Abstract
Objectives:
To investigate the antioxidative properties of sulfurous drinking water after a standard hydropinic treatment (500 ml day−1 for 2 weeks).
Subjects/Methods:
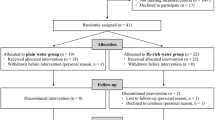
Forty apparently healthy adults, 18 men and 22 women, age 41–55 years old. The antioxidant profile and the oxidative condition were evaluated in healthy subjects supplemented for 2 weeks with (study group) or without (controls) sulfurous mineral water both before (T0) and after (T1) treatment.
Results:
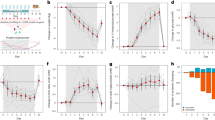
At T1, a significant decrease (P<0.05) in both lipid and protein oxidation products, namely malondialdehyde, carbonyls and AOPP, was found in plasma samples from subjects drinking sulfurous water with respect to controls. Concomitantly, a significant increment (P<0.05) of the total antioxidant capacity of plasma as well as of total plasmatic thiol levels was evidenced. Tocopherols, carotenoids and retinol remained almost unchanged before and after treatment in both groups.
Conclusions:
The improved body redox status in healthy volunteers undergoing a cycle of hydropinic therapy suggests major benefits from sulfurous water consumption in reducing biomolecule oxidation, possibly furnishing valid protection against oxidative damage commonly associated with aging and age-related degenerative diseases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebischer CP, Schierle J, Schuep W (1999). Simultaneous determination of retinol, tocopherols, carotene, lycopene and xanthophylls in plasma by means of reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Methods Enzymol 299, 348–362.
Agarwal R, Chase SD (2002). Rapid, fluorimetric-liquid chromatographic determination of malondialdehyde in biological samples. J Chromatogr B Biomed Appl 775, 121–126.
Beinert H (2000). A tribute to sulfur. Eur J Biochem 267, 5657–5664.
Bellometti S, Cecchettin M, Lalli A, Galzigna L (1996). Mud pack treatment increases serum antioxidant defences in osteoarthrosic patients. Biomed Pharmacother 50, 37.
Benzie IF, Strain JJ (1996). The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of ‘antioxidant power’: the FRAP assay. Anal Biochem 239, 70–76.
Caraglia M, Beninati S, Giuberti G, D'Alessandro AM, Lentini A, Abbruzzese A et al. (2005). Alternative therapy of earth elements increases the chondroprotective effects of chondroitin sulfate in mice. Exp Mol Med 37, 476–481.
Casetta I, Govoni V, Granieri E (2005). Oxidative stress, antioxidants and neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Pharm Des 11, 2033–2052.
Cesarone MR, Belcaro G, Caratelli M, Cornelli U, De Sanctis MT, Incandela L et al. (1999). A simple test to monitor oxidative stress. Int Angiol 18, 127–130.
Del Rio D, Stewart AJ, Pellegrini N (2005). A review of recent studies on malondialdehyde as toxic molecule and biological marker of oxidative stress. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 15, 316–328.
Ekmekcioglu C, Strauss-Blasche G, Holzer F, Marktl W (2002). Effect of sulfur baths on antioxidative defense systems, peroxide concentrations and lipid levels in patients with degenerative osteoarthritis. Forsch Komplementarmed Klass Naturheilkd 9, 216–220.
Geng B, Chang L, Pan C, Qi Y, Zhao J, Pang Y et al. (2004). Endogenous hydrogen sulfide regulation of myocardial injury induced by isoproterenol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 318, 756–763.
Gupta AK, Nicol K (2004). The use of sulfur in dermatology. J Drugs Dermatol 3, 427–431.
Hu ML (1994). Measurement of protein thiol groups and glutathione. Methods Enzymol 233, 380–385.
Jeong SO, Pae HO, Oh GS, Jeong GS, Lee BS, Lee S et al. (2006). Hydrogen sulfide potentiates interleukin-1beta-induced nitric oxide production via enhancement of extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 345, 938–944.
Kimura Y, Dargusch R, Schubert D, Kimura H (2006). Hydrogen sulfide protects HT22 neuronal cells from oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox signal 8, 661–670.
Leibetseder V, Strauss-Blasche G, Holzer F, Marktl W, Ekmekcioglu C (2004). Improving homocysteine levels through balneotherapy: effects of sulphur baths. Clin Chim Acta 343, 105–111.
Levine RL, Wehr N, Williams JA, Stadtman ER, Shacter E (2000). Determination of carbonyl groups in oxidized proteins. Methods Mol Biol 99, 15–24.
Moore K, Roberts II LJ (1998). Measurement of lipid peroxidation. Free Radic Res 28, 659–671.
Mulder GJ, Jakoby WB (1990). Sulfation. In: GJ Mulder (ed). Conjugation Reactions in Drug Metabolism. Taylor and Francis: London pp 107–161.
Oh GS, Pae HO, Lee BS, Kim BN, Kim JM, Kim HR et al. (2006). Hydrogen sulfide inhibits nitric oxide production and nuclear factor-kappaB via heme oxygenase-1 expression in RAW264.7 macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. Free Radic Biol Med 41, 106–119.
Rinaldi L, Gobbi G, Pambianco M, Micheloni C, Mirandola P, Vitale M (2006). Hydrogen sulfide prevents apoptosis of human PMN via inhibition of p38 and caspase 3. Lab Invest 86, 391–397.
Sachidanandam K, Fagan SC, Ergul A (2005). Oxidative stress and cardiovascular disease: antioxidants and unresolved issues. Cardiovasc Drug Rev 23, 115–132.
Scher JU, Pillinger MH, Abramson SB (2007). Nitric oxide synthases and osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 9, 9–15.
Stadtman ER, Levine RL (2003). Free radical-mediated oxidation of free amino acids and amino acid residues in proteins. Amino Acids 25, 207–218.
Sukenik S, Flusser D, Abu-Shakra M (1999). The role of spa therapy in various rheumatic diseases. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 25, 883–897.
Taylor D, Williams DR (1995). Trace Element Medicine and Chelation Therapy. The Royal Society of Chemistry Paperbacks: Cambridge.
Wang R (2002). Two's company, three's a crowd: can H2S be the third endogenous gaseous transmitter? FASEB J 16, 1792–1798.
Whiteman M, Cheung NS, Zhu YZ, Chu SH, Siau JL, Wong BS et al. (2005). Hydrogen sulphide: a novel inhibitor of hypochlorous acid-mediated oxidative damage in the brain? Biochem Biophys Res Commun 326, 794–798.
Witko-Sarsat V, Friedlander M, Capeillere-Blandin C, Nguyen-Khoa T, Nguyen AT, Zingraff J et al. (1996). Advanced oxidation protein products as a novel marker of oxidative stress in uremia. Kidney Int 49, 1304–1313.
Witko-Sarsat V, Friedlander M, Nguyen Khoa T, Capeillere-Blandin C, Nguyen AT, Canteloup S et al. (1998). Advanced oxidation protein products as a novel mediators of inflammation and monocyte activation in chronic renal failure. J Immunol 161, 2524–2532.
Acknowledgements
We thank Mrs Francesca Baldon (Terme di Saturnia) for technical assistance in secretarial work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benedetti, S., Benvenuti, F., Nappi, G. et al. Antioxidative effects of sulfurous mineral water: protection against lipid and protein oxidation. Eur J Clin Nutr 63, 106–112 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602892
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602892
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Hydrogen sulfide biosynthesis is impaired in the osteoarthritic joint
International Journal of Biometeorology (2020)
-
The impact of low mineral content water on cardiac function in diabetic rats: focus on oxidative stress
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2020)
-
Effects of drinking natural hydrogen sulfide (H2S) waters: a systematic review of in vivo animal studies
International Journal of Biometeorology (2020)
-
Influence of mineral waters on in vitro proliferation, antioxidant response and cytokine production in a human lung fibroblasts cell line
International Journal of Biometeorology (2019)
-
Suppressive effects of natural reduced waters on alloxan-induced apoptosis and type 1 diabetes mellitus
Cytotechnology (2012)