Abstract
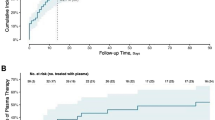
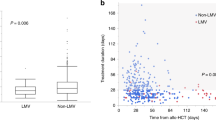
Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) causes life-threatening encephalopathy in recipients of allogeneic SCT, but no consensus has been reached regarding appropriate preventive methods. This study evaluated a plasma HHV-6 viral load-guided preemptive approach against HHV-6-associated encephalopathy. Plasma real-time PCR assay was performed once a week. Among 29 patients, 19 developed positive plasma HHV-6 DNA. Median maximum plasma HHV-6 DNA was 4593.5 copies/ml plasma (range, 150.0–127 891.0 copies/ml plasma). In one of eight events with low-level HHV-6 DNA (defined as <1000 copies/ml plasma) and four of seven events with mid-level HHV-6 DNA (1000–9999.5 copies/ml plasma), HHV-6 loads in plasma subsequently continued increasing. Ganciclovir was administered against six of nine patients with high-level HHV-6 DNA (⩾10 000 copies/ml plasma). High-level HHV-6 DNA resolved similarly in both groups with or without ganciclovir therapy. Among the nine patients with high-level HHV-6 DNA two developed encephalopathy. As encephalopathy developed before the detection of high-level HHV-6 DNA in plasma, these two patients had not received preemptive ganciclovir therapy. In conclusion, our preemptive approach against HHV-6-associated encephalopathy cannot prevent all cases of HHV-6 encephalopathy in SCT recipients due to the dynamic kinetics of plasma HHV-6 viral load.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yoshikawa T, Ihira M, Ohashi M, Suga S, Asano Y, Miyazaki H et al. Correlation between HHV-6 infection and skin rash after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2001; 28: 77–81.
Ljungman P, Wang FZ, Clark DA, Emery VC, Remberger M, Ringden O et al. High levels of human herpesvirus 6 DNA in peripheral blood leucocytes are correlated to platelet engraftment and disease in allogeneic stem cell transplant patients. Br J Haematol 2000; 111: 774–781.
Zerr DM, Corey L, Kim HW, Huang ML, Nguy L, Boeckh M . Clinical outcomes of human herpesvirus 6 reactivation after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 40: 932–940.
Ogata M, Kikuchi H, Satou T, Kawano R, Ikewaki J, Kohno K et al. Human herpesvirus 6 DNA load in plasma after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: incidence and clinical significance. J Infect Dis 2006; 193: 68–79.
Drobyski WR, Knox KK, Majewski D, Carrigan DR . Brief report: fatal encephalitis due to variant B human herpesvirus-6 infection in a bone marrow-transplant recipient. N Engl J Med 1994; 330: 1356–1360.
Wainwright MS, Martin PL, Morse RP, Lacaze M, Provenzale JM, Coleman RE et al. Human herpesvirus 6 limbic encephalitis after stem cell transplantation. Ann Neurol 2001; 50: 612–619.
Zerr DM . Human herpesvirus 6 and central nervous system disease in hematopoietic cell transplantation. J Clin Virol 2006; 37: 52–56.
Zerr DM . Human herpesvirus 6: a clinical update. Herpes 2006; 13: 20–24.
Yamane A, Mori T, Suzuki S, Mihara A, Yamazaki R, Aisa Y et al. Risk factors for developing human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) reactivation after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and its association with central nervous system disorders. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2007; 13: 100–106.
Noguchi T, Mihara F, Yoshiura T, Togao O, Atsumi K, Matsuura T et al. MR imaging of human herpesvirus-6 encephalopathy after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in adults. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2006; 27: 2191–2195.
Schmidt GM, Horak DA, Niland JC, Duncan SR, Forman SJ, Zaia JA . A randomized, controlled trial of prophylactic ganciclovir for cytomegalovirus pulmonary infection in recipients of allogeneic bone marrow transplants; The City of Hope-Stanford-Syntex CMV Study Group. N Engl J Med 1991; 324: 1005–1011.
Boeckh M, Gooley TA, Myerson D, Cunningham T, Schoch G, Bowden RA . Cytomegalovirus pp65 antigenemia-guided early treatment with ganciclovir versus ganciclovir at engraftment after allogeneic marrow transplantation: a randomized double-blind study. Blood 1996; 88: 4063–4071.
Rapaport D, Engelhard D, Tagger G, Or R, Frenkel N . Antiviral prophylaxis may prevent human herpesvirus-6 reactivation in bone marrow transplant recipients. Transpl Infect Dis 2002; 4: 10–16.
Tokimasa S, Hara J, Osugi Y, Ohata H, Matsuda Y, Fujisaki H et al. Ganciclovir is effective for prophylaxis and treatment of human herpesvirus-6 in allogeneic stem cell trensplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2002; 29: 595–598.
Sashihara J, Tanaka-Taya K, Tanaka S, Amo K, Miyagawa H, Hosoi G et al. High incidence of human herpesvirus 6 infection with a high viral load in cord blood stem cell transplant recipients. Blood 2002; 100: 2005–2011.
Matubara Y, Hori T, Morita R, Sakaguchi S, Uchiyama T . Delineation of immunoregulatory properties of adult T-cell leukemia cells. Int J Hematol 2006; 84: 63–69.
Zerr DM, Gupta D, Huang ML, Carter R Corey L . Effect of antivirals on human herpesvirus 6 replication in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis 2002; 34: 309–317.
Wang FZ, Linde A, Hagglund H, Testa M, Locasciulli A, Ljungman P . Human herpesvirus 6 DNA in cerebrospinal fluid specimens from allogeneic bone marrow transplant patients: does it have clinical significance? Clin Infect Dis 1999; 28: 562–568.
Achour A, Boutolleau D, Slim A, Agut H, Gautheret-Dejean A . Human herpesvirus-6 (HHV-6) DNA in plasma reflects the presence of infected blood cells rather than circulating viral particles. J Clin Virol 2007; 38: 280–285.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants-in-aid for scientific research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogata, M., Satou, T., Kawano, R. et al. Plasma HHV-6 viral load-guided preemptive therapy against HHV-6 encephalopathy after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: a prospective evaluation. Bone Marrow Transplant 41, 279–285 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705907
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705907
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Clinical practice recommendations for the diagnosis and management of human herpesvirus-6B encephalitis after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: the Japan Society for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2020)
-
Human herpesvirus-6 acute limbic encephalitis after unrelated umbilical cord blood transplantation successfully treated with ganciclovir
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2015)
-
Human herpesvirus-6 encephalitis after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: What we do and do not know
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2015)