Abstract
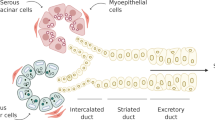
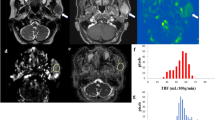
Salivary gland dysfunction is a common sequela of hematopoietic progenitor cell transplantation (HPCT). The investigation of major salivary gland dysfunction with sodium pertechnetate scintigraphy is a non-invasive method that provides images of the parotid and submandibular glands. In this prospective trial, 20 HPCT patients were submitted to scintigraphic study with 99mTc-pertechenate and 67Ga in order to evaluate the major salivary glands early involvement following HPCT. Major salivary glands were evaluated prior to HCPT as well as at Days +30, +60 and +100 post transplant. Major salivary glands uptake and clearance of 99mTc-pertechenate results did not demonstrate any functional differences between pre- versus post transplant periods. Results of the 67Ga scan revealed inflammatory infiltration following HPCT, primarily in submandibular glands, suggest a persistent involvement of major salivary glands up to Day +100 after HPCT.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dens F, Boogaerts M, Boute P, Declerck D, Demuynck H, Vinckier F et al. Caries-related salivary microorganisms and salivary flow rate in bone marrow recipients. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 1996; 81: 38–43.
Chaushu G, Itzkovitz-Chaushu S, Yefenof E, Slavin S, Or R, Garfunkel AA . A longitudinal follow-up of salivary secretion in bone marrow transplant patients. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 1995; 79: 164–169.
Bagesund M, Winiarski J, Dahllof G . Subjective xerostomia in long-term surviving children and adolescents after pediatric bone marrow transplantation. Transplantation 2000; 69: 822–826.
Dahllöf G, Bagesund M, Ringden O . Impact of conditioning regimens on salivary function, caries-associated microorganisms and dental caries in children after bone marrow transplantation. A 4-year longitudinal study. Bone Marrow Transplant 1997; 20: 479–483.
Lockhart PB, Sonis ST . Alterations in the oral mucosa caused by chemotherapeutic agents. A histologic study. J Dermatol Surg Oncol 1981; 7: 1019–1025.
Blomgren J, Jansson S, Rodjer S, Birkhed D . Secretion rate from minor salivary glands in patients with malignant haematological diseases receiving chemotherapy – a pilot study. Swed Dent J 2002; 26: 75–80.
Berk LB, Shivnani AT, Small Jr W . Pathophysiology and management of radiation-induced xerostomia. J Support Oncol 2005; 3: 191–200.
Sasse AD, de Oliveira Clark LG, Sasse EC, Clark OA . Amifostine reduces side effects and improves complete response rate during radiotherapy: Results of a meta-analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2006; 64: 784–791.
Loutfi I, Nair MK, Ebrahim AK . Salivary gland scintigraphy: the use of semiquantitative analysis for uptake and clearance. J Nucl Med Technol 2003; 31: 81–85.
Li N, Zhu W, Zuo S, Jia M, Sun J . Value of gallium-67 scanning in differentiation of malignant tumors from benign tumors or inflammatory disease in the oral and maxillofacial region. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2003; 96: 361–367.
Bagesund M, Richter S, Agren B, Ringden O, Dahllof G . Scintigraphic study of the major salivary glands in pediatric bone marrow transplant recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 26: 775–779.
Dulley FL, Vigorito AC, Aranha FJ, Sturaro D, Ruiz MA, Saboya R et al. Addition of low-dose busulfan to cyclophosphamide in aplastic anemia patients prior to allogeneic bone marrow transplantation to reduce rejection. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 33: 9–13.
Nucci M, Andrade F, Vigorito A, Trabasso P, Aranha JF, Maiolino A et al. Infectious complications in patients randomized to receive allogeneic bone marrow or peripheral blood transplantation. Transplant Infect Dis 2003; 5: 167–173.
Alborghetti MR, Correa ME, Adam RL, Metze K, Coracin FL, De Souza CA et al. Late effects of chronic graft-vs-host disease in minor salivary glands. J Oral Pathol Med 2005; 34: 486–493.
Davies AN, Broadley K, Beighton D . Salivary gland hypofunction in patients with advanced cancer. Oral Oncol 2002; 38: 680–685.
Dodds MW, Johnson DA, Yeh CK . Health benefits of saliva: a review. J Dent 2005; 33: 223–233.
Kopittke L, Gomez R, Barros HM . Opposite effects of antidepressants on unstimulated and stimulated salivary flow. Arch Oral Biol 2005; 50: 17–21.
Dawes C . How much saliva is enough for avoidance of xerostomia? Caries Res 2004; 38: 236–240.
Nagler R, Marmary Y, Krausz Y, Chisin R, Markitziu A, Nagler A . Major salivary gland dysfunction in human acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Bone Marrow Transplant 1996; 17: 219–224.
Bagesund M, Richter S, Agren B, Dahllof G . Correlation between quantitative salivary gland scintigraphy and salivary secretion rates in children and young adults treated for hematological, malignant and metabolic diseases. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 2000; 29: 264–271.
Yagmur C, Miman MC, Karatas E, Akarcay M, Erdem T, Ozturan O . Effects of the chorda tympani damage on submandibular glands: scintigraphic changes. J Laryngol Otol 2004; 118: 102–105.
Meurman JH, Laine P, Keinanen S, Pyrhonen S, Teerenhovi L, Lindqvist C . Five-year follow-up of saliva in patients treated for lymphomas. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 1997; 83: 447–452.
Visentainer JE, Lieber SR, Persoli LB, Vigorito AC, Aranha FJ, De Brito Eid KA et al. Serum cytokine levels and acute graft-versus-host disease after HLA-identical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Exp Hematol 2003; 31: 1044–1050.
Nagler A, Nagler R, Ackerstein A, Levi S, Marmary Y . Major salivary gland dysfunction in patients with hematological malignancies receiving interleukin-2-based immunotherapy post-autologous blood stem cell transplantation (ABSCT). Bone Marrow Transplant 1997; 20: 575–580.
Dahllöf G, Bagesund M, Remberger M, Ringden O . Risk factors for salivary dysfunction in children 1 year after bone marrow transplantation. Oral Oncol 1997; 33: 327–331.
Dicke KA . Late effects after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1994; 14 (Suppl 4): S11–S13.
Levy S, Nagler A, Okon S, Marmary Y . Parotid salivary gland dysfunction in chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD): a longitudinal study in a mouse model. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 25: 1073–1078.
Medina JE, Frame R, Toth B, Nguyen L, Luna MH . Head and neck manifestations of the chronic graft vs host disease. Laryngoscope 1984; 94: 1145–1151.
Nagler R, Marmary Y, Krausz Y, Chisin R, Markitziu A, Nagler A . Major salivary gland dysfunction in human acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Bone Marrow Transplant 1996; 17: 219–224.
Yamauchi K, Noguchi K, Suzuki Y, Nagao T . Gallium-67 uptake in the salivary glands in chronic graft-versus-host disease after bone marrow transplantation. Clin Nucl Med 1989; 14: 330–332.
Vogelsang GB . Graft-versus-host disease. Curr Opin Oncol 1990; 2: 285–288.
Nagler RM, Nagler A . The molecular basis of salivary gland involvement in graft-vs-host disease. J Dent Res 2004; 83: 98–103.
Nagler RM, Nagler A . Salivary gland involvement in graft-versus-host disease: the underlying mechanism and implicated treatment. Isr Med Assoc J 2004; 6: 167–172.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the support and contributions of the staff of the Nuclear Medicine Service of University Hospital – Campinas State University, HPCT Unit. The expert data management by Mrs Eliana Miranda and Mrs Amanda Margelo is also sincerely appreciated. This study was supported by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo-FAPESP-(The State of São Paulo Research Foundation) proc. 00/12188-4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coracin, F., Pizzigatti Correa, M., Camargo, E. et al. Major salivary gland damage in allogeneic hematopoietic progenitor cell transplantation assessed by scintigraphic methods. Bone Marrow Transplant 37, 955–959 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705351
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1705351
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The effect of conditioning regimen and prescribed medications on hyposalivation in haematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) patients: an 18-month prospective longitudinal study
Clinical Oral Investigations (2023)
-
Oral health in oncology: impact of immunotherapy
Supportive Care in Cancer (2015)
-
Post-allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT) changes in inorganic salivary components
Supportive Care in Cancer (2015)
-
The impact of morphological and immunohistological changes in minor salivary glands on the health of the oral cavity in HSCT patients
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2013)
-
Long-term oral complications of allogeneic haematopoietic SCT
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2012)