Abstract
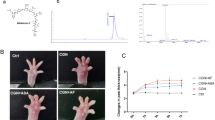
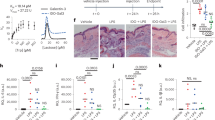
The transcription factor nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) plays a key role in the expression of several genes involved in the inflammatory process. In the present study we investigated in an acute model of inflammation, the carrageenin-induced hind paw edema, the anti-inflammatory effect of double stranded oligodeoxynucleotides (ODN) with consensus nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) sequence as transcription factor decoys (TFD) to inhibit NF-κB binding to native DNA sites. Local administration of wild-type, but not mutant-ODN decoy, dose-dependently inhibited edema formation induced by carrageenin in rat paw. Molecular analysis performed on soft tissue obtained from inflamed paw demonstrated: (1) an inhibition of NF-κB DNA binding activity; (2) a decreased nuclear level of p50 and p65 NF-κB subunits; (3) an inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) protein expression, two inflammatory enzymes transcriptionally controlled by NF-κB. Furthermore, SN-50, a cell-permeable peptide capable of inhibiting the nuclear translocation of NF-κB complexes, exhibited a similar profile of activity of ODN decoy. Our results indicate for the first time that ODN decoy, acting as an in vivo competitor for the transcription factor's ability to bind to cognate recognition sequence, may represent a novel strategy to modulate acute inflammation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Movat HZ . Mediators of the vascular phenomena of acute inflammation. In: Movat HZ (ed) The Inflammatory Reaction Elsevier: Amsterdam 1985 77–86
Di Rosa M, Giroud JP, Willoughby DA . Studies of mediators of the acute inflammatory response induced in rats in different sites by carrageenin and turpentine J Pathol 1971 104: 15–29
Ialenti A, Ianaro A, Moncada S, Di Rosa M . Modulation of acute inflammation by endogenous nitric oxide Eur J Pharmacol 1992 211: 177–182
Salvemini D et al. Nitric oxide: a key mediator in the early and late phase of carrageenan-induced rat paw inflammation Br J Pharmacol 1996 118: 829–838
Seibert K et al. Pharmacological and biochemical demonstration of the role of cyclooxygenase 2 in inflammation and pain Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1994 91: 12013–12017
Salvemini D et al. Dual inhibition of nitric oxide and prostaglandin production contributes to the anti-inflammatory properties of nitric oxide synthase inhibitors J Clin Invest 1995 96: 301–308
Tomlison A et al. Cyclo-oxygenase and nitric oxide synthase isoforms in rat carrageenan-induced pleurisy Br J Pharmacol 1994 113: 693–698
Ialenti A, Moncada S, Di Rosa M . Modulation of adjuvant arthritis by endogenous nitric oxide Br J Pharmacol 1993 110: 701–706
Ianaro A, Ialenti A, Sautebin L, Di Rosa M . Nitric oxide inhibits neutrophil infiltration in the reverse passive Arthus reaction in rat skin N-S Arch Pharmacol 1998 358: 489–495
Iuvone T et al. Differential effect of L-NAME and S-methyl-isothiourea on leukocyte emigration in carrageenin-soaked sponge implants in rat Br J Pharmacol 1997 121: 1637–1644
Iuvone T et al. Evidence that inducible nitric oxide synthase is involved in LPS-induced plasma leakage in rat skin through the activation of nuclear factor-κB Br J Pharmacol 1998 123: 1325–1330
Fletcher BS, Kujubu DA, Perrin DM, Herschman HR . Structure of the mitogen-inducible TIS10 gene and demonstration that the TIS10-encoded protein is a functional prostaglandin G/H synthase J Biol Chem 1992 267: 4338–4344
Sirois J, Levy LO, Simmons DL, Richards JS . Characterisation and hormonal regulation of the promoter of rat prostaglandin endoperoxide synyhase 2 gene in granulosa dells. Identification of functional and protein-binding regions J Biol Chem 1993 268: 12199–12206
Kosaka T et al. Characterisation of the human gene (PTGS2) encoding prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 Eur J Biochem 1994 221: 889–897
Xie QW, Whisnant R, Nathan C . Promoter of the mouse gene encoding calcium-independent nitric oxide synthase confers inducibility by interferon γ and bacterial lipopolysaccharide J Exp Med 1993 177: 1779–1784
Lowenstain CJ et al. Macrophage nitric oxide synthase gene: two upstream regions mediate induction by interferon γ and lipopolysaccharide Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993 90: 9730–9734
De Vera ME et al. Transcriptional regulation of human inducible nitric oxide synthase (NOS2) gene by cytokines: initial analysis of the human NOS2 promoter Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996 93: 1054–1059
Yamamoto K, Arakawa T, Ueda N, Yamamoto S . Transcriptional roles of nuclear factor κB and nuclear factor-interleukin-6 in the tumor necrosis factor α-dependent induction of cyclooxygenase-2 in MC3T3-E1 cells J Biol Chem 1995 270: 31315–31320
Xie Q, Kashiwabara Y, Nathan C . Role of transcription factor NF-κB/Rel in induction of nitric oxide J Biol Chem 1994 269: 4705–4708
Thanos D, Maniatis T . NF-κB: a lesson in family values Cell 1995 80: 529–532
Baeuerle PA, Baltimore D . NF-κB: ten years after Cell 1996 87: 13–20
Baldwin AS Jr . The NF-κB and IκB proteins: new discoveries and insights Ann Rev Immunol 1996 14: 649–681
Finco TS, Baldwin AS . Mechanistic aspects of NF-κB regulation: the emerging role of phosphprylation and proteolysis Immunity 1995 3: 263–272
Baeuerle PA, Henkel T . Function and activation of NF-κB in the immune system Ann Rev Immunol 1994 12: 141–179
May MJ, Ghosh S . Signal transduction through NF-κB Immunol Today 1998 19: 80–88
Schreck R et al. Dithiocarbamate as potent inhibitors of nuclear factor κB activation in intact cells J Exp Med 1992 175: 1181–1194
D'Acquisto F et al. Activation of nuclear transcription factor κB in rat carrageenin-induced pleurisy Eur J Pharmacol 1999 369: 233–236
D'Acquisto F, Ialenti A, Ianaro A, Carnuccio R . Nuclear factor-kB mediates inducible nitric oxide synthase protein expression in carrageenin-induced rat pleurisy N-S Arch Pharmacol 1999 360: 670–675
Pierce JW et al. Novel inhibitor of cytokine-induced IκBα phorphorylation and endothelial cell adhesion molecule expression show anti-inflammatory effects in vivo J Biol Chem 1997 272: 21096–21103
Bielinska A, Schivdasani RA, Zhang L, Nabel GJ . Regulation of gene expression with double stranded phosphorothioate oligonucleotides Science 1990 250: 997–1000
Morishita R et al. In vivo transfection of cis element ‘decoy’ against nuclear factor-κB site prevents myocardial infarction Nature Med 1997 8: 894–899
Kawamura I et al. Intratumoral injection of oligonucleotides to the NF-κB binding site inhibits cachexia in a mouse tumor model Gene Therapy 1999 6: 91–97
Sharma HW et al. Transcription factor decoy approach to decipher the role of NF-κB in oncogenesis Anticancer Res 1996 16: 61–70
Schmedtje JF Jr et al. Hypoxia induces cyclooxygenase-2 via the NF-κB p65 transcription factor in human vascular endothelial cells J Biol Chem 1997 272: 601–608
Roshak AK et al. Manipulation of distinct NF-κB proteins alters interleukin-1β-induced human rheumatoid synovial fibroblast prostaglandin E2 formation J Biol Chem 1996 271: 31496–31501
Lin YZ et al. Inhibition of nuclear translocation of transcription factor NF-kappa B by a synthetic peptide containing a cell membrane-permeable motif and nuclear localisation sequence J Biol Chem 1995 270: 14255–14258
Morishita R et al. A gene therapy strategy using a transcription factor decoy of the E2F binding site inhibits smooth muscle proliferation in vivo Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995 92: 5855–5859
Miagkov AV et al. NF-κB activation provides the potential link between inflammation and hyperplasia in arthritic joint Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998 95: 13859–13864
Tomita T et al. Suppressed severity of collagen-induced arthritis by in vivo transfection of nuclear factor kappaB decoy oligodeoxynucleotides as a gene therapy Arthr Rheum 1999 42: 2532–2542
Di Rosa M, Willoughby DA . Screens for anti-inflammatory drugs J Pharm Pharmacol 1971 23: 297–298
Kopp E, Ghosh S . Inhibition of NF-κB by sodium salicylate and aspirin Science 1994 265: 956–959
Auphan N et al. Immunosuppression by glucocorticoids: inhibition of NF-κB activity trough induction of IκB synthesis Science 1995 270: 286–290
Scheiman R, Cogwell P, Lofquist A, Baldwin A . Role of transcriptional activation of IκBα in mediation of immunosuppression by glucocorticoids Science 1995 270: 283–286
Adcock IM, Newton R, Barnes PJ . NF-kappa B involvement in IL-1 beta-induction of GM-CSF and COX-2: inhibition by glucocorticoids does not require I-kappa B Biochem Soc Trans 1997 25: 154S
Fernandez de Arriba A et al. Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 expression by 4-trifluoromethyl derivates of salicylate, triflusal, and its deacetylated metabolite, 2-hydroxy-4-trifluoromethylbenzoic acid Mol Pharmacol 1999 55: 753–760
De Vera ME et al. Dexamethasone suppresses iNOS gene expression by upregulating I-kappa B alpha and inhibiting NF-kappa B Am J Physiol 1997 273: G1290–G1296
Bayon Y, Alonso A, Sanchez Crespo M . 4-trifluoromethyl derivatives and its main metabolite 2-hydroxy-4-trifluoromethylbenzoic acid, are potent inhibitors of nuclear factor kappa B activation Br J Pharmacol 1999 126: 1359–1366
Goldring CEP, Narayaznan R, Lagadec P, Jeannin JF . Transcriptional inhibition of the inducible nitric oxide synthase gene by competitive binding of NF-κB/Rel proteins Biochem Biophys Res Comm 1995 209: 73–79
Morris CJ, Earl JR, Tenam CW, Blame DR . Reactive oxygen species and iron – a dangerous partnership in inflammation Int J Biochem Cell Biol 1995 27: 109–122
Schmidt KN, Amstad P, Cerruti P, Baeuerle PA . The roles of hydrogen peroxide and superoxide as messenger in the activation of transcription factor NF-κB Chem Biol 1995 2: 13–22
Sakurada S, Kato T, Okamoto T . Induction of cytokines and ICAM-1 by proinflammatory cytokines in primary rheumatoid synovial fibroblast and inhibition by N-acetyl-L-cysteine and aspirin Int Immunol 1996 8: 1483–1493
Sakurai H et al. Activation of transcription factor NF-κB in experimental glomerulonephitis in rats Biochem Biophys Acta 1996 1316: 132–138
D'Acquisto F et al. Inhibition of nuclear factor-κB prevents the loss of vascular tone in lipopolysaccharide-treated rats Eur J Pharmacol 1999 365: 253–257
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by MURST 40% and 60% research grant 1997 and 1998.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
D'Acquisto, F., Ialenti, A., Ianaro, A. et al. Local administration of transcription factor decoy oligonucleotides to nuclear factor-κB prevents carrageenin-induced inflammation in rat hind paw. Gene Ther 7, 1731–1737 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301295
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301295
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Large-scale computational modelling of the M1 and M2 synovial macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis
npj Systems Biology and Applications (2024)
-
AAV-mediated expression of NFAT decoy oligonucleotides protects from cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure
Basic Research in Cardiology (2021)
-
NFκB Activatesin vivothe Synthesis of Inducible Cox-2 in the Brain
Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism (2005)
-
Hydroxytyrosol, a phenolic compound from virgin olive oil, prevents macrophage activation
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2005)
-
Apoptosis defects and chemotherapy resistance: molecular interaction maps and networks
Oncogene (2004)