Abstract
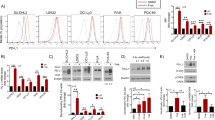
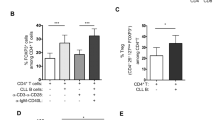
B-CLL cells are arrested in G0/early G1 phase of the cell cycle and are characterized by a marked hyporesponsiveness towards a variety of polyclonal B cell activators. We have previously demonstrated that costimulation with CpG-ODN and IL-2 can overcome this proliferative defect. Cyclin D3 is the principal D-type cyclin which mediates G1 progression in normal B cells, but in B-CLL cells both cyclin D2 and cyclin D3, were strongly upregulated upon stimulation. Both cyclins were associated with cdk4 but not with cdk6, which is the catalytic partner of D-type cyclins in normal B cells. Moreover, immune complexes consisting of cyclin D2 and cdk4 or cyclin D3 and cdk4 were both functional and phosphorylated the RB protein in vitro. The cell cycle inhibitor p27 plays a pivotal role in cell cycle progression of B lymphocytes and has been shown to be overexpressed in B-CLL cells. P27 was rapidly downregulated in B-CLL cells even when stimulated with a non-CpG-ODN or IL-2 alone, while only moderate regulation could be observed in normal B cells. Taken together, our findings demonstrate that regulation of early cell cycle progression differs between B-CLL cells and normal B cells. These findings do not only contribute to the understanding of B-CLL pathophysiology, but might ultimately lead to the identification of new therapeutic targets.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
O'Brien S, Del Giglio A, Keating M . Advances in the biology and treatment of B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia Blood 1995 85: 306–318
Meinhardt G, Wendtner CM, Hallek M . Molecular pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: factors and signaling pathways regulating cell growth and survival J Mol Med 1999 77: 282–293
Kitada S, Andresen J, Akar S, Zapata JM, Takayama S, Krajewski S, Wang HG, Zhang CM, Rai K, Hines J, Reed JC . Expression of apoptosis-regulating proteins in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: correlations with in vitro and in vivo chemoresponses Blood 1998 91: 3379–3389
Klein A, Miera O, Bauer O, Golfier S, Schriever F . Chemosensitivity of B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and correlated expression of proteins regulating apoptosis, cell cycle and DNA repair Leukemia 2000 14: 40–46
Wolowiec D, Benchaib M, Pernas P, Deviller P, Souchier C, Rimokh R, Felman P, Bryon PA, Ffrench M . Expression of cell cycle regulatory proteins in chronic lymphocytic leukemias. Comparison with non-Hodgkin's lymphomas and non-neoplastic tissue Leukemia 1995 9: 1382–1388
Delmer A, Ajchenbaum-Cymbalista F, Tang R, Ramon S, Faussat AM, Marie JP, Zittoun R . Overexpression of cyclin D2 in chronic B-cell malignancies Blood 1995 85: 2870–2876
Vrhovac R, Delmer A, Tang R, Marie JP, Zittuon R, Ajchenbaum-Cymbalista F . Prognostic significance of the cell cycle inhibitor p27 in chronic B-cell lymphocytic leukemia Blood 1998 91: 4694–4700
Porter P, Malone KE, Hengerty PJ, Alexander GM, Gatti LA, Firpo EJ, Daling JR, Roberts JM . Expression of cell cycle regulators p27kip1 and cyclin E, alone and in combination, correlate with survival in young breast cancer patients Nature Med 1997 3: 222–226
Loda M, Cukor B, Tam SW, Lawin P, Fiorentino M, Draetta GF, Jessup JM, Pagano M . Increased proteasome-dependent degradation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 in aggressive colorectal carcinomas Nature Med 1997 3: 231–234
Sherr CJ . Cancer cell cycles Science 1996 274: 1672–1677
Hirama T, Koeffler P . Role of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors in the development of cancer Blood 1995 86: 841–854
Wagner EF, Hleb M, Hanna N, Sharma S . A pivotal role of cyclin D3 and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 in the regulation of IL-2, IL-4- or IL-10-mediated human B cell proliferation J Immunol 1998 161: 1123–1131
Blanchard DA, Affredou MT, Vazquez A . Modulation of the p27kip1 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor expression during IL-4-mediated human B cell activation J Immunol 1997 160: 3054–3061
Yatabe Y, Suzuki R, Tobimai K, Matsuno Y, Ichinohasama R, Okam M, Tamaru J, Uike N, Hashimoto Y, Morishima Y, Suchi T, Seto M . Significance of cyclin D1 overexpression for the diagnosis of mantle cell lymphoma: a clinicopathologic comparison of cyclin D1-positive MCL and cyclin D1-negative MCL-like-B-cell lymphoma Blood 2000 95: 2253–2261
Solvason N, Wu WW, Kabra N, Wu X, Lees E, Howard MC . Induction of cell cycle regulatory proteins in anti-immunoglobulin-stimulated mature B lymphocytes J Exp Med 1996 184: 407–417
Tanguay DA, Chiles TC . Regulation of the catalytic subunit (p34psk-J3/cdk4) for the major D-type cyclin in mature B lymphocytes J Immunol 1996 156: 539–548
Palmero I, Holder A, Sinclair AJ, Dickson C, Peters G . Cyclins D1 and D2 are differentially expressed in human B-lymphoid cell lines Oncogene 1993 8: 1049–1054
Sherr CJ . G1 phase progression: cycling on cue Cell 1994 79: 551–555
Lankester AC, van Schijndel GM, van der Schoot CE, van Oers MH, van Noesel CJ, van Lier RA . Antigen receptor nonresponsiveness in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells Blood 1995 86: 1090–1097
Fluckiger AC, Rossi JF, Bussel A, Bryon P, Bancherau J, Defrance T . Responsiveness of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells activated via surface Igs or CD40 to B-cell tropic factors Blood 1992 80: 3173–3181
Decker T, Schneller F, Sparwasser T, Tretter T, Lipford GB, Wagner H, Peschel C . Immunstimulatory CpG-oligonucleotides cause proliferation, cytokine secretion and an immunogenic phenotype in B-CLL patients Blood 2000 95: 999–1006
Wagner H . Bacterial CpG DNA activates immune cells to signal infectious danger Adv Immunol 1999 73: 329–368
Krieg AM . The role of CpG motifs in innate immunity Curr Opin Immunol 2000 12: 35–43
Decker T, Schneller F, Kronschnabl M, Dechow T, Lipford GB, Wagner H, Peschel C . Immunostimulatory CpG-oligonucleotides induce the expression of functional IL-2 receptors on B-CLL cells: costimulation with IL-2 results in a highly immunogenic phenotype Exp Hematol 2000 28: 558–568
Liang H, Nishioka Y, Reich CF, Pisetsky DS, Lipsky P . Activation of human B cells by phosphorothioate oligonucleotides J Clin Invest 1996 98: 1119–1129
Häcker H, Mischak H, Miethke T, Liptay S, Schmid R, Sparwasser T, Heeg K, Lipford GB, Wagner H . CpG-DNA-specific activation of antigen-presenting cells requires stress kinase activity and is preceded by non-specific endocytosis and endosomal maturation EMBO J 1998 17: 6230–6240
Duyster J, Baskaran R, Wang JY . Src homology 2 domain as a specificity determinant in the c-Abl-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II carboxyl-terminal repeated domain Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995 92: 1555–1559
de Toro D, di Celle Francia, Cignetti A, Foa R . The IL-2 receptor complex: expression and function on normal and leukemic B cells Leukemia 1995 9: 1425–1431
Hartmann G, Krieg AM . Mechanism and function of a newly identified CpG DNA motif in human primary B cells J Immunol 2000 164: 944–953
Lang R, Hultner L, Lipford GB, Wagner H, Heeg K . Guanosine-rich oligonucleotides induce proliferation of macrophage progenitors in cultures of murine bone marrow cells Eur J Immunol 1999 29: 3496–3506
Nourse J, Firpo E, Flanagan WM, Coata S, Polyak K, Lee HM, Massague J, Crabtree GR, Roberts Nourse JM . Interleukin-2-mediated elimination of the p27kip1 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor is prevented by rapamycin Nature 1994 372: 570–573
Quintanilla-Martinez L, Thieblemont C, Fend F, Kumar S, Pinyol M, Campo E, Jaffe ES, Raffeld M . Mantle cell lymphoma lack expression of p27kip1, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor Am J Pathol 1998 153: 175–182
Erlanson M, Portin C, Linderholm B, Lindh J, Roos G, Landberg G . Expression of cyclin E and the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 in malignant lymphomas-prognostic implications Blood 1998 92: 770–777
Chiarle R, Budel LM, Solnik J, Frizzera G, Chilosi M, Corato A, Pizzolo G, Pagano M, Maes B, De Wolf-Peeters M, Inghirami G . Increased proteasome degradation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 is associated with a decreased overall survival in mantle cell lymphoma Blood 2000 95: 619–626
Pagano M, Tam SW, Theodoras AM, Beer-Romero P, Del Sal G, Chau V, Yew PR, Draetta GF, Rolfe M . Role of the ubiquitin proteasome pathway in regulating abundance of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 Science 1995 269: 682–685
Masdehors P, Merle-Beral H, Maloum K, Ömura S, Magdelenat H, Delic J . Deregulation of the ubiquitin system and p53 proteolysis modify the apoptotic response in B-CLL lymphocytes Blood 2000 96: 269–274
Suzuki R, Kuroda H, Komatsu H, Hosokawa Y, Kagami Y, Ogura M, Nakamura S, Kodera Y, Morishima Y, Seto M . Selective usage of D-type cyclins in lymphoid malignancies Leukemia 1999 13: 1335–1342
Dey A, She H, Kim L, Boruch A, Guris DL, Carlberg K, Sebti SM, Woodley DT, Imamoto A, Li W . Colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor utilizes multiple signaling pathways to induce cyclin D2 expression Mol Biol Cell 2000 11: 3835–3848
Bouchard C, Thieke K, Maier A, Saffrich R, Hanley-Hide J, Ansorge W, Reed S, Sicinski P, Bartek J, Eilers M . Direct induction of cyclin D2 by Myc contributes to cell cycle progression and sequestration of p27 Embo J 1999 18: 5321–5333
Coller HA, Grandori C, Tamayo P, Colbert T, Lander ES, Eisenman RN, Golub TR . Expression analysis with oligonucleotide microarrays reveals that myc regulates genes involved in growth, cell cycle, signaling and adhesion Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000 97: 3260–3265
Hermeking H, Rago C, Schuhmacher M, Li Q, Barrett JF, Obaya AJ, O‡Donell BC, Mateyak MK, Tam W, Kohlhuber F, Dang CV, Sedivy JM, Eick D, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW . Identification of CDK4 as a target of c-MYC Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000 97: 2229–2234
Frank DA, Mahajan S, Ritz J . B lymphocytes from patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia contain signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)1 and STAT3 constitutively phosphorylated on serine residues J Clin Invest 1997 100: 3140–3148
Furman RR, Asgary Z, Mascarenhas JO, Liou HC, Schattner EJ . Modulation of NF-kappa B activity and apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells J Immunol 2000 164: 2200–2206
Weinberg RA . Tumor suppressor genes Science 1991 254: 1138–1146
Kornblau SM, Chen N, del Giglio A, O'Brien S, Deisseroth AB . Retinoblastoma protein expression is frequently altered in chronic lymphocytic leukemia Cancer Res 1994 54: 242–246
Caligaris-Cappio F, Hamblin TJ . B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a bird of a different feather J Clin Oncol 1999 17: 399–408
Decker T, Flohr T, Trautmann P, Aman MJ, Holter W, Majdic O, Huber C, Peschel C . Role of accessory cells in cytokine production by T cells in chronic B-cell lymphocytic leukemia Blood 1995 86: 1115–1123
Tretter T, Brass U, Schuler M, Schneller F, Aman JM, Huber C, Peschel C . Direct cellular interaction with activated CD4+ T cells overcomes hyporesponsiveness of B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia in vitro Cell Immunol 1998 189: 41–50
Senderowicz AM . Development of cyclin-dependent kinase modulators as novel therapeutic approaches for hematological malignancies Leukemia 2001 15: 1–9
Druker BJ, Lydon NB . Lessons learned from the development of an Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor for chronic myelogenous leukemia J Clin Invest 2000 105: 3–7
Acknowledgements
We thank P Seipel for help and advice. This work was supported by a research grant from the Technical University of Munich (KKF H30–97) and a research grant from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (De 771 1/1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Decker, T., Schneller, F., Hipp, S. et al. Cell cycle progression of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells is controlled by cyclin D2, cyclin D3, cyclin-dependent kinase (cdk) 4 and the cdk inhibitor p27. Leukemia 16, 327–334 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402389
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402389
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
hsa_circ_0000231 Promotes colorectal cancer cell growth through upregulation of CCND2 by IGF2BP3/miR-375 dual pathway
Cancer Cell International (2022)
-
Multi-omics reveals clinically relevant proliferative drive associated with mTOR-MYC-OXPHOS activity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Nature Cancer (2021)
-
Berberine affects mitochondrial activity and cell growth of leukemic cells from chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
European recommendations and quality assurance for cytogenomic analysis of haematological neoplasms
Leukemia (2019)
-
Circulating microRNA-192 as a diagnostic biomarker in human chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Cancer Gene Therapy (2016)