Abstract
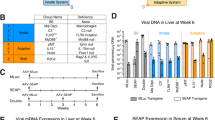
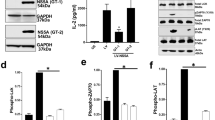
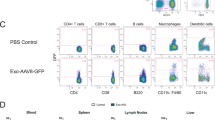
Understanding the determinants of the host innate immune response to systemic administration of adenoviral (Ad) vectors is critical for clinical gene therapy. Acute toxicity occurs within minutes to hours after vector administration and is characterized by activation of innate immune responses. Our data indicate that in mice, indicators of vector toxicity include elevations of cytokine levels, liver transaminase levels and thrombocytopenia. To discern potential targets for blunting this host response, we evaluated genetic factors in the host response to systemically administered first-generation Ad vectors (FGV) and helper-dependent Ad vectors (HDV) containing β-galactosidase expression cassettes. A preliminary screen for modulation of vector-induced thrombocytopenia revealed no role for interferon-γ, mast cells or perforin. However, vector-induced thrombocytopenia and interleukin 6 (IL-6) expression are less evident in tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα)-deficient mice. Moreover, we also demonstrated that TNFα blockade via antibody or huTNFR:Fc pretreatment attenuates both thrombocytopenia (>40% increase in platelet count) and IL-6 expression (>80% reduction) without affecting interleukin 12 , liver enzymes, hematological indices or vector transduction in a murine model. Our data indicate that the use of HDV, in combination with clinically approved TNFα immunomodulation, may represent an approach for improving the therapeutic index of Ad gene therapy for human clinical trials.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ad:
-
adenovirus
- FGV:
-
first-generation adenoviral vector
- HDV:
-
helper-dependent adenoviral vector
- IL-6:
-
interleukin 6
- IL-12:
-
interleukin 12
- TNFα:
-
tumor necrosis factor alpha
- i.v.:
-
intravenous
- i.p.:
-
intraperitoneal
References
Parks RJ, Bramson JL, Wan Y, Addison CL, Graham FL . Effects of stuffer DNA on transgene expression from helper-dependent adenovirus vectors. J Virol 1999; 73: 8027–8034.
Muruve DA . The innate immune response to adenovirus vectors. Hum Gene Ther 2004; 15: 1157–1166.
Hotchkiss RS, Karl IE . The pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 138–150.
Morral N, O'Neal WK, Rice K, Leland MM, Piedra PA, Aguilar-Cordova E et al. Lethal toxicity, severe endothelial injury, and a threshold effect with high doses of an adenoviral vector in baboons. Hum Gene Ther 2002; 13: 143–154.
Abuzakouk M, Feighery C, Jackson J . Tumour necrosis factor blocking agents: a new therapeutic modality for inflammatory disorders. Br J Biomed Sci 2002; 59: 173–179.
Hull KM, Shoham N, Chae JJ, Aksentijevich I, Kastner DL . The expanding spectrum of systemic autoinflammatory disorders and their rheumatic manifestations. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2003; 15: 61–69.
Brunetti-Pierri N, Palmer DJ, Mane V, Finegold M, Beaudet AL, Ng P . Increased hepatic transduction with reduced systemic dissemination and proinflammatory cytokines following hydrodynamic injection of helper-dependent adenoviral vectors. Mol Ther 2005; 12: 99–106.
Zhang Y, Chirmule N, Gao GP, Qian R, Croyle M, Joshi B et al. Acute cytokine response to systemic adenoviral vectors in mice is mediated by dendritic cells and macrophages. Mol Ther 2001; 3: 697–707.
Schnell MA, Zhang Y, Tazelaar J, Gao GP, Yu QC, Qian R et al. Activation of innate immunity in nonhuman primates following intraportal administration of adenoviral vectors. Mol Ther 2001; 3: 708–722.
Raper SE, Chirmule N, Lee FS, Wivel NA, Bagg A, Gao GP et al. Fatal systemic inflammatory response syndrome in a ornithine transcarbamylase deficient patient following adenoviral gene transfer. Mol Genet Metab 2003; 80: 148–158.
Liu Q, Zaiss AK, Colarusso P, Patel K, Haljan G, Wickham TJ et al. The role of capsid-endothelial interactions in the innate immune response to adenovirus vectors. Hum Gene Ther 2003; 14: 627–643.
Morral N, Parks RJ, Zhou H, Langston C, Schiedner G, Quinones J et al. High doses of a helper-dependent adenoviral vector yield supraphysiological levels of alpha1-antitrypsin with negligible toxicity. Hum Gene Ther 1998; 9: 2709–2716.
Reddy PS, Sakhuja K, Ganesh S, Yang L, Kayda D, Brann T et al. Sustained human factor VIII expression in hemophilia A mice following systemic delivery of a gutless adenoviral vector. Mol Ther 2002; 5: 63–73.
Muruve DA, Cotter MJ, Zaiss AK, White LR, Liu Q, Chan T et al. Helper-dependent adenovirus vectors elicit intact innate but attenuated adaptive host immune responses in vivo. J Virol 2004; 78: 5966–5972.
O'Neal WK, Zhou H, Morral N, Aguilar-Cordova E, Pestaner J, Langston C et al. Toxicological comparison of E2a-deleted and first-generation adenoviral vectors expressing alpha1-antitrypsin after systemic delivery. Hum Gene Ther 1998; 9: 1587–1598.
Cichon G, Schmidt HH, Benhidjeb T, Loser P, Ziemer S, Haas R et al. Intravenous administration of recombinant adenoviruses causes thrombocytopenia, anemia and erythroblastosis in rabbits. J Gene Med 1999; 1: 360–371.
Raper SE, Yudkoff M, Chirmule N, Gao GP, Nunes F, Haskal ZJ et al. A pilot study of in vivo liver-directed gene transfer with an adenoviral vector in partial ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. Hum Gene Ther 2002; 13: 163–175.
Klinger JR, Sanchez MP, Curtin LA, Durkin M, Matyas B . Multiple cases of life-threatening adenovirus pneumonia in a mental health care center. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998; 157: 645–649.
Eggerman TL, Mondoro TH, Lozier JN, Vostal JG . Adenoviral vectors do not induce, inhibit, or potentiate human platelet aggregation. Hum Gene Ther 2002; 13: 125–128.
Faraday N, Rade JJ, Johns DC, Khetawat G, Noga SJ, DiPersio JF et al. Ex vivo cultured megakaryocytes express functional glycoprotein IIb–IIIa receptors and are capable of adenovirus-mediated transgene expression. Blood 1999; 94: 4084–4092.
Brunetti-Pierri N, Palmer DJ, Beaudet AL, Carey KD, Finegold M, Ng P . Acute toxicity after high-dose systemic injection of helper-dependent adenoviral vectors into nonhuman primates. Hum Gene Ther 2004; 15: 35–46.
Sung RS, Qin L, Bromberg JS . TNFalpha and IFNgamma induced by innate anti-adenoviral immune responses inhibit adenovirus-mediated transgene expression. Mol Ther 2001; 3: 757–767.
Goodbourn S, Didcock L, Randall RE . Interferons: cell signalling, immune modulation, antiviral response and virus countermeasures. J Gen Virol 2000; 81: 2341–2364.
Elkon KB, Liu CC, Gall JG, Trevejo J, Marino MW, Abrahamsen KA et al. Tumor necrosis factor alpha plays a central role in immune-mediated clearance of adenoviral vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 9814–9819.
Trevejo JM, Marino MW, Philpott N, Josien R, Richards EC, Elkon KB et al. TNF-alpha -dependent maturation of local dendritic cells is critical for activating the adaptive immune response to virus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 12162–12167.
Piguet PF, Vesin C, Da Kan C . Activation of platelet caspases by TNF and its consequences for kinetics. Cytokine 2002; 18: 222–230.
Piguet PF, Vesin C, Guo J, Donati Y, Barazzone C . Role of mast cells and monoamines in the thrombocytopaenia and mortality elicited by tumour necrosis factor in mice. Immunology 1998; 95: 111–116.
Derkx B, Taminiau J, Radema S, Stronkhorst A, Wortel C, Tytgat G et al. Tumour-necrosis-factor antibody treatment in Crohn's disease. Lancet 1993; 342: 173–174.
Feldmann M, Brennan FM, Maini RN . Role of cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Annu Rev Immunol 1996; 14: 397–440.
Spencer-Green G . Etanercept (Enbrel): update on therapeutic use. Ann Rheum Dis 2000; 59: i46–i49.
Brunetti-Pierri N, Nichols TC, McCorquodale S, Merricks E, Palmer DJ, Beaudet AL et al. Sustained phenotypic correction of canine hemophilia B after systemic administration of helper-dependent adenoviral vector. Hum Gene Ther 2005; 16: 811–820.
Varnavski AN, Calcedo R, Bove M, Gao G, Wilson JM . Evaluation of toxicity from high-dose systemic administration of recombinant adenovirus vector in vector-naive and pre-immunized mice. Gene Ther 2005; 12: 427–436.
Russell WC . Update on adenovirus and its vectors. J Gen Virol 2000; 81: 2573–2604.
Benihoud K, Salone B, Esselin S, Opolon P, Poli V, Di Giovine M et al. The role of IL-6 in the inflammatory and humoral response to adenoviral vectors. J Gene Med 2000; 2: 194–203.
Thorne PS, McCray PB, Howe TS, O'Neill MA . Early-onset inflammatory responses in vivo to adenoviral vectors in the presence or absence of lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1999; 20: 1155–1164.
Lozier JN, Csako G, Mondoro TH, Krizek DM, Metzger ME, Costello R et al. Toxicity of a first-generation adenoviral vector in rhesus macaques. Hum Gene Ther 2002; 13: 113–124.
Murray KM, Dahl SL . Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor receptor (p75) Fc fusion protein (TNFR:Fc) in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Pharmacother 1997; 31: 1335–1338.
Grounds MD, Davies M, Torrisi J, Shavlakadze T, White J, Hodgetts S . Silencing TNFalpha activity by using Remicade or Enbrel blocks inflammation in whole muscle grafts: an in vivo bioassay to assess the efficacy of anti-cytokine drugs in mice. Cell Tissue Res 2005; 320: 509–515.
Higginbotham JN, Seth P, Blaese RM, Ramsey WJ . The release of inflammatory cytokines from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro following exposure to adenovirus variants and capsid. Hum Gene Ther 2002; 13: 129–141.
Benihoud K, Yeh P, Perricaudet M . Adenovirus vectors for gene delivery. Curr Opin Biotechnol 1999; 10: 440–447.
Yotnda P, Chen DH, Chiu W, Piedra PA, Davis A, Templeton NS et al. Bilamellar cationic liposomes protect adenovectors from preexisting humoral immune responses. Mol Ther 2002; 5: 233–241.
Croyle MA, Chirmule N, Zhang Y, Wilson JM . PEGylation of E1-deleted adenovirus vectors allows significant gene expression on readministration to liver. Hum Gene Ther 2002; 13: 1887–1900.
Mok H, Palmer DJ, Ng P, Barry MA . Evaluation of polyethylene glycol modification of first-generation and helper-dependent adenoviral vectors to reduce innate immune responses. Mol Ther 2005; 11: 66–79.
Croyle MA, Le HT, Linse KD, Cerullo V, Toietta G, Beaudet A et al. PEGylated helper-dependent adenoviral vectors: highly efficient vectors with an enhanced safety profile. Gene Therapy 2005; 12: 579–587.
Tao N, Gao GP, Parr M, Johnston J, Baradet T, Wilson JM et al. Sequestration of adenoviral vector by Kupffer cells leads to a nonlinear dose response of transduction in liver. Mol Ther 2001; 3: 28–35.
Schiedner G, Hertel S, Johnston M, Dries V, van Rooijen N, Kochanek S . Selective depletion or blockade of Kupffer cells leads to enhanced and prolonged hepatic transgene expression using high-capacity adenoviral vectors. Mol Ther 2003; 7: 35–43.
Body JJ, Diel I, Bell R . Profiling the safety and tolerability of bisphosphonates. Semin Oncol 2004; 31: 73–78.
Spencer AJ, Wilson SA, Batchelor J, Reid A, Rees J, Harpur E . Gadolinium chloride toxicity in the rat. Toxicol Pathol 1997; 25: 245–255.
Gooding LR . Regulation of TNF-mediated cell death and inflammation by human adenoviruses. Infect Agents Dis 1994; 3: 106–115.
Nasto B . Questions about systemic adenovirus delivery. Mol Ther 2002; 5: 652–653.
Varnavski AN, Zhang Y, Schnell M, Tazelaar J, Louboutin JP, Yu QC et al. Preexisting immunity to adenovirus in rhesus monkeys fails to prevent vector-induced toxicity. J Virol 2002; 76: 5711–5719.
Ng P, Parks RJ, Cummings DT, Evelegh CM, Graham FL . An enhanced system for construction of adenoviral vectors by the two-plasmid rescue method. Hum Gene Ther 2000; 11: 693–699.
Palmer D, Ng P . Improved system for helper-dependent adenoviral vector production. Mol Ther 2003; 8: 846–852.
Acknowledgements
BL was supported by NIH DK56787, NIH DK58338, NIH HD24046 and PN was supported by P50 HL59314. LP was supported by Telethon Grant GGP04039. We gratefully acknowledge Dorene M Rudman of the NIDDK-sponsored Gulf Coast Digestive Disease Center Morphology Core Laboratory (P30 DK56338) at Texas Children's Hospital (Houston, TX) for tissue sectioning, hematoxylin and eosin staining and X-gal staining. We also acknowledge Ovida Hortenstine at the Pathology Laboratory of the Center for Comparative Medicine (Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX) for all CBC and transaminase readings.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is dedicated to the memory of our colleague and friend WM McCormack Jr (12 August 1965 – 29 July 2005).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mane, V., Toietta, G., McCormack, W. et al. Modulation of TNFα, a determinant of acute toxicity associated with systemic delivery of first-generation and helper-dependent adenoviral vectors. Gene Ther 13, 1272–1280 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302792
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302792
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
PEGylated helper-dependent adenoviral vector expressing human Apo A-I for gene therapy in LDLR-deficient mice
Gene Therapy (2013)
-
Differential Type I Interferon-dependent Transgene Silencing of Helper-dependent Adenoviral vs. Adeno-associated Viral Vectors In Vivo
Molecular Therapy (2013)
-
Hyperactive Sleeping Beauty Transposase Enables Persistent Phenotypic Correction in Mice and a Canine Model for Hemophilia B
Molecular Therapy (2010)
-
Immunization Against the Transgene but not the TetON Switch Reduces Expression From Gutless Adenoviral Vectors in the Brain
Molecular Therapy (2008)
-
Substitution of Hexon Hypervariable Region 5 of Adenovirus Serotype 5 Abrogates Blood Factor Binding and Limits Gene Transfer to Liver
Molecular Therapy (2008)