndrome and Alzheimer disease Proc Natl Acad Sci 1998 86: 7611–7615
Whitaker-Azmitia P, Wingate M, Borella A, Gerlai R, Roder J, Azmitia EC . Transgenic mice overexpressing the neurotrophic factor S-100β show neuronal cytoskeletal and behavioral signs of altered aging processes: implications for Alzheimer's disease and Down's syndrome Brain Res 1997 776: 51–60
Fano G, Biocca S, Fulle S, Mariggio MA, Belia S, Calissano P . The S-100: a protein family in search of a function Prog Neurobiol 1995 46: 71–82
Missler U, Wiesmann M . Measurement of S-100 protein in human blood and cerebrospinal fluid: analytic method and preliminary clinical results Eur J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 1995 33: 743–748
Büttner T, Weyers S, Sprengelmeyer T, Postert R, Kuhn W . S-100 protein: serum marker of focal brain damage after ischemic territorial MCA infarction Stroke 1997 28: 1961–1965
Griffin WST, Yeralan O, Sheng JG, Boop FA, Mrak RE, Rovnaghi CR et al. Overexpression of the neurotrophic cytokine S100b in human temporal lobe epilepsy J Neurochem 1995 65: 228–233
Lamers KJB, van Engelen BGM, Gabreels FJM, Hommes OR, Borm GF, Wevers RA . Cerebrospinal neuron-specific enolase, S-100 and myelin basic protein in neurological disorders Acta Neurol Scand 1995 92: 247–251
Missler U, Wiesmann M, Friedrich C, Kaps M . S-100 protein and neuron-specific enolase concentrations in blood as indicators of infarction and prognosis in acute ischemic stroke Stroke 1997 28: 1956–1960
Raabe A, Grolms C, Keller M, Döhnert J, Sorge O, Seifert V . Correlation of computed tomography findings and serum brain damage markers following severe head injury Acta Neurochir 1998 140: 787–792
Rothoerl RD, Woertgen C, Holzschuh M, Metz C, Brawanski A . Rapid evaluation of S-100 serum levels. Case report and comparison to previous results Brain Inj 1999 13: 387–391
Sindic CJM, Chalon MP, Cambiaso CL, Laterre EC, Masson PL . Assessment of damage to the central nervous system by determination of S-100 protein in the cerebrospinal fluid J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1982 45: 1130–1135
Vinesi P, Geloso MC, Michetti F . S-100 proteins in trimethyltin-induced neurodegeneration in the rat hippocampus. An immunochemical and immunocytochemical study Mol Chem Neuropathol 1997 32: 129–141
Wiesmann M, Missler U, Hagenström H, Gottmann D . S-100 protein plasma levels after aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage Acta Neurochir 1997 139: 1155–1160
Wiesmann M, Wandinger KP, Missler U, Eckhoff D, Rothermundt M, Arolt V et al. Elevated plasma levels of S-100b protein in schizophrenic patients Biol Psychiatry 1999 45: 1508–1511
Gattaz WF, Lara DR, Elkis H, Portela LV, Goncalves CA, Tort AB et al. Decreased S100B protein in schizophrenia: preliminary evidence Schizophr Res 2000 43: 91–95
Waterloo K, Ingebrigtsen T, Romner B . Neuropsychological function in patients with increased serum levels of protein S-100 after minor head injury Acta Neurochir 1997 139: 26–31
Gerlai R, Roder J . Abnormal exploratory behavior in transgenic mice carrying multiple copies of the human gene for S100 beta J Psychiatry Neurosci 1995 20: 105–112
Lieberman JA . Pathophysiologic mechanisms in the pathogenesis and clinical course of schizophrenia J Clin Psychiatry 1999 60: S9–S12
Donato R . Perspectives in S-100 protein biology Cell Calcium 1991 12: 713–726
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Julian P Keogh for critically reviewing the text.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rothermundt, M., Missler, U., Arolt, V. et al. Increased S100B blood levels in unmedicated and treated schizophrenic patients are correlated with negative symptomatology. Mol Psychiatry 6, 445–449 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4000889
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4000889
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Serum S100B is related to insulin resistance and zinc-α2-glycoprotein levels in patients with chronic schizophrenia
Middle East Current Psychiatry (2023)
-
The relationship between inflammatory markers, clinical characteristics, and cognitive performance in drug-naïve patients with schizophrenia
European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience (2023)
-
Blood-brain barrier associated tight junction disruption is a hallmark feature of major psychiatric disorders
Translational Psychiatry (2020)
-
Elevated Plasma S100B, Psychotic Symptoms, and Cognition in Schizophrenia
Psychiatric Quarterly (2018)
-
Higher Plasma S100B Concentrations in Schizophrenia Patients and Dependently Associated with Inflammatory Markers
Scientific Reports (2016)