Abstract
Objective: To investigate in children with cystic fibrosis (CF) and children without CF: (1) the test–retest reproducibility of a 20 min resting energy expenditure (REE) measurement; and (2) the long-term reproducibility of REE measurements in children with CF using longitudinal data.
Design: Cross-sectional study and longitudinal cohort.
Setting: A tertiary referral paediatric hospital.
Subjects: A total of 31 (11 male, 20 female) children (aged 12.8±3.6 y) with CF and 32 (14 male, 18 female) healthy children without CF (aged 12.2±2.3 y) were enrolled in the short-term reproducibility study. Long-term REE measurement reproducibility was assessed in another 14 children (5 male, 9 female) with CF, comparing their initial REE measurement with a subsequent measurement 1–2 y later.
Methods: All children had measurements of height, weight, skinfold thickness and indirect calorimetry.
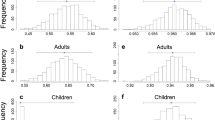
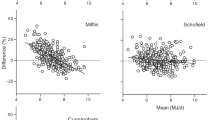
Results: There was no statistically significant difference in REE between repeated measurements in children with CF (mean±s.d., 6240±1280 and 6220±1315 kJ/24 h) and in the children without CF (6040±956 and 6015±943 kJ/24 h). For the children with CF, the intraclass correlation coefficient was 0.99 and for children without CF the intraclass correlation coefficient was 0.97. The measurement errors were 119 and 177 kJ, respectively. Approximately 80% of the variation in REE in the CF group and 70% in the group without CF was explained by fat-free mass (FFM). Analysis of the longitudinal CF data show there was no difference in REE between a child's first measurement (5140±1140 kJ) and their subsequent measurement (5460±1190 kJ), after adjustment for changes in body size between the measurements.
Conclusion: This study has demonstrated that a short-term 20 min REE measurement is reproducible and therefore valid in children with CF and children without CF. These results also indicate that in children with CF, long-term REE measurements are reproducible.
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2001) 55, 896–901
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armitage P & Berry G (1994) Statistical Methods in Medical Research 272–275 Oxford: Blackwell Science Ltd.
Bandini LG, Schoeller DA & Dietz WH (1990) Energy expenditure in obese and nonobese adolescents Pediatr. Res. 27 198–202
Bandini LG, Morelli JA, Must A & Dietz WH (1995) Accuracy of standardized equations for predicting metabolic rate in premenarcheal girls Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 62 711–714
Bell SC, Elborn JS, Nixon LE et al (1999) Repeatability and methodology of resting energy expenditure in patients with cystic fibrosis Resp. Physiol. 115 301–307
Bland JM & Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement Lancet i 307–310
Brockway JM (1987) Derivation of formula used to calculate energy expenditure in man Hum. Nutr. Clin. Nutr. 41C 43–71
Brook CGD (1971) Determination of body composition of children from skinfold measurements Arch. Dis. Child. 46 182–184
Buchdahl RM, Cox M, Fulleylove C et al (1988) Increased resting energy expenditure in cystic fibrosis J. Appl. Physiol. 64 1810–1816
Chinn S (1991) Repeatability and method comparison Thorax 46 454–456
Dibley MJ, Staehling NW, Nieburg P & Towbridge FL (1987) Interpretation of Z-score anthropometric indicators derived from the international growth reference Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 46 749–762
Dietz WH, Bandini LG, Morelli JA, Peers KF & Chin PLYH (1994) Effect of sedentary activities on resting metabolic rate Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 59 556–559
Durnin JVGA & Rahaman MM (1967) The assessment of the amount of fat in the human body from measurements of skinfold thickness Br. J. Nutr. 21 681–689
Elliot DL, Goldberg L, Kuehl K & Hanna C (1989) Metabolic evaluation of obese and nonobese siblings J. Pediatr. 114 957–962
Fontvieille AM, Harper IT, Ferraro RT, Spraul M & Ravussin E (1993) Daily energy expenditure by five-year-old children, measured by doubly labelled water J. Pediatr. 123 200–207
Gaskin KJ, Durie PR, Lee L, Hill R & Forstner GG (1984) Colipase and lipase secretion in childhood-onset pancreatic insufficiency: delineation of patients with steatorrhea secondary to relative colipase deficiency Gastroenterology 86 1–7
Giardet JP, Tounian P, Sardet A, Veinberg F, Grimfeld A, Tournier G & Fontaine JL (1994) Resting energy expenditure in infants with cystic fibrosis J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 18 214–219
Goran MI, Kaskoun M & Johnson R (1994) Determinants of resting energy expenditure in growing children J. Pediatr. 125 362 – 367
Lohman TG (1981) Skinfolds and body density and their relation to body fatness, a review Hum. Biol. 53 181–225
Lohman TG (1988) Anthropometry and body composition. In Anthropometric Standardization Reference Manual, eds. TG Lohman, AF Roche, R Martorell 125–129 Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics
McCauley JC, Allen, JR, Selby AM & Gaskin KJ (1993) Development of a paediatric indirect calorimeter Aust. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 16 129–136
Peat JK, Williams K, Xuan W & Mellis C (2001) Calculating Sample Size Health Science Research: a Handbook of Quantitative Methods 14 1 Melbourne: Allen & Unwin
Schofield WN, Schofield C & James WPT (1985) Basal metabolic rate—review and prediction, together with an annotated bibliography of sources material Hum. Nutr. Clin. Nutr. 39C (Suppl 1) S5–S41
Shepherd RW, Holt TL, Vasques-Velasquez et al (1988) Increased energy expenditure in children with cystic fibrosis Lancet i 1300–1303
Vaisman N, Pencharz PB, Corey M et al (1987a) Energy expenditure of patients with cystic fibrosis J. Pediatr. 111 496–500
Vaisman N, Levy LD, Pencharz PB, Tan YK, Soldin SJ, Canny GJ & Hahn E (1987b) Effect of salbutamol on resting energy expenditure in patients with cystic fibrosis J. Pediatr. 111 137–139
Ventham JC & Reilly JJ (1999) Reproducibility of resting metabolic rate measurement in children Br. J. Nutr. 81 435–437
WHO (1983) Reference data for weight and height of children. In Measuring Change in Nutritional Status 61–101 Geneva: WHO
Zemel BS, Kawchak DA, Cnaan A, Zhao H, Scanlin TF & Stallings VA (1996) Prospective evaluation of resting energy expenditure, nutritional status, pulmonary function, and genotype in children with cystic fibrosis Pediatr. Res. 40 578–586
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashley, M., Broomhead, L., Allen, J. et al. Variations in the measurement of resting energy expenditure in children with cystic fibrosis. Eur J Clin Nutr 55, 896–901 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601244
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601244
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Comparison of resting energy expenditure in bronchopulmonary dysplasia to predicted equation
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2006)