Abstract
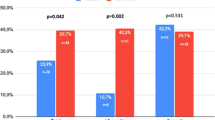
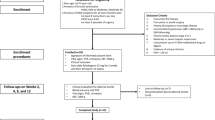
Although subgroup analyses from large randomised premarketing studies have shown that Apomorphine SL enhances the percentage of erections firm enough for sexual intercourse in diabetic men, the clinical role of the drug in this patient population remains to be elucidated. The aim of the present study was to assess the efficacy of Apomorphine SL in diabetic males with erectile dysfunction (ED) and to identify factors predicting those who may benefit from the treatment. A total of 130 diabetic patients were randomised to receive either four tablets of 3 mg Apomorphine or a matching placebo. Assessments of efficacy comprised the erectile function (EF) domain of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF) and the one-item global efficacy question (GEQ). Patients with both a positive response to the GEQ and an improvement of at least 5 points in the EF domain of the IIEF were considered responders and subanalysed by several parameters indicative of the severity of both ED and diabetes. Response rate was 17% after placebo and 22% after Apomorphine SL. The EF domain of the IIEF and both questions 3 and 4 scores did not significantly improve in either of the two arms over the baseline. A younger age and a lower Hb1Ac were significantly linked to the status of responder in the Apomorphine arm. Apomorphine SL failed to show a statistically significant benefit over a placebo, but 22% of patients had a clinically significant erectile response. These figures seem to suggest that the drug has a limited use for ED diabetic patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fedele D et al. Incidence of erectile dysfunction in Italian men with diabetes. J Urol 2001; 166: 1368–1371.
Nicolosi A et al. Epidemiology of erectile dysfunction in four countries: cross-national study of the prevalence and correlates of erectile dysfunction. Urology 2003; 61: 201–206.
Moreland RB . Is there a role of hypoxemia in penile fibrosis: a viewpoint presented to the society for the study of impotence. Int J Impot Res 1998; 10: 113–120.
Cartledge JJ, Eardley I, Morrison JF . Advanced glycation products are responsible for the impairment of corpus cavernosal smooth muscle relaxation in diabetes. Br J Urol 2001; 87: 402–407.
West IC . Radicals and oxidative stress in diabetes. Diabetic Med 2000; 17: 171–180.
Vickers MA, Satyanarayana R . Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors for the treatment of erectile dysfunction in patients with diabetes mellitus. Int J Impot Res 2002; 14: 466–471.
Lepore G, Nosari I . Efficacy of oral Sildenafil in the treatment of erectile dysfunction in diabetic men with positive response to intracavernosal injection of Alprostadil. Diabetes Care 2001; 24: 409–411.
Heaton JP, Adams MA, Morales A . A therapeutic taxonomy of treatments for erectile dysfunction: an evolutionary perspective. Int J Impot Res 1997; 9: 115–121.
Stief C, Padley RJ, Perdok RJ, Sleep DJ . Cross-study review of the clinical efficacy of Apomorphine SL 2 and 3 mg: pooled data from three placebo-controlled, fixed-dose crossover studies. Eur Urol 2002; 1: 12–20.
Dula E, Bukofzer S, Perdok R, George M, the Apomorphine SL Study Group. Double-blind, crossover comparison of 3 mg Apomorphine SL with placebo and with 4 mg Apomorphine SL in male erectile dysfunction. Eur Urol 2000; 39: 558–564.
Mulhall JP, Bukofzer S, Edmonds AL, George M, the Apomorphine SL Study Group. An open-label, uncontrolled dose-optimization study of sublingual Apomorphine in erectile dysfunction. Clin Ther 2001; 23: 1260–1271.
DeBusk R et al. Management of sexual dysfunction in patients with cardiovascular disease: recommendations of the Princeton Consensus panel. Am J Cardiol 2000; 86: 175–181.
Rosen RC, Riley A, Wagner G . The International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF): a multidimensional scale for assessment of erectile dysfunction. Urology 1997; 49: 822–825.
Gontero P et al. Is there an optimal timing for intracavernous PGE1 rehabilitation following nonnerve sparing radical prostatectomy. Results from a hemodynamic perspective study. J Urol 2003; 169: 2166–2169.
Karadeniz T et al. Value of Colour Doppler sonography in the diagnosis of venous impotence. Urol Int 1995; 55: 143–149.
Virag R, Frydman D, Legman M, Virag H . Intracavernous injection of papaverine as diagnostic and therapeutic method in erectile failure. Angiology 1984; 35: 79–82.
Breda G et al. Nomogram for penile biothesiometry. Eur Urol 1991; 20: 67–69.
Heaton JPW . Apomorphine. An update of clinical trial results. Int J Impot Res 2000; 12 (Suppl): S67–73.
Heaton JPW, Dean J, Sleep DJ . Sequential administration enhances the effect of Apomorphine Sl in men with erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 2002; 14: 61–64.
Boulton AJM, Selam J-L, Sweeney M, Ziegler D . Sildenafil citrate for the treatment of erectile dysfunction in men with type II diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2001; 44: 1296–1301.
Goldstein I et al. Vardenafil, a new phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor in the treatment of erectile dysfunction in diabetic men. Diabetes Care 2003; 26: 777–783.
Romeo JH, Seftel AD, Madhun ZT, Aron DC . Sexual function in men with diabetes type 2: association with glycemic control. J Urol 2000; 163: 788–791.
Rendell MS, Rajfer J, Wicker PA, Smith MD . Sildenafil for treatment of erectile dysfunction in men with diabetes. JAMA 1999; 281: 424–426.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gontero, P., D'Antonio, R., Pretti, G. et al. Clinical efficacy of Apomorphine SL in erectile dysfunction of diabetic men. Int J Impot Res 17, 80–85 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901273
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901273
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Apomorphine for the Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Archives of Sexual Behavior (2020)
-
Drug-Induced Impulse Control Disorders: A Prospectus for Neuroethical Analysis
Neuroethics (2011)
-
Centrally acting drugs for erectile dysfunction: Do they have a future?
Current Sexual Health Reports (2007)