Abstract
Objective: To investigate the efficacy of enhancing the content and bioavailability of micronutrients in diets of stunted rural Malawian children on their growth and body composition, morbidity, anaemia and hair zinc concentrations.
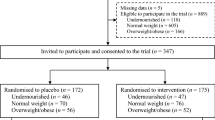
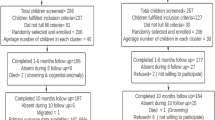
Design: A quasi-experimental design with non-equivalent control group involving 410 intervention and 220 control children aged 30–90 months.
Setting and subjects: Children from two intervention and two control villages in Mangochi District, Southern Malawi participated in a 6 month dietary intervention. Anthropometry, malarial screening, haemoglobin, and hair zinc were measured at baseline and after 12 months, as well as socio-economic status at baseline, and common infections monthly post-intervention.
Results: Groups were comparable at baseline. Post-intervention children had greater Z-scores for lean body mass (mid-upper arm circumference −0.75 vs −1.05; arm muscle area: 0.63 vs −1.03, P<0.001) than controls but Z-scores for weight-for-height and height-for-age were similar. After controlling for baseline variables, mean haemoglobin was higher (107 vs 102 g/l, P<0.01), whereas the incidence of both anaemia (62 vs 80%) and common infections (based on a median overall illness score for fever, diarrhoea, upper and lower respiratory infections) were lower in intervention compared to controls, with no change in hair zinc concentrations or malaria status post-intervention.
Conclusion: Improvements in the micronutrient adequacy of diets of post-intervention children were associated with a favourable increase in indices of lean body mass and reductions in the incidence of anaemia and common infections in these rural Malawian stunted children.
Sponsorship: Canadian International Development Agency through Micronutrient Initiative, UNICEF Malawi, World Vision Malawi. SmithKline Beecham donated albendazole.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angeles I, Schultink W, Matulessi P, Gross R . 1993 Decreased rate of stunting among anemic Indonesian preschool children through iron supplementation Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 58: 339–342
Bahl R, Bhandari N, Taneja S, Bhan M . 1997 The impact of vitamin A supplementation on physical growth of children is dependent on season Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 51: 26–29
Bates C, Evans P, Dardenne M, Prentice A, Lunn PG, Northrop-Clewes CA, Hoare S, Cole TJ, Horan SJ, Longman SC, Stirling D, Aggett PJ . 1993 A trial of zinc supplementation in young rural Gambian children Br. J. Nutr. 69: 243–255
Baumgartner RN, Roche AF, Himes JH . 1986 Incremental growth tables: supplementary to previously published charts Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 43: 711–722
Beard JL . 2001 Iron biology in immune function, muscle metabolism and neuronal functioning J. Nutr. 131: 568S–580S
Beaton GH, Martorell R, Aronson KJ, Edmonston G, McCabe G, Ross AC, Harvey B . 1993 Effectiveness of vitamin A supplementation in the control of young child morbidity and mortality in developing countries International Nutrition Program, Department of Nutritional Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto, ACC/SCN State-of-the Art Series Nutrition Policy Discussion Paper no. 13. New York: United Nations
Begin-Heick N, Dalpe-Scott M, Rowe J, Heick HMC . 1985 Zinc supplementation attenuates insulin secretory activity in pancreatic islets of the ob/ob mice Diabetes 34: 179–184
Bloem MW, Wedel M, Egger RJ, Speek AJ, Schrijver J, Saowakontha S, Schreurs WH . 1989 Iron metabolism and vitamin A deficiency in children in northeast Thailand Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 50: 332–338
Brown KH, Black RE, Becker S . 1982 Seasonal changes in nutritional status and the prevalence of malnutrition in a longitudinal study of young children in rural Bangladesh Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 36: 303–313
Brown K, Peerson J, Allen L . 1998 Effect of zinc supplementation on children's growth: a meta-analysis of intervention trials Bibl. Nutr. Dieta. 54: 76–83
Buzina R, Jusic M, Sapunar J, Milanovic N . 1980 Zinc nutrition and taste acuity in school children with impaired growth Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 33: 2262–2267
Castillo-Duran C, Garcia H, Venegas P, Torrealba I, Panteon E, Conche N, Perez P . 1994 Zinc supplementation increases growth velocity of male children and adolescents with short children Acta Paediatr. Scand. 83: 833–837
Cavan KR, Gibson RS, Grazioso CF, Isalgue AM, Ruz M, Solomons NW . 1993 Growth and body composition of periurban Guatemalan children in relation to zinc status: a longitudinal zinc intervention trial Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 57: 344–352
Clausen T, Dorup I . 1998 Micronutrients, minerals and growth control Bibl. Nutr. Dieta 54: 84–92
Davies P, Day J, Cole T . 1993 Converting Tanner-Whitehouse reference tricep and subscapular skinfold measurements to standard deviation scores Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 47: 559–566
Famine Early Warning System. 1997 Special Report 97-2, Southern Africa Food Security Update [Online], 26 March 1997 (Cited 12 February 2001). Available from URL: www.fews.org
Ferguson EL, Gibson RS, Opare-Obisaw C, Ounpuu S, Thompson LU, Lehrfeld J . 1993 The zinc nutriture of preschool children living in two African countries J. Nutr. 123: 1487–1496
Friis H, Ndhlovu P, Mduluza T, Kaondera K, Sandström B, Michaelsen KF, Vennervald BJ, Christensen NO . 1997 The impact of zinc supplementation on growth and body composition: a randomized controlled trial among rural Zimbabwean school children Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 51: 38–45
Frisancho A . 1990 Anthropometric standards for the assessment of growth and nutritional status. Ann Arbor, ME University of Michigan Press
Gibson R, DeWolfe M . 1979 The zinc, copper, manganese, vanadium and iodine content of hair from 38 Canadian neonates Pediatr. Res. 13: 959–962
Gibson RS, Hotz C . 200la Dietary diversification/modification strategies to enhance micronutrient content and bioavailability of diets in developing countries Br. J. Nutr. 85: (Suppl 2): S159–S166
Gibson RS, Hotz C . 2001b Nutritional causes of linear growth faltering in infants during the complementary feeding period. In: Nutrition and Growth, ed. R Martorells F Haschke. 47th Nestle Nutrition Workshop Series, Pediatric program. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins pp 159–196
Gibson RS, Huddle J-M . 1998 Suboptimal zinc status in pregnant Malawian women: its association with low intakes of poorly available zinc, frequent reproductive cycling, and malaria Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 67: 702–709
Gibson RS, Smit-Vanderkooy PD, MacDonald AC, Goldman A, Ryan B, Berry M . 1989 A growth limiting mild zinc deficiency syndrome in some Southern Ontario boys with low growth percentiles Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 49: 1266–1273
Gibson RS, Heywood A, Yaman C, Thompson LU, Heywood P . 1991 Food consumption patterns and trace element intakes of children from the Wosera, Papua New Guinea Ecol. Food. Nutr. 25: 69–77
Gibson RS, Yeudall F, Drost N, Mitimuni B, Cullinan T . 1998 Dietary interventions to prevent zinc deficiency Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 68: 484S–487S
Golden M, Golden B . 1981 Plasma zinc, rate of weight gain, and energy cost of tissue deposition in children recovering from severe malnutrition on a cow's milk or soya protein based diet Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 34: 892–899
Golden B, Golden M . 1992 Effect of zinc on lean tissue synthesis during recovery from malnutrition Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 46: 697–706
Giugliano R, Millward DJ . 1984 Growth and zinc homeostasis in the severely Zn-deficient rats Br. J. Nutr. 52: 545–560
Giugliano R, Millward DI . 1987 The effects of severe zinc deficiency on protein turnover in muscle and thymus Br. J. Nutr. 57: 139–155
Hambidge KM, Hambidge C, Jacobs M, Baum JD . 1972 Low levels of zinc in hair, anorexia, poor growth, and hypogeusia in children Pediatr. Res. 6: 868–874
Hauvast JLA, Tolboom JJM, Kafwembe EM, Musonda RM, Mwanakasale V, van Staveren WA, van 't Hof MA, Sauerwein RW, Willems JL, Monnens LAH . 2000 Severe linear growth retardation in rural Zambian children: the influence of biological variables Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 71: 550–559
Himes JH, Carson C, Pheley A . 1991 Measurement errors for a portable device measuring short-term growth Am. J. Hum. Biol. 3: 325–329
Kikafunda JK, Walker AF, Allan EF, Tumwine JK . 1998 Effect of zinc supplementation on growth and body composition of Ugandan preschool children: a randomized, controlled, intervention trial Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 68: 1261–1266
Latham MC, Stephenson LS, Kinoti SN, Zaman MS, Kurz KM . 1990 Improvements in growth following iron supplementation in young Kenyan school children Nutrition 6: 159–165
Lawless J, Latham M, Stephenson L, Kinoti S, Pertet A . 1994 Iron supplementation improves appetite and growth in anemic Kenyan primary school children J. Nutr. 124: 645–654
Lee DY, Prasad AS, Hydrick-Adair C, Brewer G, Johnson PE . 1993 Homeostasis of zinc in marginal human zinc deficiency: role of absorption and endogenous excretion of zinc J. Lab. Clin. Med. 122: 549–556
Lohman T, Roche A, Martorell R . 1988 Anthropometric Standardization Reference Manual. Champagne IL: Human Kinetics Books
Morgan N, Keen CL, Lönnerdal B . 1988 Effect of varying dietary zinc intake of weanling mouse pups during recovery from early undernutrition on growth, body composition and composition of gain J. Nutr. 118: 690–698
National Statistical Office. 1997 Malawi demographic and health survey Zomba: National Statistical Office
Penland JG, Sandstead HH, Alcock NW, Dayal HH, Chen XC, Li JS, Zgao F, Yang JJ . 1997 A preliminary report: effects of zinc and micronutrient repletion on growth and neuropsychological function of urban Chinese children J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 16: 268–272
Prasad AS . 1991 Discovery of human zinc deficiency and studies in an experimental human model Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 53: 403–412
Rivera JA, Ruel MT, Santizo MC, Lönnerdal B, Brown KH . 1998 Zinc supplementation improves the growth of stunted rural Guatemalan infants J. Nutr. 128: 556–562
Rivera JA, González-Cossio T, Flores M, Romero M, Rivera M, Téllez-Rojo MM, Rosado JL, Brown KH . 2001 Multiple micronutrient supplementation increases the growth of Mexican infants Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 74: 657–663
Rosado JL, Lopez P, Munoz E, Martinez H, Allen LH . 1997 Zinc supplementation reduces morbidity, but neither zinc nor iron supplementation affects growth or body composition of Mexican preschoolers Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 65: 13–29
Ruel M, Rivera J, Habicht J, Martorell R . 1995 Differential response to early nutrition supplementation: long term effects on height at adolescence Int. J. Epidemiol. 24: 404–412
Ruz M, Castillo-Duran C, Lara X, Codoceo J, Rebolledo A, Atalah E . 1997 A 14-mo zinc supplementation trial in apparently healthy Chilean preschool children Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 66: 1406–1413
Shankar AH, Prasad AS . 1998 Zinc and immune function: the biological basis of altered resistance to infection Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 68: (Suppl): 447S–463S
Smith JC Jr, Butronovitz GP, Purdy WC . 1979 Direct measurement of zinc in plasma by atomic absorption spectroscopy Clin. Chem. 25: 1487–1491
Smit-Vanderkooy PD, Gibson RS . 1987 Food consumption patterns of Canadian children in relation to zinc and growth status Am. J. Clin. Nutr 45: 609–616
Stoltzfus RJ, Dreyfuss ML . 1998 International Nutritional Anemia Consultative Group/WHO/UNICEF Guidelines for the use of iron supplements to prevent and treat iron deficiency anemia Washington, DC: ILSI Press
Stoltzfus R, Chwaya H, Albobnico M, Schulze K, Tielsch J, Savioli L . 1997 Epidemiology of iron deficiency and anemia in Zanzibari school children Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 65: 153–159
Umeta L, West CE, Haidar J, Deurenberg P, Hautvast JG . 2000 Zinc supplementation and stunted infants in Ethiopia: a randomised controlled trial Lancet 355: 2021–2026
van den Broek NR, Letsky EA . 2000 Etiology of anemia in pregnancy in south Malawi Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 72: (Suppl): 247S–256S
Walker SP, Golden M . 1988 Growth in length of children recovering from severe malnutrition Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 42: 395–404
Walravens PA, Hambidge KA . 1976 Growth of infants fed a zinc supplemented formula Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 29: 1114–1121
Walravens PA, Krebs NF, Hambidge KM . 1983 Linear growth of low income preschool children receiving a zinc supplement Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 38: 195–201
Walravens PA, Hambidge KM, Koepfer MA . 1989 Zinc supplementation in infants with a nutritional pattern of failure to thrive: a double-blind controlled study Pediatrics 83: 532–538
West K, Djunaedi E, Pandji A, Kusidiono, Tarwotjo I, Sommer A . 1988 Vitamin A supplementation and growth: a randomized community trial Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 48: 1257–1264
West KP, LeClerq SC, Shreshtha SR, Wu LS-F, Pradhan EK, Khatry SK, Katz J, Adhikari R, Sommer A . 1997 Effects of vitamin A on growth of vitamin A-deficient children: field studies in Nepal Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 127: 1957–1965
WHO. 1996 Zinc. In: Trace Elements in Human Nutrition and Health 72–104 Geneva: World Health Organization
Williams T, Young M, Ramarkrishnan U, Schroeder D . 2000 The relationship of hookworm infection to anemia among pre-school children in rural Malawi San Diego, CA FASEB A510: (abstract)
Xue-Cun C, Tai-An Y, Jin-Sheng H, Qiu-Yan M, Zhi-Min H, Li-Xiang . 1985 Low levels of zinc in hair and blood, pica, anorexia, and poor growth in Chinese preschool children Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 43: 694–700
Yeudall Y, Gibson RS, Mtimuni B . 2002 Impact of a community-based dietary intervention on micronutrient adequacy of high phytate maize-based diets of rural Malawian children Pub. Hlth Nutr. (in press)
Acknowledgements
Special thanks to the people of the communities, and our co-investigators (Beatrice Mtimuni, Timothy Cullinan, Nancy Drost), who implemented the intervention and oversaw the community development aspects of the project. Thanks also to our federal collaborators at the Ministries of Health, Agriculture and Community Services. Our Malawian programme staff the late W Makwenda, L Gonani and M Kulumunyu, field staff and our consultatory committee members from the Ministries of Health, Agriculture and Community Services and Save the Children US were crucial to the success of the programme. Thanks to SmithKline Beecham for donating the albendazole.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeudall, F., Gibson, R., Kayira, C. et al. Efficacy of a multi-micronutrient dietary intervention based on haemoglobin, hair zinc concentrations, and selected functional outcomes in rural Malawian children. Eur J Clin Nutr 56, 1176–1185 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601469
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601469
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Nutritional Zinc Status in Weaning Infants: Association with Iron Deficiency, Age, and Growth Profile
Biological Trace Element Research (2012)
-
A framework to explore micronutrient deficiency in maternal and child health in Malawi, Southern Africa
Environmental Health (2009)
-
Micronutrient deficiencies in maternity and child health: a review of environmental and social context and implications for Malawi
Environmental Geochemistry and Health (2009)