Abstract
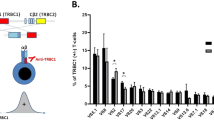
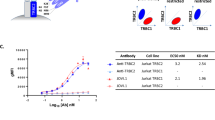
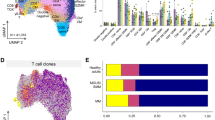
Selected patients with Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) are responsive to immunosuppressive therapy, suggesting that hematopoietic suppressive T cells have a pathogenic role in ineffective hematopoiesis. We assessed T-cell receptor (TCR) clonality through combined flow cytometry and molecular analysis of the complementarity determining region (CDR)-3 of the T-cell receptor-Vβ gene. We identified clonal T cells in 50% of MDS patients (n=52) compared to 5% of age-matched normal controls (n=20). The presence of T-cell clones was not associated with features linked previously to immunosuppression response, including WHO diagnostic category, karyotype, marrow cellularity, IPSS category, sex or age ⩽60. Using flow cytometry to identify expanded Vβ-families, we found that T cells showed greater expansion in the bone marrow compared with peripheral blood, and were characterized as CD8+/CD57+/CD28− effector T cells. Expanded effector T cell were CD62L negative and expressed the natural killer C-lectin-family receptor NKG2D and CD244 (2B4). We conclude that clonal T-cell expansion is common among all MDS prognostic subgroups.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett JM, Komrokji RS . The myelodysplastic syndromes: diagnosis, molecular biology and risk assessment. Hematology 2005; 10 (Suppl 1): 258–269.
Davies FE, Raje N, Hideshima T, Lentzsch S, Young G, Tai Y et al. Thalidomide and immunomodulatory derivatives augment natural killer cell cytotoxicity in multiple myeloma. Blood 2001; 98: 210–216.
Shannon E, Aseffa A, Pankey G, Sandoval F, Lutz B . Thalidomide's ability to augment the synthesis of IL-2 in vitro in HIV-infected patients is associated with the percentage of CD4+ cells in their blood. Immunopharmacology 2000; 46: 175–179.
Kochenderfer JN, Kobayashi S, Wieder ED, Su C, Molldrem JJ . Loss of T-lymphocyte clonal dominance in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome responsive to immunosuppression. Blood 2002; 100: 3639–3645.
Saunthararajah Y, Nakamura R, Nam JM, Robyn J, Loberiza F, Maciejewski JP et al. HLA-DR15 (DR2) is overrepresented in myelodysplastic syndrome and aplastic anemia and predicts a response to immunosuppression in myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 2002; 100: 1570–1574.
Sloand EM, Kim S, Fuhrer M, Risitano AM, Nakamura R, Maciejewski JP et al. Fas-mediated apoptosis is important in regulating cell replication and death in trisomy 8 hematopoietic cells but not in cells with other cytogenetic abnormalities. Blood 2002; 100: 4427–4432.
Molldrem JJ, Caples M, Mavroudis D, Plante M, Young NS, Barrett AJ . Antithymocyte globulin for patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Br J Haematol 1997; 99: 699–705.
Molldrem JJ, Jiang YZ, Stetler-Stevenson M, Mavroudis D, Hensel N, Barrett AJ . Haematological response of patients with myelodysplastic syndrome to antithymocyte globulin is associated with a loss of lymphocyte-mediated inhibition of CFU-GM and alterations in T-cell receptor Vbeta profiles. Br J Haematol 1998; 102: 1314–1322.
Jonasova A, Neuwirtova R, Cermak J, Vozobulova V, Mocikova K, Siskova M et al. Cyclosporin A therapy in hypoplastic MDS patients and certain refractory anaemias without hypoplastic bone marrow. Br J Haematol 1998; 100: 304–309.
Yazji S, Giles FJ, Tsimberidou AM, Estey EH, Kantarjian HM, O'Brien SA et al. Antithymocyte globulin (ATG)-based therapy in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia 2003; 17: 2101–2106.
Steensma DP, Dispenzieri A, Moore SB, Schroeder G, Tefferi A . Antithymocyte globulin has limited efficacy and substantial toxicity in unselected anemic patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 2003; 101: 2156–2158.
Killick SB, Mufti G, Cavenagh JD, Mijovic A, Peacock JL, ordon-Smith EC et al. A pilot study of antithymocyte globulin (ATG) in the treatment of patients with ”low-risk” myelodysplasia. Br J Haematol 2003; 120: 679–684.
Saunthararajah Y, Molldrem JL, Rivera M, Williams A, Stetler-Stevenson M, Sorbara L et al. Coincident myelodysplastic syndrome and T-cell large granular lymphocytic disease: clinical and pathophysiological features. Br J Haematol 2001; 112: 195–200.
Saunthararajah Y, Nakamura R, Wesley R, Wang QJ, Barrett AJ . A simple method to predict response to immunosuppressive therapy in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 2003; 102: 3025–3027.
Maciejewski JP, Rivera C, Kook H, Dunn D, Young NS . Relationship between bone marrow failure syndromes and the presence of glycophosphatidyl inositol-anchored protein-deficient clones. Br J Haematol 2001; 115: 1015–1022.
Maciejewski JP, Risitano A, Kook H, Zeng W, Chen G, Young NS . Immune pathophysiology of aplastic anemia. Int J Hematol 2002; 76 (Suppl 1): 207–214.
Kook H, Zeng W, Guibin C, Kirby M, Young NS, Maciejewski JP . Increased cytotoxic T cells with effector phenotype in aplastic anemia and myelodysplasia. Exp Hematol 2001; 29: 1270–1277.
Maciejewski JP, Follmann D, Nakamura R, Saunthararajah Y, Rivera CE, Simonis T et al. Increased frequency of HLA-DR2 in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and the PNH/aplastic anemia syndrome. Blood 2001; 98: 3513–3519.
Molldrem JJ, Leifer E, Bahceci E, Saunthararajah Y, Rivera M, Dunbar C et al. Antithymocyte globulin for treatment of the bone marrow failure associated with myelodysplastic syndromes. Ann Intern Med 2002; 137: 156–163.
Nakao S, Feng X, Sugimori C . Immune pathophysiology of aplastic anemia. Int J Hematol 2005; 82: 196–200.
Borg NA, Ely LK, Beddoe T, Macdonald WA, Reid HH, Clements CS et al. The CDR3 regions of an immunodominant T cell receptor dictate the ”energetic landscape” of peptide-MHC recognition. Nat Immunol 2005; 6: 171–180.
Lamy T, Loughran TP . Large Granular Lymphocyte Leukemia. Cancer Control 1998; 5: 25–33.
Plasilova M, Risitano A, Maciejewski JP . Application of the molecular analysis of the T-cell receptor repertoire in the study of immune-mediated hematologic diseases. Hematology 2003; 8: 173–181.
O'Keefe CL, Plasilova M, Wlodarski M, Risitano AM, Rodriguez AR, Howe E et al. Molecular analysis of TCR clonotypes in LGL: a clonal model for polyclonal responses. J Immunol 2004; 172: 1960–1969.
Wlodarski MW, Gondek LP, Nearman ZP, Plasilova M, Kalaycio M, Hsi ED et al. Molecular strategies for detection and quantitation of clonal cytotoxic T-cell responses in aplastic anemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 2006; 108: 2632–2641.
Wechsler J, Bagot M, Nikolova M, Parolini S, Martin-Garcia N, Boumsell L et al. Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor expression delineates in situ Sezary syndrome lymphocytes. J Pathol 2003; 199: 77–83.
Loughran Jr TP, Aprile JA, Ruscetti FW . Anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody-mediated cytotoxicity occurs through an interleukin-2-independent pathway in CD3+ large granular lymphocytes. Blood 1990; 75: 935–940.
Kasten-Sportes C, Zaknoen S, Steis RG, Chan WC, Winton EF, Waldmann TA . T-cell receptor gene rearrangement in T-cell large granular leukocyte leukemia: preferential V alpha but diverse J alpha usage in one of five patients. Blood 1994; 83: 767–775.
Goronzy JJ, Zettl A, Weyand CM . T cell receptor repertoire in rheumatoid arthritis. Int Rev Immunol 1998; 17: 339–363.
Young NS, Maciejewski JP, Sloand E, Chen G, Zeng W, Risitano A et al. The relationship of aplastic anemia and PNH. Int J Hematol 2002; 76 (Suppl 2): 168–172.
Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 1997; 89: 2079–2088.
Epling-Burnette PK, Bai F, Wei S, Chaurasia P, Painter JS, Olashaw N et al. ERK couples chronic survival of NK cells to constitutively activated Ras in lymphoproliferative disease of granular lymphocytes (LDGL). Oncogene 2004; 23: 9220–9229.
Bernardin F, Doukhan L, Longone-Miller A, Champagne P, Sekaly R, Delwart E . Estimate of the total number of CD8+ clonal expansions in healthy adults using a new DNA heteroduplex-tracking assay for CDR3 repertoire analysis. J Immunol Methods 2003; 274: 159–175.
Shen DF, Doukhan L, Kalams S, Delwart E . High-resolution analysis of T-cell receptor beta-chain repertoires using DNA heteroduplex tracking: generally stable, clonal CD8+ expansions in all healthy young adults. J Immunol Methods 1998; 215: 113–121.
List AF, Vardiman J, Issa JP, DeWitte TM . Myelodysplastic syndromes. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2004; 1: 297–317.
Maes B, Meeus P, Michaux L, Bijnens L, Boogaerts M, Hagemeijer A et al. Application of the International Prognostic Scoring System for myelodysplastic syndromes. Ann Oncol 1999; 10: 825–829.
Sloand EM, Mainwaring L, Fuhrer M, Ramkissoon S, Risitano AM, Keyvanafar K et al. Preferential suppression of trisomy 8 compared with normal hematopoietic cell growth by autologous lymphocytes in patients with trisomy 8 myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 2005; 106: 841–851.
Pilch H, Hohn H, Freitag K, Neukirch C, Necker A, Haddad P et al. Improved assessment of T-cell receptor (TCR) VB repertoire in clinical specimens: combination of TCR-CDR3 spectratyping with flow cytometry-based TCR VB frequency analysis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 2002; 9: 257–266.
Rosenfeld C, Cheever MA, Gaiger A . WT1 in acute leukemia, chronic myelogenous leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome: therapeutic potential of WT1 targeted therapies. Leukemia 2003; 17: 1301–1312.
Zou GM, Martinson J, Hu WY, Tam Y, Klingemann HG . The effect of LIGHT in inducing maturation of monocyte-derived dendritic cells from MDS patients. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2004; 53: 681–689.
Oka Y, Tsuboi A, Kawakami M, Elisseeva OA, Nakajima H, Udaka K et al. Development of WT1 peptide cancer vaccine against hematopoietic malignancies and solid cancers. Curr Med Chem 2006; 13: 2345–2352.
Warrington KJ, Takemura S, Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM . CD4+,CD28- T cells in rheumatoid arthritis patients combine features of the innate and adaptive immune systems. Arthritis Rheum 2001; 44: 13–20.
Zambello R, Falco M, Della Chiesa M, Trentin L, Carollo D, Castriconi R et al. Expression and function of KIR and natural cytotoxicity receptors in NK-type lymphoproliferative diseases of granular lymphocytes. Blood 2003; 102: 1797–1805.
Epling-Burnette PK, Painter JS, Chaurasia P, Bai F, Wei S, Djeu J Y et al. Dysregulated NK receptor expression in patients with lymphoproliferative disease of granular lymphocytes. Blood 2004; 103: 3431–3439.
Melenhorst JJ, Eniafe R, Follmann D, Nakamura R, Kirby M, Barrett AJ . Molecular and flow cytometric characterization of the CD4 and CD8 T-cell repertoire in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Br J Haematol 2002; 119: 97–105.
Maasho K, Opoku-Anane J, Marusina AI, Coligan JE, Borrego F . NKG2D is a costimulatory receptor for human naive CD8+ T cells. J Immunol 2005; 174: 4480–4484.
Caillat-Zucman S . How NKG2D ligands trigger autoimmunity? Hum Immunol 2006; 67: 204–207.
Jamieson AM, Diefenbach A, McMahon CW, Xiong N, Carlyle JR, Raulet DH . The role of the NKG2D immunoreceptor in immune cell activation and natural killing. Immunity 2002; 17: 19–29.
McNerney ME, Lee KM, Kumar V . 2B4 (CD244) is a non-MHC binding receptor with multiple functions on natural killer cells and CD8+ T cells. Mol Immunol 2005; 42: 489–494.
Costello RT, Sivori S, Marcenaro E, Lafage-Pochitaloff M, Mozziconacci MJ, Reviron D et al. Defective expression and function of natural killer cell-triggering receptors in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2002; 99: 3661–3667.
Speiser DE, Colonna M, Ayyoub M, Cella M, Pittet MJ, Batard P et al. The activatory receptor 2B4 is expressed in vivo by human CD8+ effector alpha beta T cells. J Immunol 2001; 167: 6165–6170.
Kim I, He S, Yilmaz OH, Kiel MJ, Morrison SJ . Enhanced purification of fetal liver hematopoietic stem cells using SLAM family receptors. Blood 2006; 108: 737–744.
Garland RJ, El-Shanti N, West SE, Hancock JP, Goulden NJ, Steward CG et al. Human CD8+ CTL recognition and in vitro lysis of herpes simplex virus-infected cells by a non-MHC restricted mechanism. Scand J Immunol 2002; 55: 61–69.
Di Rosa F, Santoni A . Memory T-cell competition for bone marrow seeding. Immunology 2003; 108: 296–304.
Battiwalla M, Melenhorst J, Saunthararajah Y, Nakamura R, Molldrem J, Young NS et al. HLA-DR4 predicts haematological response to cyclosporine in T-large granular lymphocyte lymphoproliferative disorders. Br J Haematol 2003; 123: 449–453.
Epperson DE, Nakamura R, Saunthararajah Y, Melenhorst J, Barrett AJ . Oligoclonal T cell expansion in myelodysplastic syndrome: evidence for an autoimmune process. Leuk Res 2001; 25: 1075–1083.
Acknowledgements
Supported by grants from the Veterans' Administration and NCI (CA112112-01A1). Work was performed in conjunction with the Department of Esoteric Testing, Tampa, FL and the Flow Cytometry Core Facility at the H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, FL 33612. We thank Ms Candace Fennell of the Department of Esoteric Testing, Tampa, FL, for contribution to this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Epling-Burnette, P., Painter, J., Rollison, D. et al. Prevalence and clinical association of clonal T-cell expansions in Myelodysplastic Syndrome. Leukemia 21, 659–667 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404590
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404590
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
What role for somatic mutations in systemic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases associated with myelodysplastic neoplasms and chronic myelomonocytic leukemias?
Leukemia (2023)
-
The immunome of mobilized peripheral blood stem cells is predictive of long-term outcomes and therapy-related myeloid neoplasms in patients with multiple myeloma undergoing autologous stem cell transplant
Blood Cancer Journal (2023)
-
Cutaneous T cell lymphoma
Nature Reviews Disease Primers (2021)
-
The bone-marrow niche in MDS and MGUS: implications for AML and MM
Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology (2018)
-
Management of anemia in low-risk myelodysplastic syndromes treated with erythropoiesis-stimulating agents newer and older agents
Medical Oncology (2018)