Abstract
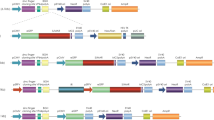
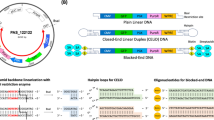
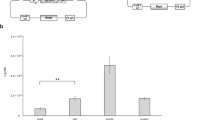
The latent replication of oriP-based plasmids in human cells depends on the viral oriP-binding transactivator EBNA1. In this report, the effect of the internal repeat 3 (IR3 or GlyAla repeat) domain of EBNA1 on long-term maintenance and transgene expression of OriP-based plasmids was examined in dividing human cells. To assess the potential contribution of different isoforms of EBNA1 specifically, the long-term stability of oriP-based plasmids was determined after stable transfection of various CMV-driven EBNA1 genes in EBV-negative human B cells. Episome copy number was quantified using a novel sensitive assay based on human mitochondrial DNA as an internal extrachromosomal control. Using this assay, the standard B95.8-derived EBNA1 was compared with its truncated, IR3-deleted, form, as well as a new EBNA1 isoform cloned from Raji. The results of a 6-month study indicate that the isoforms of EBNA1 differ with respect to their efficiency of plasmid maintenance. While the EBNA-1 Raji encoding plasmid was the most stable, the oriP-based vector expressing the truncated EBNA1 (IR3del) gene was lost at a much higher rate than those transducing full size EBNA1s. In parallel, long-term reporter gene expression in various human B cell lines was shown to persist at the highest level with the oriP-based Raji EBNA-1 construct. These results show that the GlyAla domain can positively influence long-term plasmid stability and episomal transgene expression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wendelburg, B., Vos, JM. An enhanced EBNA1 variant with reduced IR3 domain for long-term episomal maintenance and transgene expression of oriP-based plasmids in human cells. Gene Ther 5, 1389–1399 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3300736
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3300736