Abstract
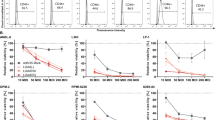
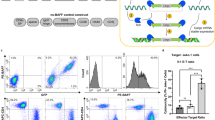
Gene transfer of the costimulatory molecules of B7–1 and B7–2 induces a potent antitumor immune response in a variety of tumor models. B cell neoplasms including multiple myeloma (MM) often show little or no expression of B7 antigens; they are therefore a potential target for this approach. To increase the expression of human B7 genes in MM cells, both genes and the neomycin phosphotransferase gene were packaged into recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors (rAAV). The resulting recombinant viruses rAAV/B7–1, rAAV/B7–2 and rAAV/Neo were used to transduce the MM cell lines LP-1 and RPMI 8226. This allowed the transduction of up to 80% of LP-1 cells 4 days after infection with purified rAAV particles. The response of human allogeneic T cells to rAAV/B7–1 and rAAV/B7–2 transduced, γ-irradiated LP-1 cells was assessed by [3H]thymidine incorporation, by RT-PCR-based detection of immunostimulatory cytokine transcripts and by ELISA quantification of cytokines in the supernatant. Stimulation of T cells with rAAV/B7–1 or rAAV/B7–2 transduced LP-1 cells resulted in an up to 10-fold increase of T cell proliferation when compared with LP-1 cells transduced with rAAV/Neo. Similar results were obtained with RPMI 8226 cells. Both rAAV/B7–1 and rAAV/B7–2 transduced LP-1 cells stimulated the T cell secretion of IL-2 and IFN-γ. Furthermore, [51Cr] release assays showed that rAAV/B7–1 or rAAV/B7–2 transduced LP-1 cells induced a cytolytic T cell (CTL) response, in contrast to LP-1 cells transduced with rAAV/Neo. In all assays, the effects of rAAV/B7–1 and rAAV/B7–2 were similar. Taken together, the results show that rAAV-mediated transfer of B7 genes into MM cell lines is able to enhance the antitumor T cell response and to elicit a cytolytic T cell response.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wendtner, CM., Nolte, A., Mangold, E. et al. Gene transfer of costimulatory molecules B7–1 and B7–2 into human multiple myeloma cells by recombinant adeno-associated virus enhances the cytolytic T cell response. Gene Ther 4, 726–735 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3300447
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3300447
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Adenoviral-mediated transfer of human wild-type p53, GM-CSF and B7-1 genes results in growth suppression and autologous anti-tumor cytotoxicity of multiple myeloma cells in vitro
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2006)
-
Tricistronic viral vectors co-expressing interleukin-12 (1L-12) and CD80 (B7-1) for the immunotherapy of cancer: Preclinical studies in myeloma
Cancer Gene Therapy (2001)
-
Potentiation of a recombinant oncolytic parvovirus by expression of Apoptin
Cancer Gene Therapy (2001)