Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effect of a probiotic milk product containing the culture CAUSIDO® and of two alternative products on risk factors for cardiovascular disease in overweight and obese subjects.
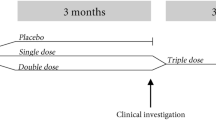
Design: An 8 week randomized, double-blind, placebo- and compliance-controlled, parallel study.
Subjects: Seventy healthy, weight-stable, overweight and obese (25.0<BMI<37.5 kg/m2) males (n=20) and females (n=50), 18–55 y old, were randomly assigned into five groups.
Intervention: Four groups consumed 450 ml fermented milk products (yoghurt) daily. Group 1: a yoghurt fermented with two strains of Streptococcus thermophilus and two strains of Lactobacillus acidophilus (StLa). Group 2: a placebo yoghurt fermented with delta-acid-lactone (PY). Group 3: a yoghurt fermented with two strains of Streptococcus thermophilus and one strain of Lactobacillus rhamnosus (StLr). Group 4: a yoghurt fermented with one strain of Enterococcus faecium and two strains of Streptococcus thermophilus (CAUSIDO® culture), GAIO® (G). The dietary composition of the yoghurt was otherwise similar. The fifth group was given two placebo pills (PP) daily.
Results: When comparing all five treatment groups, unadjusted for changes in body weight, no statistical effects were observed in week 8 in the G-group on low density lipoproteins (LDL)-cholesterol (P=0.29). After adjustment for small changes in body weight, LDL-cholesterol decreased by 8.4% (0.26±0.10 mmol/l; P<0.05) and fibrinogen increased (0.74±0.32 mmol/l; P<0.05) after 8 weeks in the G-group. This was significantly different from the group consuming chemically fermented yoghurt and the group consuming placebo pills (P<0.05). After 8 weeks, systolic blood pressure was significantly more reduced in the StLa and G-group compared to StLr. No other differences were found.
Conclusion: The CAUSIDO® culture reduced LDL-cholesterol and increased fibrinogen in the overweight subjects at a 450 ml consumption daily for 8 weeks. The effect on LDL-cholesterol confirms previous studies. An immunostimulation by one of the strains in the product might explain the effect on fibrinogen in the G-group.
Sponsorship: MD Foods A/S, Denmark.
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2000) 54, 288–297
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guarantor: Arne Astrup.
Contributors: A Raben and A Astrup initiated the project, which also was a part of a bachelor-project of N Haulrik and AS Hansen. M Manders was responsible for the compliance pilot-study and the compliance measurements as part of her student exchange programme (ERASMUS) at the department. All the authors were involved in the carrying out the experimental work. N Haulrik, AS Hansen and L Agerholm-Larsen made the statistical analysis. L Agerholm-Larsen wrote the article in collaboration with A Raben and A Astrup.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agerholm-Larsen, L., Raben, A., Haulrik, N. et al. Effect of 8 week intake of probiotic milk products on risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. Eur J Clin Nutr 54, 288–297 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600937
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600937