Abstract
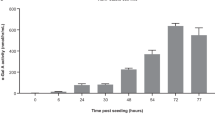
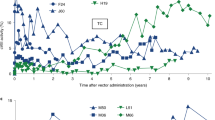
Gene therapy using recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors (rAAV) is generally considered safe. During the course of a study designed to determine the long-term efficacy of rAAV-mediated gene therapy initiated in newborn mice with the lysosomal storage disease, mucopolysaccharidosis type VII (MPSVII), a significant incidence of hepatocellular carcinomas and angiosarcomas was discovered. A hepatocellular carcinoma was first detected in a 35-week-old mouse and by 72 weeks of age, three out of five rAAV-treated MPSVII mice had similar lesions. These types of tumors had not been seen previously in long-term studies of MPSVII mice using recombinant enzyme or bone marrow transplantation. In an attempt to ascertain whether mouse strain or GUSB expression confers susceptibility to tumor formation, we histopathologically examined untreated normal mice of the same strain, untreated MPSVII mice, and normal mice overexpressing human GUSB for the presence of tumors and increased hepatocyte replication. The results of these studies do not indicate that MPSVII mice or mice overexpressing human GUSB are susceptible to tumor formation; however, the number of animals examined is too small to draw definitive conclusions. Results from quantitative PCR performed on the tumor samples suggest that the tumors are probably not caused by an insertional mutagenesis event followed by the clonal expansion of a transformed cell. In a separate study, a relatively large group of mice injected with varying doses and types of rAAV vectors had no evidence of hepatic or vascular tumors. Although the mechanism of tumor formation is currently unknown, the tumorigenic potential of rAAV vectors must be rigorously determined in long-term in vivo studies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Monahan PE, Samulski RJ . AAV vectors: is clinical success on the horizon? Gene Therapy 2000 7: 24–30
Flotte TR, Afione SA, Zeitlin PL . Adeno-associated virus vector gene expression occurs in nondividing cells in the absence of vector DNA integration Am J Resp Cell Mol Biol 1994 11: 517–521
Kearns WG et al. Recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV-CFTR) vectors do not integrate in a site-specific fashion in an immortalized epithelial cell line Gene Therapy 1996 3: 748–755
Ponnazhagan S et al. Differential expression in human cells from the p6 promoter of human parvovirus B19 following plasmid transfection and recombinant adeno-associated virus 2 (AAV) infection: human megakaryocytic leukemia cells are non-permissive for AAV infection J Gen Virol 1996 77: 1111–1122
Afione SA et al. In vivo model of adeno-associated virus vector persistence and rescue J Virol 1996 70: 3235–3241
Daly TM et al. Prevention of systemic clinical disease in MPSVII mice following AAV-mediated neonatal gene transfer Gene Therapy 2001 8: 1291–1298
Birkenmeier EH et al. Murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII: characterization of a mouse with β-glucuronidase deficiency J Clin Invest 1989 83: 1258–1266
Birkenmeier EH et al. Increased life span and correction of metabolic defects in murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII after syngeneic bone marrow transplantation Blood 1991 11: 1381–1392
Daly TM et al. Neonatal intramuscular injection with recombinant AAV results in prolonged β-glucuronidase expression in situ and correction of liver and spleen pathology in mucopolysaccharidosis type VII mice Hum Gene Ther 1999 10: 85–94
Niwa H, Yamamura K, Miyazaki J . Efficient selection for high-expression transfectants with a novel eukaryotic vector Gene 1991 108: 193–200
Sands MS et al. Treatment of murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII by syngeneic bone marrow transplantation in neonates Lab Invest 1993 68: 676–686
Sands MS et al. Syngeneic bone marrow transplantation reduces the hearing loss associated with murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII Blood 1995 86: 2033–2040
Vogler CA et al. Enzyme replacement with recombinant β-glucuronidase in murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII-impact of therapy during the first week of life on subsequent lysosomal storage, growth and survival Ped Res 1996 39: 1050–1054
Sands MS et al. Murine mucopolysaccharidosis type VII: long-term therapeutic effects of enzyme replacement and enzyme replacement followed by bone marrow transplantation J Clin Invest 1997 99: 1596–1605
Song S et al. Stable therapeutic serum levels of human alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) after portal vein injection of recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) vectors Gene Therapy 2001 8: 1299–1306
Zolotukhin S et al. Recombinant adeno-associated virus purification using novel methods improves infectious titer and yield Gene Therapy 1999 6: 973–985
Acknowledgements
Many thanks to Dr Ronald Marks who assisted with the statistical comparisons, Amy Pourier for technical support for the real-time PCR assays and Dr Kathy Ponder for assistance with BrdU labeling. This work was funded by grants from the NIDDK DK58327 (NM, TF), the NHLBI HL59412 (NM, TF), NIDDK 27726 (JEB), and NIDDK 53920 (MSS). Many thanks to Barry Byrne, Alfred Lewin, and Philip Laipis for contributing retrospective data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Donsante, A., Vogler, C., Muzyczka, N. et al. Observed incidence of tumorigenesis in long-term rodent studies of rAAV vectors. Gene Ther 8, 1343–1346 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301541
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301541
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Recent advances in various adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) as gene therapy agents in hepatocellular carcinoma
Virology Journal (2024)
-
Integrated vector genomes may contribute to long-term expression in primate liver after AAV administration
Nature Biotechnology (2023)
-
High spontaneous integration rates of end-modified linear DNAs upon mammalian cell transfection
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
A long-term study of AAV gene therapy in dogs with hemophilia A identifies clonal expansions of transduced liver cells
Nature Biotechnology (2021)
-
Gene Therapy for Hemophilia: Progress to Date
BioDrugs (2018)