Abstract
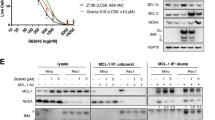
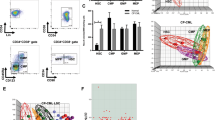
CD95 (Fas/APO-1) is a member of the TNFR superfamily that induces apoptosis following cross-linking with its cognate ligand, CD95L (FasL/APO-1L) or agonist antibody. The human myeloma cell line, RPMI 8226, has limited sensitivity to CD95-mediated apoptosis, with a maximum of 65% of the population responding. To determine the source of the limited sensitivity to CD95-mediated apoptosis, we isolated multiple clones from the RPMI-8226 cell line by limiting dilution. Analysis of these clones demonstrated that sensitivity to CD95-mediated cell death directly correlated with CD95 expression. Clones with high levels of CD95 expression had greater than 90% cell death, whereas cells with low levels of expression had less than 10% cell death. In contrast, no correlative differences were identified for other members of the DISC complex, or for members of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family. We further examined the sensitivity of the 8226 clones to various cytotoxic agents. Although modest clonal variability was demonstrated in response to the chemotherapeutic drugs, doxorubicin, etoposide (VP-16), and vincristine, there was no correlation between CD95 function and sensitivity to chemotherapeutic drugs. These results indicate that in this cell line, receptor expression is rate limiting in CD95-mediated apoptosis, whereas CD95 expression was not a determinant in drug-induced programmed cell death.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Itoh N, Nagata S . A novel protein domain required for apoptosis: mutational analysis of human Fas antigen J Biol Chem 1993 268: 10932–10937
Chinnaiyan AM, O'Rourke K, Tewari M, Dixit VM . FADD, a novel death domain-containing protein, interacts with the death domain of Fas and initiates apoptosis Cell 1995 81: 505–512
Boldin MP, Goncharov TM, Goltsev YV, Wallach D . Involvement of MACH, a novel Mort1/FADD-interacting protease, in Fas/APO-1 and TNF receptor-induced cell death Cell 1996 85: 803–815
Muzio M, Chinnaiyan AM, Kischkel FC, O'Rourke K, Shevchenko A, Ni J, Scaffidi C, Bretz JD, Zhang M, Gentz R, Mann M, Krammer PH, Peter ME, Dixit VM . FLICE, a novel FADD-homologous ICE/CED-3-like protease, is recruited to the CD95 (Fas/APO-1) death-inducing signaling complex Cell 1996 85: 817–827
Muzio M . Signalling by proteolysis: death receptors induce apoptosis Int J Clin Lab Res 1998 28: 141–147
Scaffidi C, Fulda S, Srinivasan A, Friesen C, Li F, Tomaselli KJ, Debatin K-M, Krammer PH, Peter ME . Two CD95 (APO-1/Fas) signaling pathways EMBO J 1998 6: 1675–1687
Zou H, Li Y, Liu X, Wang X . An APAF-1 cytochrome c multimeric complex is a functional apoptosome that activates procaspase-9 J Biol Chem 1999 274: 11549–11556
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES, Wang X . Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade Cell 1997 91: 479–489
Slee EA, Harte MT, Kluck RM, Wolf BB, Casiano CA, Newmeyer DD, Wang HG, Reed JC, Nicholson DW, Alnemri ES, Green DR, Martin SJ . Ordering the cytochrome c-initiated caspase cascade: hierarchical activation of caspases-2, −3, −6, −7, −8, and −10 in a caspase-9-dependent manner J Cell Biol 1999 144: 281–292
Sato T, Irie S, Kitada S, Reed JC . FAP-1: a protein tyrosine phosphatase that associates with Fas Science 1995 268: 411–415
Zhou YW, Komada Y, Inaba H, Azuma E, Sakurai M . Down-regulation of Fas-associated phosphatase-1 (FAP-1) in interleukin-2-activated T cells Cell Immunol 1998 186: 103–110
Ungefroren H, Voss M, Jansen M, Roeder C, Henne-Bruns D, Kremer B, Kalthoff H . Human pancreatic adenocarcinomas express Fas and Fas ligand yet are resistant to Fas-mediated apoptosis Cancer Res 1998 58: 1741–1749
Yanagisawa J, Takahashi M, Kanki H, Yano-Yanagisawa H, Tazunoli T, Sawa E, Nishitoba T, Kamishohara M, Kobayashi E, Kataoka S, Sato T . The molecular interaction of Fas and FAP-1: a tripeptide blocker of human Fas interaction with FAP-1 promotes Fas-induced apoptosis J Biol Chem 1997 272: 8539–8545
Reed JC . The Bcl-2 family of proteins Oncogene 1999 17: 3225–3236
Boise LH, Thompson CB . Bcl-XL can inhibit apoptosis in cells that have undergone Fas-induced protease activation Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997 94: 3759–3764
Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, Kim CN, Ibrado AM, Cai J, Peng T, Jones DP, Wang X . Prevention of apoptosis by Bcl-2: release of cytochrome c from mitochondria blocked Science 1997 275: 1129–1132
Catlett-Falcone R, Landowski TH, Oshiro MM, Turkson J, Levitzki A, Savino R, Ciliberto G, Moscinski L, Fernandez-Luna JL, Nunez G, Dalton WS, Jove R . Constitutive activation of Stat3 signaling confers resistance to apoptosis in human U266 myeloma cells Immunity 1999 10: 105–115
Eischen CM, Kottke TJ, Martins LM, Basi GS, Tung JS, Earnshaw WC, Leibson PJ, Kaufmann SH . Comparison of apoptosis in wild-type and Fas-resistant cells: chemotherapy-induced apoptosis is not dependent on Fas/Fas ligand interactions Blood 1997 90: 935–943
Fulda S, Sieverts H, Friesen C, Herr I, Debatin K-M . The CD95 (APO-1/Fas) system mediates drug-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells Cancer Res 1997 57: 3823–3829
Antoku K, Liu Z, Johnson DE . Inhibition of caspase proteases by CrmA enhances the resistance of human leukemic cells to multiple chemotherapeutic agents Leukemia 1997 11: 1665–1672
Fulda S, Susin SA, Kroemer G, Debatin KM . Molecular ordering of apoptosis induced by anticancer drugs in neuroblastoma cells Cancer Res 1998 58: 4453–4460
Landowski TH, Shain KH, Oshiro MM, Buyuksal I, Painter JS, Dalton WS . Myeloma cells selected for resistance to CD95-mediated apoptosis are not cross-resistant to cytotoxic drugs: evidence for independent mechanisms of caspase activation Blood 1999 94: 265–274
Friesen C, Herr I, Krammer PH, Debatin K-M . Involvement of the CD95 (APO-1/fas) receptor/ligand system in drug-induced apoptosis in leukemia cells Nature Med 1996 2: 574–577
Landowski TH, Gleason-Guzman MC, Dalton WS . Selection for drug resistance results in resistance to Fas mediated apoptosis Blood 1997 89: 1180–1187
Westendorf JJ, Lammert JM, Jelinek DF . Expression and function of Fas (APO-1/CD95) in patient myeloma cells and myeloma cell lines Blood 1995 12: 3466–3576
Nishiuchi R, Yoshino T, Matsuo Y, Sakuma I, Cao L, Seino Y, Takahashi K, Akagi T . The Fas antigen is detected on immature B cells and the representative cell lines show Fas-mediated apoptosis Br J Haematol 1996 92: 302–307
Medema JP, Toes RE, Scaffidi C, Zheng TS, Flavell RA, Melief CJ, Peter ME, Offringa R, Krammer PH . Cleavage of FLICE (caspase-8) by granzyme B during cytotoxic T lymphocyte-induced apoptosis Eur J Immunol 1997 27: 3492–3498
Martins LM, Kottke TJ, Kaufmann SH, Earnshaw WC . Phosphorylated forms of activated caspases are present in cytosol from HL-60 cells during etoposide-induced apoptosis Blood 1998 92: 3042–3049
Boise LH, Gonzalez-Garcia M, Postema CE, Ding L, Lindsten T, Turka LA, Mao X, Nunez G, Thompson CB . Bcl-x, a bcl-2 related gene that functions as a dominant regulator of apoptotic cell death Cell 1993 74: 597–608
Imai Y, Kimura T, Murakami A, Yajima N, Sakamaki K, Yonehara S . The CED-4-homologous protein FLASH is involved in Fas-mediated activation of caspase-8 during apoptosis Nature 1999 398: 777–785
Aragane Y, Kulms D, Metze D, Wilkes G, Poppelmann B, Luger TA, Schwarz T . Ultraviolet light induces apoptosis via direct activation of CD95 (Fas/APO-1) independently of its ligand CD95L J Cell Biol 1998 140: 171–182
Micheau O, Solary E, Hammann A, Dimanche-Boitrel MT . Fas ligand-independent, FADD-mediated activation of the Fas death pathway by anticancer drugs J Biol Chem 1999 274: 7987–7992
Gamen S, Anel A, Lasierra P, Alava MA, Martinez-Lorenzo MJ, Pineiro A, Naval J . Doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in human T cell leukemia is mediated by caspase-3 activation in a Fas-independent way FEBS Lett 1997 417: 360–364
Wesselborg S, Engels IH, Rossmann E, Los M, Schulze-Osthoff K . Anticancer drugs induce caspase-8/FLICE activation and apoptosis in the absence of CD95 receptor/ligand interaction Blood 1999 93: 3053–3063
Villunger A, Egle A, Kos M, Hartmann BL, Geley S, Kofler R, Greil R . Drug-induced apoptosis is associated with enhanced Fas (APO-1/CD95) ligand expression but occurs independently of Fas (APO-1/CD95) signaling in human T-acute lymphatic leukemia cells Cancer Res 1997 57: 3331–3334
Sun XM, MacFarlane M, Zhuang J, Wolf BB, Green DR, Cohen GM . Distinct caspase cascades are initiated in receptor-mediated and chemical-induced apoptosis J Biol Chem 1999 274: 5053–5060
Dirks W, Schone S, Uphoff C, Quentmeier H, Pradella S, Drexler HG . Expression and function of CD95 (Fas/APO-1) in leukaemia-lymphoma toumor lines Br J Haematol 1997 96: 584–593
Shima Y, Nishimoto N, Ogata A, Fujii Y, Yoshizaki K, Kishimoto T . Myeloma cells express Fas antigen/APO-1 (CD95) but only some are sensitive to anti-Fas antibody resulting in apoptosis Blood 1995 3: 757–764
Hua C, Zorn S, Jensen JP, Coupland RW, Ko HS, Wright JJ, Bakhshi A . Consequences of the t(14;18) chromosomal translocation in follicular lymphoma: deregulated expression of a chimeric and mutated BCL-2 gene Oncogene Res 1988 2: 263–275
McDonnell TJ, Nunez G, Platt FM, Hockenberry D, London L, McKearn JP, Korsmeyer SJ . Deregulated Bcl-2-immunoglobulin transgene expands a resting but responsive immunoglobulin M and D-expressing B-cell population Mol Cell Biol 1990 10: 1901–1907
Takahashi T, Tanaka M, Brannan CI, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Suda T, Nagata S . Generalized lymphoproliferative disease in mice, caused by a point mutation in the Fas ligand Cell 1994 76: 969–976
Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Brannan CI, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Nagata S . Lymphoproliferation disorder in mice explained by defects in Fas antigen that mediates apoptosis Nature 1992 356: 314–317
Tillman DM, Harwood FG, Gibson AA, Houghton JA . Expression of genes that regulate Fas signalling and Fas-mediated apoptosis in colon carcinoma cells Cell Death Diff 1998 5: 450–457
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by grants from the National Cancer Institute, CA77859 (WSD), core grant CA76292-01, and the flow cytometry and biostatistics core facilities at the H Lee Moffitt Center and Research Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shain, K., Landowski, T., Buyuksal, I. et al. Clonal variability in CD95 expression is the major determinant in Fas-mediated, but not chemotherapy-mediated apoptosis in the RPMI 8226 multiple myeloma cell line. Leukemia 14, 830–840 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401776
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401776
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
T and B leukemic cell lines exhibit different requirements for cell death: correlation between caspase activation, DFF40/DFF45 expression, DNA fragmentation and apoptosis in T cell lines but not in Burkitt's lymphoma
Leukemia (2002)
-
The kiss of death: promises and failures of death receptors and ligands in cancer therapy
Leukemia (2001)