Abstract
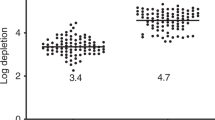
Autologous transplantation is a treatment option for relapsed childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in second complete remission (CR2) when a suitable donor is not available. In an attempt to prevent relapses originating from graft leukemic contamination, the experimental protocol of in vitro purification of leukapheretic products with monoclonal antibodies (MoAbs), previously reported for adults, was adopted in 11 of 12 consecutive patients (median age, 9 years) with B cell precursor ALL in CR2 after late relapse (median, 37; range, 31–51 months after the onset) enrolled between July 1997 and July 1999 at a single pediatric center. At a median of 12 days after the mobilizing chemotherapy followed by G-CSF, a median of 13.9 (range, 5.9–18.7) × 106 CD34+ cells/kg were collected from each patient and a median of 7.5 (range, 4.1–12.6) × 106 CD34+ cells/kg underwent the purification procedure. The first step of immunorosetting allowed a one-log reduction of the total cell count, by eliminating more than 90% of the CD11b+ cells; the second step, performed after incubation with anti-CD19 MoAbs, allowed the depletion of 99% (range, 93–100) of the CD19+ cells, kept within the magnetic field of the immunodepletion column, with a median recovery of 73% (range, 55–87) of the collected CD34+ cells. Molecular analysis assessed the in vitro eradication of detectable leukemic cells. A median reinfusion of 5.2 (range, 3.2–9.1) × 106 CD34+ cells/kg for each patient (median viability, 90%), after conditioning with the ‘TBI-VP16-CY’ regimen, allowed prompt engraftment and immunological reconstitution; no patients experienced severe transplant-related toxicity or major infections. One patient relapsed 7 months after transplantation, while 10 patients are alive in clinical and molecular remission, at a median follow-up of 29 months (range, 15–40) (2-year EFS, 89%, s.e. 9). In conclusion, the procedure proved to be reproducible for pediatric purified autografting, highly efficient concerning stem cell recovery and depletion of leukemia-lineage specific cells, and promising in terms of final outcome.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrett AJ, Horowitz MM, Ollack BH, Zhang M-J, Bortin MM, Buchanan GR, Camitta BM, Ochs J, Graham-Pole J, Rowlings PA, Rimm AA, Klein JP, Shuster JJ, Sobocinski KA, Gale RP . Bone marrow transplants from HLA-identical siblings as compared with chemotherapy for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in second remission New Engl J Med 1994 331: 1253–1258
Sadowitz PD, Stephen SD, Smith SD, Shuster J, Wharam MD, Buchanan GR, Rivera GK . Treatment of late bone marrow relapse in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a Pediatric Oncology Group Study Blood 1993 81: 602–609
Rivera GK, Hudson MM, Liu Q, Benaim E, Ribeiro RC, Crist WM, Pui C-H . Effectiveness of intensified rotational combination chemotherapy for late hematologic relapse of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia Blood 1996 88: 831–837
Henze G, Fengler R, Kornhuber B, Janka-Schaub G, Niethammer D, Riehm H . Six-year experience with a comprehensive approach to the treatment of recurrent childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL-REZ BFM 85). A relapse study of the BFM group Blood 1991 78: 1166–1172
Weisdorf DJ, Billet AL, Hannan P, Ritz J, Sallan SE, Steinbuch M, Ramsay NKC . Autologous versus unrelated donor allogeneic marrow transplantation for acute lymphoblastic leukemia Blood 1997 90: 2962–2968
Balduzzi A, Gooley T, Anasetti C, Sanders J, Martin PJ, Petersdorf EW, Appelbaum FR, Buckner CD, Matthews D, Storb R, Sullivan KM, Hansen JA . Unrelated donor marrow transplantation in children Blood 1995 86: 3247–3256
Casper J, Camitta B, Truitt R . Unrelated bone marrow donor transplants for children with leukemia or myelodysplasia Blood 1995 85: 2354–2360
Brenner MK, Rill DR, Moen RC . Gene marking to trace origin of relapse after autologous bone-marrow transplantation Lancet 1993 341: 85–86
Dunbar CE, Cottler-Fox M, O'Shaunessy JA, Doren S, Carter C, Berenson R, Brown S, Moen RC, Greenblatt J, Stewart FM . Retrovirally marked CD34-enriched peripheral blood and marrow cells contribute to long-term engraftment after autologous transplantation Blood 1995 85: 3048–3057
Billet AL, Sallan SE . Autologous bone marrow transplantation in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia with using of purging Am J Hematol Oncol 1993 15: 162–168
Rambaldi A, Borleri G, Dotti G, Bellavita P, Amaru R, Biondi A, Barbui T . Innovative two-step negative selection of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-mobilized circulating progenitor cells: adequacy for autologous and allogeneic transplantation Blood 1998 91: 2189–2196
To LB, Haylock DN, Simmons PJ, Juttner CA . The biology and clinical use of blood stem cells Blood 1997 89: 2233–2258
Coffe C, Counteret Y, Devillers M, Fest T, Morel P, Pouthier-Stein, Calot JP, Novakovitch G, Sitthy X, Tremisi PJ . Peripheral blood stem cell transplantation: approaches to an optimal blood stem cell collection Transfus Sci 1992 13: 387–398
Gorin NC . Collection, manipulation and freezing of haemopoietic stem cells Clin Haematol 1986 15: 19–48
Rowley SD, Bensinger WI, Gooley TA, Buckner CD . Effect of cell concentration on bone marrow and peripheral blood stem cell cryopreservation Blood 1994 83: 2731–2736
Perseghin P, Epis R, Viganò M, Malacrida A, Pastorini A, Camerone G . Satisfactory recovery and viability of stem cells cryopreserved at high cell concentration Transfus Sci 1997 18: 399–403
Billet AL, Kornmehl E, Tarbell NJ, Weinstein HJ, Gelber RD, Ritz J, Sallan SS . Autologous bone marrow transplantation after a long first remission children with recurrent acute lymphoblastic leukemia Blood 1993 81: 1651–1657
Uderzo C, Rondelli R, Dini G, Dallorso S, Messina C, Miniero R, Locatelli F, De Manzin A, Pession A, Balduzzi A, Locasciulli A, Masera G . High-dose vincristine, fractionated total-body irradiation and cyclophosphamide as conditioning regimen in allogeneic and autologous bone marrow transplantation for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in second remission: a 7-year Italian multicentre study Br J Haematol 1995 89: 790–797
van Dongen JJM, Seriu T, Panzer-Grümayer ER, Biondi A, Pongers-Willemse MJ, Corral L, Stolz F, Schrappe M, Masera G, Kamps WA, Gadner H, van Wering ER, Ludwig W-D, Basso G, de Bruijn MAC, Cazzaniga G, Hettinger K, van der Does-van den Berg A, Hop WCJ, Riehm H, Bartram CR . Prognostic value of minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in childhood Lancet 1998 352: 1731–1735
Privitera E, Rivolta A, Ronchetti D, Mosna G, Giudici G, Biondi A . Reverse transcriptase/polymerase chain reaction follow-up and minimal residual disease detection in t(1,19)-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia Br J Haematol 1996 92: 653–658
van Dongen JJM, Macintyre EA, Gabert JA, Delabesse E, Rossi V, Saglio G, Gottardi E, Dotti G, Griesinger A, Parreira A, Gameiro P, Gonzalez Diaz M, Malec M, Langerak AW, San Miguel JF, Biondi A . Standardized RT-PCR anlysis of fusion gene transcripts from chromosome aberrations in acute leukemia for detection of minimal residual disease. Report of the BIOMED-1 Concerted Action: investigation of minimal residual disease Leukemia 1999 13: 1901–1928
Pongers-Willemse MJ, Seriu T, Stolz F, d'Aniello E, Gameiro P, Pisa P, Gonzalez M, Bartram CR, Panzer-Grümayer ER, Biondi A, San Miguel JF, van Dongen JJM . Primers and protocols for standardized detection of minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukemia using immunoglobulin and T cell receptor gene rearrangements and TAL1 deletions as PCR targets. Report of the BIOMED-1 Concerted Action: investigation of minimal residual disease Leukemia 1999 13: 110–118
Kaplan EL, Meier P . Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations J Am Stat Assoc 1958 53: 457
Conter V, Aricò M, Valsecchi MG, Rizzari C, Testi AM, Miniero R, Di Tullio MT, Lo Nigro L, Pession A, Rondelli R, Messina C, Santoro N, Mori PG, De Rossi G, Tamaro P, Silvestri D, Biondi A, Basso G, Masera G for the Associazione Italiana di Ematologia e Oncologia Pediatrica AIEOP . Intensive BFM chemotherapy for childhood ALL: interim analysis of the AIEOP-ALL 91 study Haematologica 1998 83: 791–799
Lee CK, Gingrich RD, Hohl RJ, Ajram KA . Engraftment syndrome in autologous bone marrow and peripheral blood stem cell transplantation Bone Marrow Transplant 1995 16: 175–182
Gorin NC, Lopez M, Laporte JP, Quittet P, Lesage S, Lemoine F, Berenson RJ, Isnard F, Grande M, Stachowiak J, Labopin M, Fouillard L, Morel P, Jouet JP, Noel-Walther MP, Detourmignies L, Aoudjhane M, Bauters F, Najman A, Douay L . Preparation and successful engraftment of purified CD34+ bone marrow progenitor cells in patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma Blood 1995 85: 1647–1654
Brenner MK, Rill DR, Holladay MS, Heslop HE, Moen RC, Buschle M, Krance RA, Santana VM, Anderson WF, Ihle JN . Gene marking to determine whether autologous marrow infusion restores long-term haemopoiesis in cancer patients Lancet 1993 342: 1134–1137
Kamani N, Kattamis A, Carroll A, Campbell D, Bunin N . Immune reconstitution after autologous purged bone marrow transplantation in children J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2000 22: 13–19
Mizuta S, Ito Y, Kohno A, Kiyoi H, Miyamura K, Tanimoto M, Takamatsu J, Naoe T, Morishima Y, Ueda R, Saito H for the Nagoya BMT group . Accurate quantitation of residual tumor burden at bone marrow harvest predicts timing of subsequent relapse in patients with common ALL treated by autologous bone marrow transplantation Bone Marrow Transplant 1999 24: 777–784
Chessells JM, Leiper AD, Richards SM . A second course of treatment for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: long-term follow-up is needed to assess results Br J Haematol 1994 86: 48–54
Miniero R, Saracco P, Pastore G, Zurlo MG, Terracini B, Rosso P, Masera G for the Italian Association of Pediatric Hematology-Oncology (AIEOP) . Relapse after first cessation of therapy in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a 10-year follow-up study Med Ped Oncol 1995 24: 71–76
Bührer C, Hartmann R, Schoeber S, Arlt I, Loewke M, Henze G for the BFM (Berlin–Frankfurt–Münster) Relapse Study Group . Importance of effective central nervous system therapy in isolated one marrow relapse of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia Blood 1994 83: 3468–3472
Bührer C, Hartmann R, Fenglrer R, Rath B, Schrappe M, Janka-Schaub G, Henze G for the Berlin–Frankfurt–Münster Relapse Study Group . Peripheral blast counts at diagnosis of late isolated bone marrow relapse of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia predict response to salvage chemotherapy and outcome J Clin Oncol 1996 14: 2812–2817
Buchanan G, Boyett JM, Pollock BH, Smith SD, Yanofsky RA, Ghim T, Wharam MD, Crist WM, Vietti TJ, Johnson W, Rivera GK . Improved treatment results in boys with overt testicular relapse during or shortly after initial therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. A Pediatric Oncology Group Study Cancer 1991 68: 48–54
Ribeiro RC, Rivera GK, Hudson M, Mulhern RK, Hancock ML, Kun L, Mahmoud H, Sandlund JT, Crist WM, Pui C-H . An intensive re-treatment protocol for children with an isolated CNS relapse of acute lymphoblastic leukemia J Clin Oncol 1995 13: 333–338
Borgmann A, Schmid H, Hartmann R, Baumgarten E, Hermann K, Klingebiel T, Ebell W, Zintl F, Gadner H, Henze G for the Berlin–Frankfurt–Munster Study Group . Autologous bone-marrow transplants compared with chemotherapy for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in a second remission: a matched pair analysis Lancet 1995 346: 873–876
Messina C, Cesaro S, Rondelli R, Rossetti F, Locatelli F, Pession A, Miniero R, Dini G, Uderzo C, Dallorso S, Meloni G, Vignetti M, Andolina M, Porta F, Amici A, Favre C, Basso G, Sotti G, Varotto S, Destro R, Gazzola MV, Pillon M, Petris MG, Rabusin M, Scarzello G, Zanesco L on behalf of the AIEOP/FONOP-TMO Group . Autologous bone marrow transplantation for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in Italy Bone Marrow Transplant 1998 21: 1015–1021
Borgmann A, Hartmann R, Schmid H, Klingebiel T, Ebell W, Göbel U, Peters C, Gadner H, Henze G for the BFM Relapse Study Group . Isolated extramedullary relapse in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a comparison between treatment results of chemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation Bone Marrow Transplant 1995 15: 515–521
Messina C, Valsecchi MG, Aricò M, Locatelli F, Rossetti F, Rondelli R, Cesaro S, Uderzo C, Conter V, Pession A, Sotti G, Loiacono G, Santoro N, Miniero R, Dini G, Favre C, Meloni G, Testi AM, Werner B, Silvestri D, Arrighini A, Varotto S, Pillon M, Basso G, Lombardi A, Masera G, Zanesco L on behalf of the AIEOP/FONOP-TMO Group . Autologous bone marrow transplantation for treatment of isolated central nervous system relapse of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia Bone Marrow Transplant 1998 21: 9–14
Hoogerbrugge PM, Gerritsen EJA, vd Does van den Berg A, vd Berg H, Zwinderman AH, Hermans J, Vossen JMJJ . Case-control analysis of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation versus maintenance chemotherapy for relapsed ALL in children Bone Marrow Transplant 1995 15: 255–259
Grañena A, Castellsaguè X, Badell I, Ferra C, Ortega JJ, Brunet S, Puntí C, Sureda A, Picón M, Valls A, Rutlant ML, García J . Autologous bone marrow transplantation for high risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia: clinical relevance of ex vivo bone marrow purging with monoclonal antibodies and complement Bone Marrow Transplant 1999 24: 621–627
Maldonado MS, Díaz-Heredia C, Badell I, Ortega JJ, Cubells J, Otheo E, Olive T, Canals C, Pérez-Oteyza J from the Spanish Working Party for BMT in Children . Autologous bone marrow transplantation with monoclonal antibody purged marrow for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in second remission Bone Marrow Transplant 1998 22: 1043–1047
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the ‘Comitato Maria Letizia Verga per lo studio e la cura della leucemia del bambino’ and the ‘Fondazione Tettamanti’ for their continuous support, Miss Sara Vaghi for secretarial assistance and Miss Joanna Upton for linguistic consultancy. This work was partially supported by grants from the Associazione Italiana Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC) and Ministero Università Ricerca Scientifica e Tecnologica (MURST) (to AB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balduzzi, A., Gaipa, G., Bonanomi, S. et al. Purified autologous grafting in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia in second remission: evidence for long-term clinical and molecular remissions. Leukemia 15, 50–56 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402004
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402004
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Autologous purified peripheral blood SCT in childhood low-risk relapsed ALL
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2011)
-
Allogeneic and autologous transplantation for haematological diseases, solid tumours and immune disorders: current practice in Europe 2009
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2010)
-
PCR-based clonality assessment in patients with lymphocytic leukaemias: a single-institution experience
Journal of Genetics (2009)
-
Strategies of the donor search for children with second CR ALL lacking a matched sibling donor
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2008)
-
Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation trends in children over the last three decades: a survey by the paediatric diseases working party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2007)