Abstract
Objectives: To compare whole body and regional (arms, legs and trunk) fat mass, fat-free mineral-free mass, bone mineral content and bone mineral density, measured by DXA, in cirrhotic patients and age, sex and BMI matched healthy volunteers.
Design: Cross-sectional study.
Setting: Two medical research institutions.
Subjects: Twenty-two non ascitic cirrhotic patients and 16 age, sex and BMI matched healthy volunteers.
Interventions: The Lunar DPX whole-body X-ray densitometer with Lunar software version 3.6z (Lunar Radiation Corp., Madison WI, USA) was used. Regional analysis was performed on the arms, legs, trunk and head.
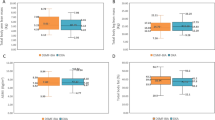
Results: Compared to controls, cirrhotic patients showed a significant reduction in percentage body fat. When differentiated by gender, however, the reduction in percentage body fat was evident in female cirrhotics only, particularly in the trunk. In male cirrhotic patients fat-free mineral-free mass was reduced in absolute terms in the whole body and the limbs. For both genders and in each body segment bone mineral content and density were reduced in cirrhotics compared to controls. In cirrhotic patients bone mineral density was significantly correlated to both fat-free, mineral-free mass (r=0.85; P<0.001) and to the Physical Activity Index (r=0.52; P<0.01).
Conclusions: Two different patterns of soft tissue loss may be found in cirrhotic patients: in women lean tissue is maintained while fat stores are reduced, as in early starvation; in men lean tissue is reduced, as seen under conditions of stress. Moreover, factors influencing lean body mass, such as nutritional depletion and physical inactivity, may contribute to the reduction of bone density frequently observed in cirrhotic patients.
Sponsorship: This work has been funded by the University of Rome, ‘La Sapienza’ research grant MURST 60%, 1995.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riggio, O., Andreoli, A., Diana, F. et al. Whole body and regional body composition analysis by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in cirrhotic patients. Eur J Clin Nutr 51, 810–814 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600490
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600490
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Lower values of handgrip strength and adductor pollicis muscle thickness are associated with hepatic encephalopathy manifestations in cirrhotic patients
Metabolic Brain Disease (2016)
-
The effects of weight loss approaches on bone mineral density in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Osteoporosis International (2016)