Abstract
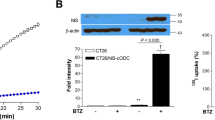
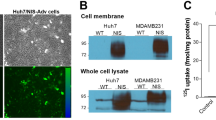
We investigated the feasibility of using radioiodine therapy in colon carcinoma cells (HCT 116) following tumor-specific expression of the human sodium iodide symporter (hNIS) using the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) promoter. HCT 116 cells were stably transfected with an expression vector, in which hNIS cDNA has been coupled to a CEA promoter fragment. This promoter is responsible for tissue-specific expression of CEA in gastrointestinal tract epithelium, and has been shown to target therapeutic genes to colorectal cancer cells. Functional NIS expression was confirmed by iodide uptake assay, Western blot analysis, immunostaining and in vitro clonogenic assay. The stably transfected HCT 116 cells concentrated 125I about 10-fold in vitro without evidence of iodide organification. In contrast, transfection of control cancer cells without CEA expression did not result in iodide accumulation. Western blot analysis using a hNIS-specific antibody revealed a band of approximately 90 kDa. In addition, immunostaining of stably transfected HCT 116 cells revealed hNIS-specific membrane-associated immunoreactivity. In an in vitro clonogenic assay approximately 95% of stably transfected HCT 116 cells were killed by exposure to 131I, while only about 5% of NIS-negative control cells were killed. Further, using an adenovirus carrying the NIS gene linked to the CEA promoter, high levels of tumor-specific radioiodide accumulation were induced in HCT 116 cells. In conclusion, a therapeutic effect of 131I has been demonstrated in colon carcinoma cells following induction of tumor-specific iodide uptake activity by CEA promoter-directed NIS expression in vitro. This study demonstrates the potential of NIS as a therapeutic gene allowing radioiodine therapy of colon cancer following tumor-specific NIS gene transfer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carrasco N . Iodide transport in the thyroid gland. Biochem Biophys Acta 1993; 1154: 65–82.
Dai G, Levy O, Carrasco N . Cloning and characterization of the thyroid iodide transporter. Nature 1996; 379: 458–460.
Smanik PA et al. Cloning of the human sodium iodide symporter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1996; 226: 339–345.
Smanik PA et al. Expression, exon–intron organization, and chromosome mapping of the human sodium iodide symporter. Endocrinology 1997; 138: 3555–3558.
Mazzaferri EL . Carcinoma of follicular epithelium: radioiodine and other treatments and outcomes. In: Braverman LE, Utiger RD (eds). The Thyroid: A Fundamental and Clinical Text, 7th edn. Lippincott, Raven: Philadelphia, 1996, pp 922–945.
Spitzweg C et al. The sodium iodide symporter and its potential role in cancer therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 3327–3335.
Dingli D, Russell SJ, Morris JC . In vivo imaging and tumor therapy with the sodium iodide symporter. J Cell Biochem 2003; 90: 1079–1086.
Hart IR . Tissue specific promoters in targeting systemically delivered gene therapy. Semin Oncol 1996; 23: 154–158.
Spitzweg C et al. Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) promoter-driven androgen-inducible expression of sodium iodide symporter in prostate cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 2136–2141.
Spitzweg C et al. Treatment of prostate cancer by radioiodine therapy after tissue-specific expression of the sodium iodide symporter. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 6526–6530.
Spitzweg C et al. In vivo sodium iodide symporter gene therapy of prostate cancer. Gene Therapy 2001; 8: 1524–1531.
Okabe S, Arai T, Yamashita H, Sugihara K . Adenovirus-mediated prodrug-enzyme therapy for CEA-producing colorectal cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2003; 129: 367–373.
Ueno M et al. Tumor-specific chemo-radio-gene therapy for colorectal cancer cells using adenovirus vector expressing the cytosine deaminase gene. Anticancer Res 2001; 21: 2601–2608.
Konishi F et al. Transcriptionally targeted in vivo gene therapy for carcinoembryonic antigen-producing adenocarcinoma. Hiroshima J Med Sci 1999; 48: 79–89.
Cao GW et al. Gene therapy for human colorectal carcinoma using human CEA promoter controlled bacterial ADP-ribosylating toxin genes human CEA: PEA & DTA gene transfer. World J Gastroenterol 1998; 4: 388–391.
Shen LZ et al. Specific CEA-producing colorectal carcinoma cell killing with recombinant adenoviral vector containing cytosine deaminase gene. World J Gastroenterol 2002; 8: 270–275.
Midgley R, Kerr DJ . Seminar in colorectal cancer. Lancet 1999; 353: 391–399.
Chung-Faye GA, Kerr DJ, Young LS, Searle PF . Gene therapy strategies for colon cancer. Mol Med Today 2000; 6: 82–87.
Shimura H et al. Iodide uptake and experimental 131I therapy in transplanted undifferentiated thyroid cancer cells expressing the Na+/I− symporter gene. Endocrinology 1997; 138: 4493–4496.
Cho J-Y et al. Expression and activity of human Na+/I− symporter in human glioma cells by adenovirus-mediated gene delivery. Gene Therapy 2000; 7: 740–749.
Mandell RB, Mandell LZ, Link CJ . Radioisotope concentrator gene therapy using the sodium/iodide symporter gene. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 661–668.
Boland A et al. Adenovirus-mediated transfer of the thyroid sodium/iodide symporter gene into tumors for a targeted radiotherapy. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 3484–3492.
Smit JWA et al. Reestablishment of in vitro and in vivo iodide uptake by transfection of the human sodium iodide symporter (hNIS) in a hNIS defective human thyroid carcinoma cell line. Thyroid 2000; 10: 939–943.
Smit JW et al. Iodide kinetics and experimental (131)I therapy in a xenotransplanted human sodium-iodide symporter-transfected human follicular thyroid carcinoma cell line. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002; 87: 1247–1253.
Nakamato Y et al. Establishment and characterization of a breast cancer cell line expressing Na+/I− symporters for radioiodide concentrator gene therapy. J Nucl Med 2000; 41: 1898–1904.
Carlin S et al. Experimental targeted radioiodide therapy following transfection of the sodium iodide symporter gene: effect on clonogenicity in both two- and three-dimensional models. Cancer Gene Ther 2000; 7: 1529–1536.
Haberkorn U et al. Transfer of the human NaI symporter gene enhances iodide uptake in hepatoma cells. J Nucl Med 2001; 42: 317–325.
La Perle KMD et al. In vivo expression and function of the sodium iodide symporter following gene transfer in the MATLyLu rat model of metastatic prostate cancer. Prostate 2001; 50: 170–178.
Schipper ML et al. Radioiodide treatment after sodium iodide symporter gene transfer is a highly effective therapy in neuroendocrine tumor cells. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 1333–1338.
Dingli D et al. Genetically targeted radiotherapy for multiple myeloma. Blood 2003; 102: 489–496.
Cleutjens KBJM et al. A 6-kb promoter fragment mimics in transgenic mice the prostate-specific and androgen-regulated expression of the endogenous prostate-specific antigen gene in humans. Mol Endocrinol 1997; 11: 1256–1265.
Dannull J, Belldegrun AS . Development of gene therapy for prostate cancer using a novel promoter of prostate-specific antigen. Br J Urol 1997; 79: 97–103.
Hrouda D, Dalgleish AG . Gene therapy for prostate cancer. Gene Therapy 1996; 3: 845–852.
Gold P, Freedman SO . Demonstration of tumor-specific antigens in human colonic carcinomata by immunological tolerance and absorption techniques. J Exp Med 1965; 121: 439–462.
Cao G et al. Comparison of carcinoembryonic antigen promoter regions isolated from human colorectal carcinoma and normal adjacent mucosa to induce strong tumor-selective gene expression. Int J Cancer 1998; 78: 242–247.
Schrewe H et al. Cloning of the complete gene for carcinoembryonic antigen: analysis of its promoter indicates a region conveying cell type-specific expression. Mol Cell Biol 1990; 10: 2738–2748.
Hauck W, Stanners CP . Transcriptional regulation of the carcinoembryonic antigen gene. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 3602–3610.
Willcocks TC, Craig IW . Characterization of the genomic organization of human carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA): comparison with other family members and sequence analysis of 5′ controlling region. Genomics 1990; 8: 492–500.
Fichera A, Michelassi F, Arenas RB . Selective expression of carcinoembryonic antigen promoter in cancer cell lines. Dis Colon Rectum 1998; 41: 747–754.
Mitrofanova E et al. Sodium iodide symporter/radioactive iodine system has more efficient antitumor effect in three-dimensional spheroids. Anticancer Res 2003; 23: 2397–2404.
Weiss SJ, Philip NJ, Grollmann EF . Iodine transport in a continuous line of cultured cells from rat thyroid. Endocrinology 1984; 114: 1090–1098.
Urabe M et al. Effect of lithium on function and growth of thyroid cells in vitro. Endocrinology 1991; 129: 807–814.
Kaminsky SM et al. Na+-I− symport activity is present in membrane vesicles from thyrotropin-deprived non-I-transporting cultured thyroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91: 3789–3793.
Castro MR et al. Monoclonal antibodies against the human sodium iodide symporter: utility for immunocytochemistry of thyroid cancer. J Endocrinol 1999; 163: 495–504.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Sissy M Jhiang, PhD, Department of Physiology, Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA, for supplying the full-length human NIS cDNA. This study was supported by grants to C Spitzweg (Sp 581/3-1, Sp 581/3-2) from the German Research Council (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Bonn, Germany), and by the Mayo Foundation Prostate Cancer SPORE grant (CA91956) to JC Morris.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scholz, I., Cengic, N., Baker, C. et al. Radioiodine therapy of colon cancer following tissue-specific sodium iodide symporter gene transfer. Gene Ther 12, 272–280 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302410
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302410
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The sodium iodide symporter (NIS) as theranostic gene: potential role in pre-clinical therapy of extra-thyroidal malignancies
Clinical and Translational Imaging (2023)
-
124I-PET Assessment of Human Sodium Iodide Symporter Reporter Gene Activity for Highly Sensitive In Vivo Monitoring of Teratoma Formation in Mice
Molecular Imaging and Biology (2015)
-
Sodium iodide symporter (NIS) in extrathyroidal malignancies: focus on breast and urological cancer
BMC Cancer (2014)
-
A novel oncolytic viral therapy and imaging technique for gastric cancer using a genetically engineered vaccinia virus carrying the human sodium iodide symporter
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2014)
-
Viral dose, radioiodide uptake, and delayed efflux in adenovirus-mediated NIS radiovirotherapy correlates with treatment efficacy
Gene Therapy (2013)