Abstract
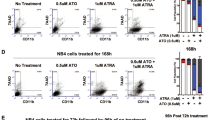
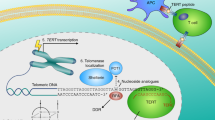
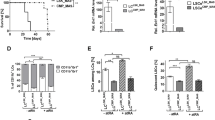
Numerous strategies have been proposed to specifically inhibit telomerase (human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT)) but to date only a few are clinically relevant in anticancer therapy. Recently, we have shown that long-term treatment with all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA), a compound clinically approved for differentiation therapy of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL), represses hTERT in differentiation-resistant APL cell lines leading to telomere shortening and death. This signaling requires the co-activation of the retinoic acid receptor α (RARα) and the retinoic X receptor (RXR). In contrast to differentiation-therapy, which is only successful in this subtype of leukemia, the telomerase-targeted pathway could also be of use in non-APL. Here, we demonstrate that repression of hTERT occurs in fresh blasts cells from patients with myeloid leukemias of various subtypes exposed ex vivo to ATRA or synthetic retinoids. These results support the idea that, by hTERT targeting, retinoids can induce telomere shortening and cell death and their integration in therapy protocols for myeloid leukemias refractory to maturation should be considered.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Broccoli D, Young JW, de Lange T . Telomerase activity in normal and malignant hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92: 9082–9086.
Counter CM, Gupta J, Harley CB, Leber B, Bacchetti S . Telomerase activity in normal leukocytes and in hematologic malignancies. Blood 1995; 85: 2315–2320.
Greenwood MJ, Lansdorp PM . Telomeres, telomerase, and hematopoietic stem cell biology. Arch Med Res 2003; 34: 489–495.
Zhang W, Piatyszek MA, Kobayashi T, Estey E, Andreeff M, Deisseroth AB et al. Telomerase activity in human acute myelogenous leukemia: inhibition of telomerase activity by differentiation-inducing agents. Clin Cancer Res 1996; 2: 799–803.
Engelhardt M, Mackenzie K, Drullinsky P, Silver RT, Moore MA . Telomerase activity and telomere length in acute and chronic leukemia, pre- and post-ex vivo culture. Cancer Res 2000; 60: 610–617.
Li G, Song YH, Qian LS, Ma XT, Wu KF . Telomerase: obviously activated in the accelerated phase of chronic myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2000; 85: 1222–1224.
Ohyashiki JH, Sashida G, Tauchi T, Ohyashiki K . Telomeres and telomerase in hematologic neoplasia. Oncogene 2002; 21: 680–687.
Roth A, Vercauteren S, Sutherland HJ, Lansdorp PM . Telomerase is limiting the growth of acute myeloid leukemia cells. Leukemia 2003; 17: 2410–2417.
Ohyashiki JH, Ohyashiki K, Fujimura T, Kawakubo K, Shimamoto T, Iwabuchi A et al. Telomere shortening associated with disease evolution patterns in myelodysplastic syndromes. Cancer Res 1994; 54: 3557–3560.
Sieglova Z, Zilovcova S, Cermak J, Rihova H, Brezinova D, Dvorackova R et al. Dynamics of telomere erosion and its association with genome instability in myelodysplasic syndromes (MDS) and acute myelogenous leukemia arising from MDS: a marker of disease prognosis? Leuk Res 2004; 28: 1013–1021.
Mergny JL, Riou JF, Mailliet P, Teulade-Fichou MP, Gilson E . Natural and pharmacological regulation of telomerase. Nucleic Acids Res 2002; 30: 839–865.
Huang ME, Ye YC, Chen SR, Chai JR, Lu JX, Zhoa L et al. Use of all-trans retinoic acid in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood 1988; 72: 567–572.
Castaigne S, Chomienne C, Daniel MT, Ballerini P, Berger R, Fenaux P et al. All-trans retinoic acid as a differentiation therapy for acute promyelocytic leukemia. I. Clinical results Blood 1990; 76: 1704–1709.
Mistry AR, Pedersen EW, Solomon E, Grimwade D . The molecular pathogenesis of acute promyelocytic leukaemia: implications for clinical management of the disease. Blood Rev 2003; 17: 71–97.
Pendino F, Flexor M, Delhommeau F, Buet D, Lanotte M, Segal-Bendirdjian E . Retinoids down-regulate telomerase and telomere length in a pathway distinct from leukemia cell differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 6662–6667.
Pendino F, Sahraoui T, Lanotte M, Segal-Bendirdjian E . A novel mechanism of retinoic acid resistance in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells through a defective pathway in telomerase regulation. Leukemia 2002; 16: 826–832.
Pendino F, Dudognon C, Delhommeau F, Sahraoui T, Flexor M, Bennaceur-Griscelli A et al. Retinoic acid receptor alpha and retinoid-X receptor-specific agonists synergistically target telomerase expression and induce tumor cell death. Oncogene 2003; 22: 9142–9150.
Segal-Bendirdjian E, Jacquemin-Sablon A . Cisplatin resistance in a murine leukemia cell line is associated with a defective apoptotic process. Exp Cell Res 1995; 218: 201–212.
Xu D, Gruber A, Peterson C, Pisa P . Supression of telomerase activity in HL60 cells after treatment with differentiating agents. Leukemia 1996; 10: 1354–1357.
Tarkanyi I, Dudognon C, Hillion J, Pendino F, Lanotte M, Aradi J et al. Retinoid/arsenic combination therapy of promyelocytic leukemia: induction of telomerase-dependent cell death. Leukemia 2005; 19: 1806–1811.
Sumi M, Tauchi T, Sashida G, Nakajima A, Gotoh A, Shin-Ya K et al. A G-quadruplex-interactive agent, telomestatin (SOT-095), induces telomere shortening with apoptosis and enhances chemosensitivity in acute myeloid leukemia. Int J Oncol 2004; 24: 1481–1487.
El-Daly H, Kull M, Zimmermann S, Pantic M, Waller CF, Martens UM . Selective cytotoxicity and telomere damage in leukemia cells using the telomerase inhibitor BIBR1532. Blood 2005; 105: 1742–1749.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by INSERM, the Association pour la Recherche contre le Cancer (ARC nos. 3416). FP was funded by the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (FRM), International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and European Commission (Marie Curie Intra-European fellowship). CD is a research fellow of Association pour la Recherche contre le Cancer. We are indebted to Dr Marc Maynadie (Service d'Hématologie Biologique 21000 Dijon, France) and Dr Loïc Fouillard (Département d'hématologie et de Thérapie Cellulaire, Hôpital Saint-Antoine, Paris, France) for providing some of the patient samples, to Dr Nedime Serakinci and Dr Eigil Kjeldsen, (Aarhus, Denmark) for helpful discussions at the beginning of the project, to Pr Eric Solary (INSERM U517, IFR 100, Faculté de Médecine, 21000 Dijon, France) and Dr Bodil Bjørndal, (Department of Molecular Biology, University of Bergen, Norway) for critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pendino, F., Hillion, J., Dudognon, C. et al. Telomerase targeting by retinoids in cells from patients with myeloid leukemias of various subtypes, not only APL. Leukemia 20, 599–603 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404127
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404127
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Involvement of epigenetic modification of TERT promoter in response to all-trans retinoic acid in ovarian cancer cell lines
Journal of Ovarian Research (2019)
-
Antisense oligonucleotides and all-trans retinoic acid have a synergistic anti-tumor effect on oral squamous cell carcinoma
BMC Cancer (2008)