Abstract
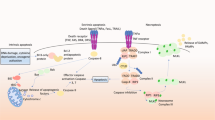
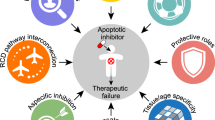
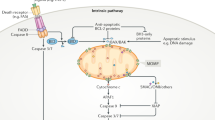
This report summarizes recent findings in the field of basic and translational apoptosis research which were presented at the 1st Conference on ‘Mechanisms of Cell Death and Disease: Advances in Therapeutic Intervention’ organized by the European School of Hematology and the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, 13–17 May, in Dublin, Ireland, and puts them in the context of the literature. Recent discoveries have significantly advanced the understanding of biochemical and genetic requirements of distinct apoptosis pathways (ie mitochondrial, death-receptor and endoplasmic reticulum-mediated apoptosis) and their dysregulation in disease. Progress has been made especially in the elucidation of the mechanisms of action of the Bcl-2 family members, in detail the formation of channels and their regulation in the mitochondrial membranes, conformational changes in Bax and Bak, and crosstalk of death receptor-triggered apoptosis to the mitochondria by activation of Bax via Bid. In addition, novel insights have been gained about the regulation of caspases and novel caspase signaling pathways, such as activation of caspase-12 by the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Therapeutic applications of apoptosis manipulation include (1) the inhibition of caspases in acute and chronic neurodegenerative diseases, ie stroke, Alzheimer's or Huntington's disease by drugs and (2) sensitization of cancer cells for drug/radiation-induced apoptosis by modulation of survival signals and viral transfer of apoptosis promoting genes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, Li E, Xu J, Yankner BA, Yuan J . Caspase-12 mediates endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by amyloid-beta Nature 2000 403: 98–103
Li H, Zhu H, Xu C, Yuan J . Cleavage of BID by caspase 8 mediates the mitochondrial damage in the Fas pathway of apoptosis Cell 1998 94: 491–501
Luo X, Budihardjo I, Zou H, Slaughter C, Wang X . Bid, a Bcl-2 interacting protein, mediates cytochrome c release in response to activation of cell surface death receptors Cell 1998 94: 481–490
Desagher S, Osen-Sand A, Nichols A, Eskes R, Montessuit S, Lauper S, Maundrell K, Antonsson B, Martinou J . Bid-induced conformational change of Bax is responsible for mitochondrial cytochrome c release during apoptosis J Cell Biol 1999 144: 891–901
Krammer PH . CD95(APO-1/Fas)-mediated apoptosis: live and let die Adv Immunol 1999 71: 163–210
Koseki T, Inohara N, Chen S, Carrio R, Merino J, Hottiger MO, Nabel GJ, Nunez G . CIPER, a novel NF kappaB-activating protein containing a caspase recruitment domain with homology to Herpesvirus-2 protein E10 J Biol Chem 1999 274: 9955–9961
Koseki T, Inohara N, Chen S, Nunez G . ARC, an inhibitor of apoptosis expressed in skeletal muscle and heart that interacts selectively with caspases Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998 95: 5156–5160
Blagosklonny MV . Cell death beyond apoptosis Leukemia 2000 14: 1502–1508
Van der Heiden MG, Thompson CB . Bcl-2 proteins: regulators of apoptosis or of mitochondrial homeostasis? Nat Cell Biol 1999 1: E209–E216
Kroemer G, Reed JC . Mitochondrial control of death Nature Med 2000 6: 513–519
Shimizu S, Tsujimoto Y . Proapoptotic BH3-only Bcl-2 family members induce cytochrome c release, but not mitochondrial membrane potential loss, and do not directly modulate voltage-dependent anion channel activity Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000 97: 577–582
Bargou RC, Daniel PT, Mapara MY, Bommert K, Wagener C, Kallinich B, Royer HD, Dörken B . Expression of the bcl-2 gene family in normal and malignant breast tissue: low bax-alpha expression in tumor cells correlates with resistance towards apoptosis Int J Cancer 1995 60: 854–859
Prokop A, Wieder T, Sturm I, Eßmann F, Seeger KH, Wuchter C, Ludwig WD, Henze G, Dörken B, Daniel PT . Relapse in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia is associated with decrease of Bax/Bcl-2- ratio and loss of spontaneous caspase-3 processing in vivo Leukemia 2000 14: 1606–1613
Sturm I, Kohne CH, Wolff G, Petrowsky H, Hillebrand T, Hauptmann S, Lorenz M, Dörken B, Daniel PT . Analysis of the p53/BAX pathway in colorectal cancer: low BAX is a negative prognostic factor in patients with resected liver metastases J Clin Oncol 1999 17: 1364–1374
Sturm I, Papadopoulos S, Lück HJ, Hillebrand T, Benter T, Wolff G, Dörken B, Daniel PT . Differential BAX expression in breast cancer is independent of BAX mutation Int J Cancer 2000 87: 517–521
Muchmore SW, Sattler M, Liang H, Meadows RP, Harlan JE, Yoon HS, Nettesheim D, Chang BS, Thompson CB, Wong SL, Ng SL, Fesik SW . Protein, Structure X-ray and NMR structure of human Bcl-xL, an inhibitor of programmed cell death Nature 1996 381: 335–341
Lorenzo HK, Susin SA, Penninger J, Kroemer G . Apoptosis inducing factor (AIF): a phylogenetically old, caspase-independent effector of cell death Cell Death Differ 1999 6: 516–524
Chapman R, Sidrauski C, Walter P . Intracellular signaling from the endoplasmic reticulum to the nucleus Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 1998 14: 459–485
Pahl HL . Signal transduction from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cell nucleus Physiol Rev 1999 79: 683–701
Squier MK, Miller AC, Malkinson AM, Cohen JJ . Calpain activation in apoptosis J Cell Physiol 1994 159: 229–237
Soussi T, Debouche K, Béroud C . P53 website and analysis of p53 gene mutations in cancer: forging a link between epidemiology and carcinogenesis Hum Mutat 2000 15: 105–113
Waldman T, Lengauer C, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B . Uncoupling of S phase and mitosis induced by anticancer agents in cells lacking p21 Nature 1996 381: 713–716
Hollander M, Sheikh M, Bulavin D, Lundgren K, Augeri-Henmueller L, Shehee R, Molinaro T, Kim K, Tolosa E, Ashwell J, Rosenberg M, Zhan Q, Fernandez-Salguero P, Morgan W, Deng C, Fornace A . Genomic instability in Gadd45a-deficient mice Nat Genet 1999 23: 176–184
Sherr C, Weber J . The ARF/p53 pathway Curr Opin Genet Dev 2000 10: 94–99
Schmitz I, Walczak H, Krammer PH, Peter ME . Differences between CD95 type I and II cells detected with the CD95 ligand Cell Death Differ 1999 6: 821–822
Irmler M, Thome M, Hahne M, Schneider P, Hofmann K, Steiner V, Bodmer JL, Schroter M, Burns K, Mattmann C, Rimoldi D, French LE, Tschopp J . Inhibition of death receptor signals by cellular FLIP Nature 1997 388: 190–195
Lagresle C, Bella C, Daniel PT, Krammer PH, Defrance T . Regulation of germinal center B cell differentiation: role of the human APO-1/fas (CD95) antigen J Immunol 1995 154: 5746–5756
Daniel PT, Krammer PH . Activation induces sensitivity towards APO-1 (CD95)-mediated apoptosis in human B cells J Immunol 1994 152: 5624–5632
Daniel PT, Oettinger U, Mapara MY, Bommert K, Bargou R, Dörken B . Activation and activation-induced death of human tonsillar B cells and Burkitt lymphoma cells: lack of CD95 (Fas/APO-1) ligand expression and function Eur J Immunol 1997 27: 1029–1034
Nicholson DW . Caspase structure, proteolytic substrates, and function during apoptotic cell death Cell Death Differ 1999 6: 1028–1042
Zheng TS, Flavell RA . Divinations and surprises: genetic analysis of caspase function in mice Exp Cell Res 2000 256: 67–73
Roth JA, Nguyen D, Lawrence DD, Kemp BL, Carrasco CH, Ferson DZ, Hong WK, Komaki R, Lee JJ, Nesbitt JC, Pisters KM, Putnam JB, Schea R, Shin DM, Walsh GL, Dolormente MM, Han CI, Martin FD, Yen N, Xu K, Stephens LC, McDonnell TJ, Mukhopadhyay T, Cai D . Retrovirus-mediated wild-type p53 gene transfer to tumors of patients with lung cancer Nature Med 1996 2: 985–991
Heise C, Sampson-Johannes A, Williams A, McCormick F, Von Hoff DD, Kirn DH . ONYX-015, an E1B gene-attenuated adenovirus, causes tumor-specific cytolysis and antitumoral efficacy that can be augmented by standard chemotherapeutic agents Nature Med 1997 3: 639–645
Walker A, Taylor ST, Hickman JA, Dive C . Germinal center-derived signals act with Bcl-2 to decrease apoptosis and increase clonogenicity of drug-treated human B lymphoma cells Cancer Res 1997 57: 1939–1945
Graeber T, Osmanian C, Jacks T, Housman D, Koch C, Lowe S, Giaccia A . Hypoxia-mediated selection of cells with diminished apoptotic potential in solid tumours Nature 1996 379: 88–91
Newton K, Strasser A . Ionizing radiation and chemotherapeutic drugs induce apoptosis in lymphocytes in the absence of Fas or FADD/MORT1 signaling. Implications for cancer therapy J Exp Med 2000 191: 195–200
Villunger A, Egle A, Kos M, Hartmann BL, Geley S, Kofler R, Greil R . Drug-induced apoptosis is associated with enhanced Fas (Apo-1/CD95) ligand expression but occurs independently of Fas (Apo-1/CD95) signaling in human T-acute lymphatic leukemia cells Cancer Res 1997 57: 3331–3334
Wesselborg S, Engels IH, Rossmann E, Los M, Schulze-Osthoff K . Anticancer drugs induce caspase-8/FLICE activation and apoptosis in the absence of CD95 receptor/ligand interaction Blood 1999 93: 3053–3063
Chlichlia K, Moldenhauer G, Daniel PT, Busslinger M, Gazzolo L, Schirrmacher V, Khazaie K . Immediate effects of reversible HTLV-1 tax function: T-cell activation and apoptosis Oncogene 1995 10: 269–277
Fernandes R, Gorman A, McGahon A, Lawlor M, McCann S, Cotter T . The repression of apoptosis by activated abl oncogenes in chronic myelogenous leukemia Leukemia 1996 10: (Suppl. 2) S17–21
McGahon A, Bissonnette R, Schmitt M, Cotter K, Green D, Cotter T . Bcr-abl maintains resistance of chronic myelogenous leukemia cells to apoptotic cell death Blood 1994 83: 1179–1187
Gianni M, de Thé H . In acute promyelocytic leukemia NB4 cells, the synthetic retinoid CD437 induces contemporaneously apoptosis, a caspase-3-mediated degradation of PML/RARalpha protein and the PML retargeting on PML-nuclear bodies Leukemia 1999 13: 739–749
Grignani F, Ferrucci PF, Testa U, Talamo G, Fagioli M, Alcalay M, Mencarelli A, Grignani F, Peschle C, Nicoletti I . The acute promyelocytic leukemia-specific PML-RAR fusion protein inhibits differentiation and promotes survival of myeloid precursor cells Cell 1993 74: 423–431
Wang ZG, Ruggero D, Ronchetti S, Zhong S, Gaboli M, Rivi R, Pandolfi PP . PML is essential for multiple apoptotic pathways Nat Genet 1998 20: 266–272
Dierlamm J, Baens M, Wlodarska I, Stefanova-Ouzounova M, Hernandez JM, Hossfeld DK, De Wolf-Peeters C, Hagemeijer A, van den Berghe H, Marynen P . The apoptosis inhibitor gene AP12 and a novel 18q gene, MLT, are recurrently rearranged in the t(11;18)(q21;q21) associated with mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas Blood 1999 93: 3601–3609
Yan M, Lee J, Schilbach S, Goddard A, Dixit V . mE10, a novel caspase recruitment domain-containing proapoptotic molecule J Biol Chem 1999 274: 10287–10292
Zhang Q, Siebert R, Yan M, Hinzmann B, Cui X, Xue L, Rakestraw KM, Naeve CW, Beckmann G, Weisenburger DD, Sanger WG, Nowotny H, Vesely M, Callet-Bauchu E, Salles G, Dixit VM, Rosenthal A, Schlegelberger B, Morris SW . Inactivating mutations and overexpression of BCL10, a caspase recruitment domain-containing gene, in MALT lymphoma with t(1;14)(p22;q32) Nat Genet 1999 22: 63–68
Le Coutre P, Tassi E, Varella-Garcia M, Barni R, Mologni L, Cabrita G, Marchesi E, Supino R, Gambacort-Passerini C . Induction of resistance to the Abelson inhibitor ST1571 in leukemic cells through gene amplification Blood 2000 95: 1758–1766
Gianni M, Koken MH, Chelbi-Alix MK, Benoit G, Lanotte M, Chen Z, de Thé H . Combined arsenic and retinoic acid treatment enhances differentiation and apoptosis in arsenic-resistant NB4 cells Blood 1998 91: 4300–4310
Lallemand-Breitenbach V, Guillemin MC, Janin A, Daniel MT, Degos L, Kogan SC, Bishop JM, de Thé H . Retinoic acid and arsenic synergize to eradicate leukemic cells in a mouse model of acute promyelocytic leukemia J Exp Med 1999 189: 1043–1052
Acknowledgements
I wish to thank Frank Essmann, Karin Schmelz, Bernd Gillissen, Isrid Sturm and Thomas Wieder for critically reading and their comments on the manuscript. I also wish to thank Prof Bernd Dörken for his most generous support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daniel, P. Dissecting the pathways to death. Leukemia 14, 2035–2044 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401940
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401940