Abstract
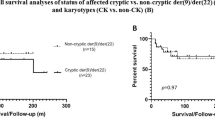
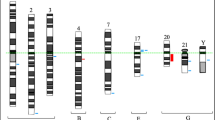
In CLL data from chromosome banding analysis (CBA) have been scarce due to the low proliferative activity of CLL cells in vitro. We improved the cultivation technique using an immunostimulatory CpG-oligonucleotide DSP30 and IL-2. A total of 506 CLL samples were analysed with CBA and interphase FISH using probes for the detection of trisomy 12, IgH rearrangements and deletions of 6q21, 11q22.3 (ATM), 13q14 (D13S25 and D13S319) and 17p13 (TP53). A total of 500 of 506 (98.8%) cases were successfully stimulated for metaphase generation and are subject to this study. Aberrations were detected in 415 of 500 (83.0%) cases by CBA and in 392 of 500 (78.4%) cases by FISH. CBA detected 832 abnormalities and FISH only 502. Therefore, CBA offers important information in addition to FISH. (1) CLL is characterized mainly by genomic imbalances and reciprocal translocations are rare. (2) A subgroup with complex aberrant karyotype (16.4%) is identified which is associated with an unmutated IgVH status and CD38 expression (P=0.034 and 0.02, respectively). (3) Additional abnormalities are detectable providing new biological insights into different CLL subclasses revealing a much more heterogeneous pattern of cytogenetic abnormalities as assumed so far based on FISH data only. Therefore, prospective clinical trials should evaluate the prognostic impact of newly available CBA data.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shanafelt TD, Geyer SM, Kay NE . Prognosis at diagnosis: integrating molecular biologic insights into clinical practice for patients with CLL. Blood 2004; 103: 1202–1210.
Kay NE, O’brien SM, Pettitt AR, Stilgenbauer S . The role of prognostic factors in assessing ‘high-risk’ subgroups of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2007, Leukemia (2007) 21, –;, 14 June 2007.
Gahrton G, Robert KH, Friberg K, Zech L, Bird AG . Nonrandom chromosomal aberrations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia revealed by polyclonal B-cell-mitogen stimulation. Blood 1980; 56: 640–647.
Juliusson G, Oscier DG, Fitchett M, Ross FM, Stockdill G, Mackie MJ et al. Prognostic subgroups in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia defined by specific chromosomal abnormalities. N Engl J Med 1990; 323: 720–724.
Oscier DG, Gardiner AC, Mould SJ, Glide S, Davis ZA, Ibbotson RE et al. Multivariate analysis of prognostic factors in CLL: clinical stage, IGVH gene mutational status, and loss or mutation of the p53 gene are independent prognostic factors. Blood 2002; 100: 1177–1184.
Bentz M, Huck K, du MS, Joos S, Werner CA, Fischer K et al. Comparative genomic hybridization in chronic B-cell leukemias shows a high incidence of chromosomal gains and losses. Blood 1995; 85: 3610–3618.
Döhner H, Stilgenbauer S, Benner A, Leupolt E, Kröber A, Bullinger L et al. Genomic aberrations and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 1910–1916.
Grever MR, Lucas DM, Dewald GW, Neuberg DS, Reed JC, Kitada S et al. Comprehensive assessment of genetic and molecular features predicting outcome in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: results from the US Intergroup Phase III Trial E2997. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 799–804.
Buhmann R, Kurzeder C, Rehklau J, Westhaus D, Bursch S, Hiddemann W et al. CD40L stimulation enhances the ability of conventional metaphase cytogenetics to detect chromosome aberrations in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells. Br J Haematol 2002; 118: 968–975.
Decker T, Schneller F, Hipp S, Miething C, Jahn T, Duyster J et al. Cell cycle progression of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells is controlled by cyclin D2, cyclin D3, cyclin-dependent kinase (cdk) 4 and the cdk inhibitor p27. Leukemia 2002; 16: 327–334.
Dicker F, Schnittger S, Haferlach T, Kern W, Schoch C . Immunostimulatory oligonucleotide-induced metaphase cytogenetics detect chromosomal aberrations in 80% of CLL patients: a study of 132 CLL cases with correlation to FISH, IgVH status, and CD38 expression. Blood 2006; 108: 3152–3160.
Matutes E, Owusu-Ankomah K, Morilla R, Garcia MJ, Houlihan A, Que TH et al. The immunological profile of B-cell disorders and proposal of a scoring system for the diagnosis of CLL. Leukemia 1994; 8: 1640–1645.
Moreau EJ, Matutes E, A’Hern RP, Morilla AM, Morilla RM, Owusu-Ankomah KA et al. Improvement of the chronic lymphocytic leukemia scoring system with the monoclonal antibody SN8 (CD79b). Am J Clin Pathol 1997; 108: 378–382.
Schoch C, Haferlach T, Bursch S, Gerstner D, Schnittger S, Dugas M et al. Loss of genetic material is more common than gain in acute myeloid leukemia with complex aberrant karyotype: a detailed analysis of 125 cases using conventional chromosome analysis and fluorescence in situ hybridization including 24-color FISH. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2002; 35: 20–29.
ISCN In: Mitelman F (eds). ISCN 1995, Guidelines for Cancer Cytogenetics, Supplement to: An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature. S Karger: Basel, 1995, pp 1–110.
Schoch C, Schnittger S, Bursch S, Gerstner D, Hochhaus A, Berger U et al. Comparison of chromosome banding analysis, interphase- and hypermetaphase-FISH, qualitative and quantitative PCR for diagnosis and for follow-up in chronic myeloid leukemia: a study on 350 cases. Leukemia 2002; 16: 53–59.
Kern W, Haferlach T, Schnittger S, Schoch C . Detection of t(14;18)(q32;q21) in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005; 129: 410–411.
Hiller B, Bradtke J, Balz H, Rieder H . CyDAS: a cytogenetic data analysis system. Bioinformatics 2005; 21: 1282–1283.
Haferlach C, Rieder H, Lillington DM, Dastugue N, Hagemeijer A, Harbott J et al. Proposals for standardized protocols for cytogenetic analyses of acute leukemias, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, chronic myeloid leukemia, chronic myeloproliferative disorders, and myelodysplastic syndromes. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2007; 46: 494–499.
Damle RN, Wasil T, Fais F, Ghiotto F, Valetto A, Allen SL et al. IgV gene mutation status and CD38 expression as novel prognostic indicators in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999; 94: 1840–1847.
Crespo M, Bosch F, Villamor N, Bellosillo B, Colomer D, Rozman M et al. ZAP-70 expression as a surrogate for immunoglobulin-variable-region mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 1764–1775.
Orchard JA, Ibbotson RE, Davis Z, Wiestner A, Rosenwald A, Thomas PW et al. ZAP-70 expression and prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Lancet 2004; 363: 105–111.
Wiestner A, Rosenwald A, Barry TS, Wright G, Davis RE, Henrickson SE et al. ZAP-70 expression identifies a chronic lymphocytic leukemia subtype with unmutated immunoglobulin genes, inferior clinical outcome, and distinct gene expression profile. Blood 2003; 101: 4944–4951.
Reddy KS . Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia profiled for prognosis using a fluorescence in situ hybridisation panel. Br J Haematol 2006; 132: 705–722.
Stilgenbauer S, Dohner K, Bentz M, Lichter P, Dohner H . Molecular cytogenetic analysis of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Ann Hematol 1998; 76: 101–110.
Mayr C, Speicher MR, Kofler DM, Buhmann R, Strehl J, Busch R et al. Chromosomal translocations are associated with poor prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2006; 107: 742–751.
Van Den Neste E, Robin V, Francart J, Hagemeijer A, Stul M, Vandenberghe P et al. Chromosomal translocations independently predict treatment failure, treatment-free survival and overall survival in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients treated with cladribine. Leukemia 2007; 21: 1715–1722.
Stilgenbauer S, Bullinger L, Lichter P, Dohner H . Genetics of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: genomic aberrations and V(H) gene mutation status in pathogenesis and clinical course. Leukemia 2002; 16: 993–1007.
Dewald GW, Brockman SR, Paternoster SF, Bone ND, O’Fallon JR, Allmer C et al. Chromosome anomalies detected by interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization: correlation with significant biological features of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol 2003; 121: 287–295.
Chen YH, Peterson LC, Dittmann D, Evens A, Rosen S, Khoong A et al. Comparative analysis of flow cytometric techniques in assessment of ZAP-70 expression in relation to IgVH mutational status in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Am J Clin Pathol 2007; 127: 182–191.
Shankey TV, Forman M, Scibelli P, Cobb J, Smith CM, Mills R et al. An optimized whole blood method for flow cytometric measurement of ZAP-70 protein expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2006; 70: 259–269.
Kern W, Dicker F, Schnittger S, Schoch C, Haferlach T . Correlation of flow cytometrically determined expression of ZAP-70 using two different antibodies with IgVH mutation status and cytogenetics in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2006; 108: 150a (Abstract 495).
Juliusson G, Robert KH, Ost A, Friberg K, Biberfeld P, Nilsson B et al. Prognostic information from cytogenetic analysis in chronic B-lymphocytic leukemia and leukemic immunocytoma. Blood 1985; 65: 134–141.
Juliusson G . Immunologic and cytogenetic studies improve prognosis prediction in chronic B-lymphocytic leukemia. A multivariate analysis of 24 variables. Cancer 1986; 58: 688–693.
Greenberg P, Cox C, Le Beau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 1997; 89: 2079–2088.
Schoch C, Kern W, Schnittger S, Buchner T, Hiddemann W, Haferlach T . The influence of age on prognosis of de novo acute myeloid leukemia differs according to cytogenetic subgroups. Haematologica 2004; 89: 1082–1090.
Schoch C, Kern W, Kohlmann A, Hiddemann W, Schnittger S, Haferlach T . Acute myeloid leukemia with a complex aberrant karyotype is a distinct biological entity characterized by genomic imbalances and a specific gene expression profile. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2005; 43: 227–238.
Sole F, Luno E, Sanzo C, Espinet B, Sanz GF, Cervera J et al. Identification of novel cytogenetic markers with prognostic significance in a series of 968 patients with primary myelodysplastic syndromes. Haematologica 2005; 90: 1168–1178.
Pfeifer D, Pantic M, Skatulla I, Rawluk J, Kreutz C, Martens UM et al. Genome-wide analysis of DNA copy number changes and LOH in CLL using high-density SNP arrays. Blood 2007; 109: 1202–1210.
Cuneo A, Bigoni R, Negrini M, Bullrich F, Veronese ML, Roberti MG et al. Cytogenetic and interphase cytogenetic characterization of atypical chronic lymphocytic leukemia carrying BCL1 translocation. Cancer Res 1997; 57: 1144–1150.
Sen F, Lai R, Albitar M . Chronic lymphocytic leukemia with t(14;18) and trisomy 12. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2002; 126: 1543–1546.
Crossen PE . Genes and chromosomes in chronic B-cell leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1997; 94: 44–51.
Dyer MJ, Zani VJ, Lu WZ, O’Byrne A, Mould S, Chapman R et al. BCL2 translocations in leukemias of mature B cells. Blood 1994; 83: 3682–3688.
Vizcarra E, Martinez-Climent JA, Benet I, Marugan I, Terol MJ, Prosper F et al. Identification of two subgroups of mantle cell leukemia with distinct clinical and biological features. Hematol J 2001; 2: 234–241.
Haslinger C, Schweifer N, Stilgenbauer S, Dohner H, Lichter P, Kraut N et al. Microarray gene expression profiling of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia subgroups defined by genomic aberrations and VH mutation status. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 3937–3949.
Byrd JC, Smith L, Hackbarth ML, Flinn IW, Young D, Proffitt JH et al. Interphase cytogenetic abnormalities in chronic lymphocytic leukemia may predict response to rituximab. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 36–38.
Byrd JC, Gribben JG, Peterson BL, Grever MR, Lozanski G, Lucas DM et al. Select high-risk genetic features predict earlier progression following chemoimmunotherapy with fludarabine and rituximab in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: justification for risk-adapted therapy. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24: 437–443.
Lozanski G, Heerema NA, Flinn IW, Smith L, Harbison J, Webb J et al. Alemtuzumab is an effective therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia with p53 mutations and deletions. Blood 2004; 103: 3278–3281.
Acknowledgements
We thank all clinicians for sending CLL samples to our laboratory for diagnostic purposes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website (http://www.nature.com/leu)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haferlach, C., Dicker, F., Schnittger, S. et al. Comprehensive genetic characterization of CLL: a study on 506 cases analysed with chromosome banding analysis, interphase FISH, IgVH status and immunophenotyping. Leukemia 21, 2442–2451 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404935
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404935
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The complex karyotype in hematological malignancies: a comprehensive overview by the Francophone Group of Hematological Cytogenetics (GFCH)
Leukemia (2022)
-
Proteomic profiling based classification of CLL provides prognostication for modern therapy and identifies novel therapeutic targets
Blood Cancer Journal (2022)
-
Mapping incidence and mortality of leukemia and its subtypes in 21 world regions in last three decades and projections to 2030
Annals of Hematology (2022)
-
The impact of complex karyotype on the overall survival of patients with relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with idelalisib plus rituximab
Leukemia (2020)
-
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia in 2020: the Future Has Arrived
Current Oncology Reports (2020)