Abstract
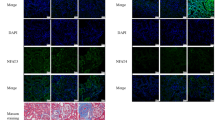
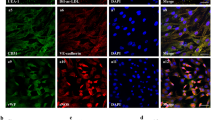
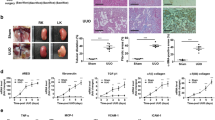
Nuclear factor κB (NFκB) plays a pivotal role in the coordinated transactivation of a series of genes of cytokines and adhesion molecules that are highly involved in the onset of acute rejection in organ transplantation. We previously developed decoy cis-elements oligo deoxyribonucleic acid against NFκB (NFκB-decoy) that effectively inhibited the activation of major inflammatory mediators in vitro and in vivo. Accordingly, we hypothesized that transfection of NFκB-decoy into the donor kidney would prevent acute rejection and prolong graft survival, and thus provide effective therapy for renal acute rejection. To transfect NFκB-decoy, we employed a novel approach using ultrasound exposure with an echocardiographic contrast agent, Optison, and clearly demonstrated successful transfection of NFκB-decoy into renal tissue. The therapeutic effect of NFκB-decoy on renal allografts was then evaluated in a rat renal allograft model (Wistar–Lewis). In the control group, graft function significantly deteriorated with marked destruction of renal tissue, accompanied by increased production of major inflammatory mediators, and all animals died of renal failure by 9 days. In contrast, graft function (serum creatinine on day 2, NFκB-treated: 0.97±0.16 versus control: 1.84±0.23 mg/dl, P<0.01) and histological structure were well preserved with significantly decreased expression of NFκB-regulated cytokines and adhesion molecules, including IL-1, iNOS, MCP-1, TNF-α, and ICAM-1, in allografts transfected with NFκB-decoy. As a result, animal survival was significantly prolonged in this group as compared to controls (14.2±5.2 versus 7.1±1.2 days, P<0.01). Thus, we established a novel ultrasound–Optison-mediated gene transfection approach and demonstrated the significant prolongation of graft survival by the successful transfection of NFκB-decoy into the donor kidney in a rat renal allograft model.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hancock WW, Thomson NM, Atkins RC . Composition of interstitial cellular infiltrate identified by monoclonal antibodies in renal biopsies of rejecting human renal allografts. Transplantation 1983; 35: 458–463.
Shannon MF, Himes SR, Coles LS . GM-CSF and IL-2 share common control mechanisms in response to costimulatory signals in T cells. J Leukocyte Biol 1995; 57: 767–773.
Sehajpal PK et al. Synergism between the CD3 antigen- and CD2 antigen-derived signals. Transplantation 1993; 55: 1118–1124.
Baeuerle PA, Henkel T . Function and activation of NF-κB in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol 1994; 12: 141–179.
Lenardo MJ, Baltimore D . NF-kappa B: a pleiotropic mediator of inducible and tissue-specific gene control. Cell 1989; 58: 227–229.
Read MA, Whitney MZ, Williams AJ, Collins T . NF-κB and IκB: an inducible regulatory system in endothelial activation. J Exp Med 1994; 179: 503–512.
Libermann TA, Baltimore D . Activation of interleukin-6 gene expression through the NP-kappa B transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol 1990; 10: 2327–2334.
Schlondorff SJ . Activation and attenuation of transcription factor NF-κB in mouse glomerular mesangial cells in response to tumor necrosis factor-alpha, immunoglobulin GF, and adenosine 3′: 5′-cyclic monophosphate: evidence for involvement of reactive oxygen species. J Clin Invest 1994; 94: 1629–1636.
Denk A et al. Activation of NF-κB via the IκB kinase complex is both essential and sufficient for proinflammatory gene expression in primary endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 28 451–28 458.
Xie QW, Kashiwabara Y, Nathan C . Role of transcription factor NF-kappa B/Rel in induction of nitric oxide synthase. J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 4705–4708.
Taylor BS et al. Multiple NF-kappaB enhancer elements regulate cytokine induction of the human inducible nitric oxide synthase gene. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 15 148–15 156.
Neish AS et al. Functional analysis of the human vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 promoter. J Exp Med 1992; 176: 1583–1593.
Collins T et al. Transcriptional regulation of endothelial cell adhesion molecules: NFκB and cytokine-inducible enhancers. FASEB J 1995; 9: 899–909.
Xia YF, Liu LP, Zhong CP, Geng JG . NF-kappaB activation for constitutive expression of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 on B limphocytes and plasma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2001; 289: 851–856.
Cooper M et al. Myocardial nuclear factor-kappaB activity and nitric oxide production in rejecting cardiac allografts. Transplantation 1998; 66: 838–844.
Mattila PS et al. The actions of cyclosporin A and FK506 suggest a novel step in the activation of T lymphocytes. EMBO J 1990; 9: 4425–4433.
McCaffrey PG et al. Cyclosporin A sensitivity of the NF-kappa B site of the IL2R alpha promoter in untransformed murine T cells. Nucleic Acids Res 1994; 22: 2134–2142.
Kanno T, Siebenlist U . Activation of nuclear factor-κB via T cell receptor requires a Raf kinase and Ca2+ influx Functional synergy between Raf and calcineurin. J Immunol 1996; 157: 5277–5283.
Scheinman RI, Cogswell PC, Lofquist AK, Baldwin ASJ . Role of transcription activation of IκB α in mediation of immunosuppression by glucocorticoids. Science 1995; 270: 283–286.
Auphan N et al. Immunosuppression by glucocorticoids: inhibition of NF-κB activity through induction of IκB synthesis. Science 1995; 270: 286–290.
Sullenger BA, Gallardo HF, Ungers GE, Gilboa E . Overexpression of TAR sequence renders cells resistant to human immunodeficiency virus replication. Cell 1990; 63: 601–608.
Bielinska A, Shivdasani RA, Zhang LQ, Nabel GJ . Regulation of gene expression with double-stranded phosphorothioate oligonucleotides. Science 1990; 250: 997–1000.
Morishita R et al. Role of transcriptional cis-elements, angiotensinogen gene-activating element, of angiotensinogen gene in blood pressure regulation. Hypertension 1996; 27: 502–507.
Morishita R et al. A gene therapy strategy using a transcription factor decoy of the E2F binding site inhibits smooth muscle proliferation in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92: 5855–5859.
Morishita R et al. In vivo transfection of cis elemeny “decoy” against nuclear factor-κB binding site prevents myocardial infarction. Nature Med 1997; 3: 894–899.
Sawa Y et al. A novel strategy for myocardial protection using in vivo transfection of cis element decoy against NFκB binding site. Evidence for a role of NFκB in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Circulation 1997; 96(Suppl 2): 280–285.
Tomita N et al. Transcription factor decoy for nuclear factor-kappaB inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced expression of interleukin-6 and intracellular adhesion molecule-1 in endothelial cells. J Hypertens 1998; 16: 993–1000.
Tomita N et al. Transcription factor decoy for NFkappaB inhibits TNF-alpha-induced cytokine and adhesion molecule expression in vivo. Gene Ther 2000; 7: 1326–1332.
Tomita N et al. In vivo administration of a nuclear transcription factor-kappaB decoy suppresses experimental crescentic glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 2000; 11: 1244–1252.
Tomita N et al. Inhibition of TNF-alpha, induced cytokine and adhesion molecule. Expression in glomerular cells in vitro and in vivo by transcription factor decoy for NFkappaB. Exp Nephrol 2001; 9: 181–190.
Lawrie A et al. Ultrasound enhances reporter gene expression after transfection of vascular cells in vitro. Circulation 1999; 99: 2617–2620.
Kim HJ et al. Ultrasound-mediated transfection of mammalian cells. Human Gene Ther 1996; 7: 1339–1346.
Miller DL, Bao S, Gies RA, Thrall BD . Ultrasonic enhancement of gene transfection in murine melanoma tumors. Ultrasound Med Biol 1999; 25: 1425–1430.
Miller DL, Gies RA . Enhancement of ultrasonically-induced hemolysis by perfluorocarbon-based compared to air-based echo-contrast agent. Ultrasound Med Biol 1998; 24: 285–292.
Miller DL, Gies RA, Chrisler WB . Ultrasonically induced hemolysis at high cell and gas body concentrations in a thin-disc exposure chmber. Ultrasound Med Biol 1997; 23: 625–633.
Killam A, Dittrich H . In: Goldberg B. (ed). Ultrasound Contrast Agents. Martin Dunitz: London, 1997, pp. 43–55.
Miller DL, Quddus J . Diagnostic ultrasound activation of contrast agent gas bodies induces capillary rupture in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 10179–10184.
Ward M, Wu J . Ultrasound-induced cell lysis and sonoporation enhanced by contrast agents. J Acoust Soc Am 1999; 105: 2951–2957.
Pober JS, Cotran RS . Immunologic interactions of T lymphocytes with vascular endothelium. Adv Immunol 1991; 50: 261–302.
Brand K et al. Role of nuclear factor-κB in atherogenesis. Exp Physiol 1997; 82: 297–304.
Bach FH, Hancock WW, Ferran C . Protective genes expressed in endothelial cells: a regulatory response to injury. Immunol Today 1997; 18: 483–486.
Sedmak DD, Orosz CG . The role of vascular endothelial cells in transplantation. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1991; 115: 260–265.
Noris M, Remuzzi G . New insights into circulating cell–endothelium interactions and their significance for glomerular pathophysiology. Am J Kidney Dis 1995; 26: 541–548.
Elliot MJ, Finn AH . Interaction between neutrophils and endothelium. Ann Thorac Surg 1993; 56: 1503.
Azuma H, Paul LC, Tilney NL . Insights into acute and chronic rejection. Transplant Proc 1996; 28: 2081–2084.
Vos IHC et al. NFκB decoy oligodeoxynucleotides reduce mono-cyte infiltration in renal allografts. FASEB J 2000;14: 815–822.
Azuma H et al. Hepatocyte growth factor prevents development of chronic allograft nephropathy in rats. J Am Soc Nephrol 2001; 12: 1280–1292.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azuma, H., Tomita, N., Kaneda, Y. et al. Transfection of NFκB-decoy oligodeoxynucleotides using efficient ultrasound-mediated gene transfer into donor kidneys prolonged survival of rat renal allografts. Gene Ther 10, 415–425 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301882
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301882
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A new approach to transfect NF-κB decoy oligodeoxynucleotides into the periodontal tissue using the ultrasound-microbubble method
International Journal of Oral Science (2017)
-
Stimuli-Responsive Polymeric Nanocarriers for Efficient Gene Delivery
Topics in Current Chemistry (2017)
-
Gene therapy progress and prospects: Ultrasound for gene transfer
Gene Therapy (2007)
-
Transcription factor decoy oligonucleotide-based therapeutic strategy for renal disease
Clinical and Experimental Nephrology (2007)
-
Ultrasound-mediated gene transfection: problems to be solved and future possibilities
Journal of Medical Ultrasonics (2006)