Abstract
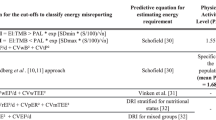
Objectives: To compare validation of reported dietary intakes from weighed records against urinary nitrogen excretion and energy expenditure measured by DLW, and to examine the utility of the Goldberg cut-off for EI:BMR in the identification of under-reporters. Design: Energy (EI) and nitrogen (protein) intake (NI) were measured by 16 d of weighed diet records collected over 1 y. They were validated against urinary nitrogen excretion in 5–8 (mean 6.0) 24 h urine collections and total energy expenditure (EE) measured by doubly labelled water (DLW). Basal metabolic rate (BMR) as measured by whole body calorimetry in women or bedside ventilated hood (Deltatrac) in men. Individual subjects were identified as under-reporters if Urine N:NI was >1.00 or if EI:EE was <0.79. The agreement between the two ratios in detecting under-reporting was examined. The results from the direct validation by DLW were also compared with validation using the Goldberg cut-off for EI:BMR (). Subjects: Eighteen women aged 50–65 y and 27 men aged 55–87 y were selected from participants in two larger dietary surveys as representing the full range of dietary reporting as measured by Urine N:NI. Data from a previous study of 11 post-obese subjects were also included. Results: The two ratios, Urine N:NI and EI:EE, were significantly related (r=−0.48, P<0.01). Using the above cut-offs, seven (4F, 3M) subjects were identified as under-reporters by both methods, one (1M) by Urine N:NI only and 8 (3F, 5M) by EI:EE only. There was close agreement in post-obese subjects where 6 subjects showed a substantial degree of under-reporting by both methods (r=−0.87, P<0.001). The correlation between direct validation by DLW and EI:BMRest was 0.65 (P<0.001). Some limitations of the Goldberg cut-off for identifying individual under-reporters were demonstrated. Conclusions: EI:EE provides an estimate of the degree of under-reporting of energy at the group and individual level. Urine N:NI identifies under-reporting of protein intake and the most obvious under-reporters of energy, but is probably of lesser value in estimating the overall degree of under-reporting of energy at group level. Good validation by EI:BMR depends on knowledge of physical activity at both group and individual level. However, the correlation of 0.65 between EI:EE and EI:BMRest suggests that EI:BMR could be usefully incorporated into analysis of data from epidemiological studies. Validation measures consisting of at least predicted EI:BMR ratios and urinary measures should be incorporated into dietary surveys. Sponsorship: This work was funded by the Ministry of Agriculture Fisheries and Food, the Medical Research Council, the Cancer Research Council and the Swedish Medical Research Council and the Henning and Johan Throne-Holst Foundation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Black, A., Bingham, S., Johansson, G. et al. Validation of dietary intakes of protein and energy against 24 hour urinary N and DLW energy expenditure in middle-aged women, retired men and post-obese subjects: comparisons with validation against presumed energy requirements. Eur J Clin Nutr 51, 405–413 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600425
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600425
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Yogurt consumption is associated with higher nutrient intake, diet quality and favourable metabolic profile in children: a cross-sectional analysis using data from years 1–4 of the National diet and Nutrition Survey, UK
European Journal of Nutrition (2019)
-
Assessment of energy intake in women with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A doubly labeled water method study
The journal of nutrition, health & aging (2015)
-
A comparison of two screening methods to determine the validity of 24-h food and drink records in children and adolescents
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2011)
-
Dietary intakes assessed by 24-h recalls in peri-urban African adolescents: validity of energy intake compared with estimated energy expenditure
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2011)
-
Evaluation of urinary iodine excretion as a biomarker for intake of milk and dairy products in pregnant women in the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study (MoBa)
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2009)