Abstract
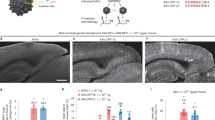
The owl monkey (Aotus trivirgatus) has served as the standard non-human primate model of herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) infection because it is highly susceptible to HSV-1 encephalitis. Owl monkeys, however, are expensive, difficult to obtain, and difficult to maintain in captivity, thus greatly hampering the efficiency of preclinical gene therapy trials for brain tumors using HSV-1-based vectors. We have therefore compared the susceptibility of the common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus) with the owl monkey in a model of intracerebral inoculation of wildtype HSV-1 F-strain at increasing titers. The common marmosets consistently succumbed earlier to viral encephalitis than the owl monkeys. The histological evaluation of the common marmoset revealed extensive HSV-1 infection with a concomitant yet less marked inflammatory response compared to the owl monkeys. PCR for HSV-1 demonstrated a similar extra-CNS shedding route in both experimental models. Our findings show that the common marmoset is at least as susceptible to intracerebral HSV-infection as the owl monkey and that it can therefore serve as a valid and reliable experimental model for the important preclinical safety tests of HSV-based therapeutic viral vector constructs in the brain.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Katzin DS, Connor JD, Wilson LA, Sexton RS . Experimental herpes simplex infection in the owl monkey. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 1967; 125: 391–398.
Hunt RD, Melendez LV . Herpes virus infections of non-human primates: a review. Lab Anim Care 1969; 19: 221–234.
Hunt RD, Melendez LV . Clinical, epidemiologic, and pathologic features of cytocidal and oncogenic herpesviruses in South American monkeys. J Natl Cancer Inst 1972; 49: 261–271.
Cho CT, Liu C, Voth DW, Feng KK . Effects of idoxuridine on herpes hominis encephalitis and disseminated infections in marmosets. J Infect Dis 1973; 128: 718–723.
Cho CT, Feng KK . Sensitivity of the virus isolation and immunofluorescent staining methods in diagnosis of infections with herpes simplex virus. J Infect Dis 1978; 138: 536–540.
Genain CP et al. Inhibition of allergic encephalomyelitis in marmosets by vaccination with recombinant vaccinia virus encoding for myelin basic protein. J Neuroimmunol 1997; 79: 119–128.
Hibino H et al. The common marmoset as a target preclinical model for cytokine and gene therapy studies. Blood 1999; 93: 2839–2848.
Meignier B . Genetically engineered attenuated herpes simplex viruses. J Infect Dis 1991; 13(Suppl 11): S895–S897.
Howard MK et al. High efficiency gene transfer to the central nervous system of rodents and primates using herpes virus vectors lacking functional ICP27 and ICP34.5. Gene Therapy 1998; 5: 1137–1147.
Melendez LV et al. Natural herpes simplex infection in the owl monkey (Aotus trivirgatus). Lab Anim Care 1969; 19: 38–45.
Hunter WD et al. Attenuated, replication-competent herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant G207: safety evaluation of intracerebral injection in nonhuman primates. J Virol 1999; 73: 6319–6326.
Meignier B et al. Immunization of experimental animals with reconstituted glycoprotein mixtures of herpes simplex virus 1 and 2: protection against challenge with virulent virus. J Infect Dis 1987; 155: 921–930.
Meignier B, Martin B, Whitley RJ, Roizman B . In vivo behavior of genetically engineered herpes simplex viruses R7017 and R7020. II. Studies in immunocompetent and immunosuppressed owl monkeys (Aotus trivirgatus). J Infect Dis 1990; 162: 313–321.
Juan-Salles C et al. Spontaneous herpes simplex infection in common marmosets (Callithrix jacchus). J Vet Diagn Invest 1997; 9: 341–345.
Todo T et al. Viral shedding and biodistribution of G207, a multimutated, conditionally replicating herpes simplex virus type 1, after intracerebral inoculation in aotus. Mol Ther 2000; 2: 588–595.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by Grant CA69246 from the National Institutes of Health (to FHH, EAC, DNL) as well as by the Primate Center PHS Grant P51RR00168-40. UN is the recipient of a 2001 Toennis Scholarship of the German Society of Neurosurgery (DGNC). We thank Dr Angela Carville and Dr Paul Johnson (both New England Regional Primate Research Center, Harvard University) and Dr David Knipe (Harvard Medical School) for inspiring discussions. The valuable technical assistance of Mrs Linda Fernstein, Ms Kristen Suling, Mrs Edita Tyminski, Ms Andrea Cutone, Ms Melissa Brower, and Ms Wendy Cohen is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deisboeck, T., Wakimoto, H., Nestler, U. et al. Development of a novel non-human primate model for preclinical gene vector safety studies. Determining the effects of intracerebral HSV-1 inoculation in the common marmoset: a comparative study. Gene Ther 10, 1225–1233 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302003
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302003
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Animal Models for Target Diseases in Gene Therapy — using DNA and siRNA Delivery Strategies
Pharmaceutical Research (2009)
-
Safety and biodistribution studies of an HSV multigene vector following intracranial delivery to non-human primates
Gene Therapy (2004)
-
Gene transfer vector biodistribution: pivotal safety studies in clinical gene therapy development
Gene Therapy (2004)