Abstract
Objective: To compare the effects of a lipid emulsion containing medium-chain triglycerides (MCT) and supplemented with α-tocopherol to a conventional long-chain triglyceride (LCT) emulsion.
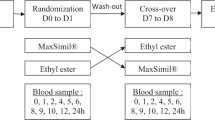
Design: Randomised double blind study.
Setting: Department of Internal Medicine, Antwerp University Hospital.
Subjects and interventions: Twenty-four patients with an indication for total parenteral nutrition for a minimum of 10 days were randomly assigned to two groups: group E received as lipid source MCT/LCT (50/50) suplemented with 100 mg dl-α-tocopherol/day and group C received LCT. Blood samples were analysed at inclusion, after 4–6 and after 9–11 days.
Results: In group E, serum α-tocopherol doubled from 11.4±6.9 at inclusion to 20.9±7.9 and to 23.8±8.8 µg/ml after 4 and 9 days, respectively, but did not change in group C (P=0.008). Production of thiobarbituric acid-reacting substances (TBARS) after 120 min incubation with copper decreased from 66±34 at inclusion to 29±25 nmol MDA/mg LDL and VLDL-cholesterol after 4 and to 42±17 after 9 days (P=0.022 when compared to group C, which underwent no significant changes). Velocity of production of fluorescent products decreased in group E but not in group C (P=0.026).
Conclusions: Supplementation of TPN containing MCT/LCT with 100 mg dl-α-tocopherol/day leads to a doubling in serum α-tocopherol and to a decrease in the susceptibility of LDL and VLDL to peroxidation in vitro.
Sponsorship: This study was partly financed by B Braun Medical NVSA, Diegem, Belgium.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babineau TJ, Pomposelli J, Forse RA, Blackburn G . 1994 Lipids In Nutrition in Critical Care, ed. GP Zaloga 191–203 St Louis, MO: Mosby
Brown KM, Morrice PC, Duthie GG . 1994 Vitamin E supplementation suppresses indexes of lipid peroxidation and platelet counts in blood of smokers and nonsmokers but plasma lipoprotein concentrations remain unchanged Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 60: 383–387
Cadenas S, Rojas C, Mendez J, Herrero A, Barja G . 1996 Vitamin E decreases urine lipid peroxidation products in young healthy human volunteers under normal conditions Pharmac. Toxicol. 79: 247–253
Caye-Vaugien C, Krempf M, Lamarche P, Charbonnel B, Pieri J . 1990 Determination of α-tocopherol in plasma, platelets and erythrocytes of type I and type II diabetic patients by HPLC Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 60: 324–330
De Bosscher H, Schrans S, Nonneman L, De Leeuw I . 1997 Addition of alpha-tocopherol in TPN mixtures Clin. Nutr. 16 Suppl 2: 31
Diplock AT . 1995 Safety of antioxidant vitamins and β-carotene Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 62 Suppl: 1510S–1516S
Endres S . 1993 Messengers and mediators: interactions among lipids, eicosanoids, and cytokines Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 57 Suppl: 798S–800S
Esterbauer H, Scaur JS, Szollner H . 1991 Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxynonenal, malondialdehyde and related aldehydes Free Radic. Biol. Med. 11: 81–128
Frei B, Gaziano JM . 1993 Content of antioxidants, preformed lipid hydroperoxides, and cholesterol as predictors of the susceptibility of human LDL to metal-ion-dependent and -independent oxidation J. Lipid Res. 34: 2135–2145
Frei B, Stocker R, Ames BN . 1988 Antioxidant defenses and lipid peroxidation in human plasma Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85: 9748–9752
Friedewald WT, Levy M, Frederickson DS . 1972 Estimation of the concentration of low density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma without the use of the preparative ultracentrifuge Clin. Chem. 18: 499–502
Hack S, Merrit R, Morgan RM, Keefe MT . 1990 Serum vitamin A and E concentrations in paediatric total parenteral nutrition patients J. Parent. Enter. Nutr. 14: 189–194
Hajri T, Ferezou J, Lutton C . 1990 Effects of intravenous infusions of commercial fat emulsions (Intralipid 10 or 20%) on rat plasma lipoproteins: phospholipids in excess are the main precursors of lipoprotein-X-like particles Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1047: 121–130
Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation Study Investigation . 2000 Vitamin E supplementation and cardiovascular events in high-risk patients New Engl. J. Med. 342: 154–160
Kayden HJ, Traber M . 1993 Absorption, lipoprotein transport, and regulation of plasma concentrations of vitamin E in humans J. Lipid Res. 34: 343–358
Keith ME, Jeejeebhoy KN, Langer A, Kurian R, Barr A, O'Kelly B, Sole MJ . 2001 A controlled clinical trial of vitamin E supplementation in patients with congestive heart failure Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 73: 219–224
Kelly F, Sutton GLJ . 1989 Plasma and red blood cell vitamin E status of patients on total parenteral nutrition J. Parente. Enter. Nutr. 13: 510–515
Kontush A, Hübner C, Finckh B, Kohlschütter A, Beisiegel U . 1994 Low density lipoprotein oxidability to copper correlates to its initial ubiquinol-10 and polyunsaturated fatty acid content F.E.B.S. Lett. 341: 69–73
Kosugi H, Asano Y, Nagayama T, Beppu M, Kikugawa K . 1995 Urinary excretion of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances of healthy subjects supplemented with a high dose of d-alpha-tocopherol Biol. Pharm. Bull. 18: 1275–1278
Lemoyne M, Van Gossum A, Kurian R, Ostro M, Axler J, Jeejeebhoy KN . 1987 Breath pentane analysis as an index of lipid peroxidation: a functional test of vitamin status Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 46: 267–272
Lemoyne M, Van Gossum A, Kurian R, Jeejeebhoy K . 1988 Plasma vitamin E and selenium and breath pentane in home parenteral nutrition patients Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 48: 1310–1315
Linseisen J, Hoffmann J, Lienhard S, Jauch K-W . 2000 Antioxidant status of surgical patients receiving TPN with Ω-3-fatty acid-containing lipid emulsion supplemented with α-tocopherol Clin. Nutr. 19: 177–184
Manuel-y-Keenoy B, Moorkens G, Vertommen J, De Leeuw I . 2001 Antioxidant status and lipoprotein peroxidation in the chronic fatigue syndrome Life Sci. 68: 2037–2049
Meydani SN, Meydani M . 1998 Assessment of the safety of supplementation with different amounts of vitamin E in healthy older adults Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 68: 311–318
National Research Council . 1980 Recommended Dietary Allowances. Washington, DC: National Academy Press
Neuzil J, Stocker R . 1994 Free and albumin-bound bilirubin are efficient co-antioxidants for α-tocopherol, inhibiting plasma and low density lipoprotein peroxidation J. Biol. Chem. 269: 16712–16719
Nordenström J, Neeser G, Olivecrona T, Wahren J . 1991 Effect of medium- and long-chain triglyceride infusion on lipoprotein and hepatic lipase in healthy subjects Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 21: 580–585
Peck M, Alexander JW . 1991 Survival in septic guinea pigs is influenced by vitamin E, but not by vitamin C in enteral diets J. Parent. Enter. Nutr. 15: 433–436
Pincemail J, Defraigne JO, Limet R . 1996 Oxidative stress in clinical situations–fact or fiction? Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 13: 219–234
Pitkanen OM . 1992 Peroxidation of lipid emulsions: a hazard for the premature infant receiving parenteral nutrition? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 13: 239–245
Pitkanen O, Hallman M, Andersson S . 1991 Generation of free radicals in lipid emulsion used in parenteral nutrition Pediatr. Res. 29: 56–59
Simons LA, Von Koningsmark M, Balasubramaniam . 1996 What dose of vitamin E is required to reduce susceptibility of LDL to oxidation? Aust. N.Z. J. Med. 26: 496–503
Stampfer MJ, Hennekens CH, Manson JE, Colditz GA, Willett WC . 1993 Vitamin E consumption and the risk of coronary heart disease in women New Engl. J. Med. 328: 1444–1449
Steephen A, Traber M, Ito Y, Lewis HL, Kayden HJ . 1991 Vitamin E status of patients receiving long-term parenteral nutrition: is vitamin E supplementation adequate? J. Parent. Enter. Nutr. 15: 647–652
Stephens NG, Parsons A, Schofiels PM, Kelly F, Cheeseman K, Mitchinson MJ, Brown MJ . 1996 Randomised controlled trial of vitamin E in patients with coronary disease: Cambridge Heart Antioxidant Study (CHAOS) Lancet 347: 781–786
Traber MG, Carpentier YA, Kayden HJ, Richelle M, Galeano NF, Deckelbaum RJ . 1993 Alterations in plasma alpha and gamma tocopherol concentrations in response to intravenous infusion of lipid emulsions in humans Metabolism 42: 701–709
Treskova E, Carpentier YA, Ramakrishnan R, Al-Haideri M, Seo T, Deckelbaum RJ . 1999 Blood clearance and tissue uptake of intravenous lipid emulsions containing long-chain and medium-chain triglycerides and fish oil in a mouse model J. Parent. Enter. Nutr. 23: 253–259
Vandewoude MG, Vandewoude MFJ, De Leeuw I . 1986 Vitamin E status in patients on parenteral nutrition receiving intralipid J. Parent. Enter. Nutr. 10: 303–305
Zhang A, Vertommen J, Van Gaal L, De Leeuw I . 1994 A rapid and simple method for measuring the susceptibility of low-density-lipoprotein and very-low-density lipoprotein to copper-catalysed oxidation Clin. Chim. Acta 227: 159–173
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the patients who participated in the study, M Vinckx and P Aerts for skilful technical assistance, the nursing staff of the Antwerp University Hospital and B Braun Medical NVSA, Belgium for partly financing the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manuel-y-Keenoy, B., Nonneman, L., De Bosscher, H. et al. Effects of intravenous supplementation with α-tocopherol in patients receiving total parenteral nutrition containing medium- and long-chain triglycerides. Eur J Clin Nutr 56, 121–128 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601294
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601294
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Lipid emulsions in parenteral nutrition of intensive care patients: current thinking and future directions
Intensive Care Medicine (2010)
-
Fettemulsionen in der parenteralen Ernährung — Gegenwart und Zukunftsperspektiven
Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift (2003)