Abstract
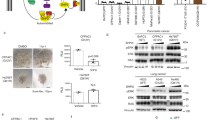
SHP-2 protein tyrosine phosphatase plays an important role in activation of the RAS-dependent signaling. Gain-of-function mutations in the PTPN11 gene, which encodes SHP-2, have been found in the leukemia-prone developmental disorder Noonan syndrome as well as sporadic childhood leukemias, indicating that SHP-2 is a bona fide human oncoprotein. However, the role of SHP-2 mutations in non-hematological malignancies remains obscure. Here, we screened for PTPN11 mutations in primary solid tumors and identified a 1520C>A mutation that causes threonine-507 to lysine (T507K) substitution in the phosphatase domain of SHP-2 in a case of hepatocellular carcinoma. T507K SHP-2 exhibited altered substrate specificity with slightly elevated basal phosphatase activity. Upon expression in NIH3T3 cells, T507K SHP-2 induced transformed foci, which was not observed with wild type, Noonan-specific or leukemia-specific SHP-2. Furthermore, NIH3T3 cells transformed by T507K SHP-2 showed anchorage-independent growth and developed tumors in nude mice. These results indicate that quantitative and/or qualitative alteration in phosphatase activity determines the transforming potential as well as target cell/tissue spectrum of individual SHP-2 mutants as oncoproteins. Although rare in solid tumors, the identified T507K SHP-2 represents a distinct class of SHP-2 mutants with oncogenic RAS-like transforming activity, which could contribute to the development of solid tumors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agazie YM, Hayman MJ . (2003). Development of an efficient ‘substrate-trapping’ mutant of Src homology phosphotyrosine phosphatase 2 and identification of the epidermal growth factor receptor, Gab1, and three other proteins as target substrates. J Biol Chem 278: 13952–13958.
Andersen JN, Mortensen OH, Peters GH, Drake PG, Iversen LF, Olsen OH et al. (2001). Structural and evolutionary relationships among protein tyrosine phosphatase domains. Mol Cell Biol 21: 7117–7136.
Aoki Y, Niihori T, Kawame H, Kurosawa K, Ohashi H, Tanaka Y et al. (2005). Germline mutations in HRAS proto-oncogene cause Costello syndrome. Nat Genet 37: 1038–1040.
Bentires-Alj M, Gil SG, Chan R, Wang ZC, Wang Y, Imanaka N et al. (2006). A role for the scaffolding adapter GAB2 in breast cancer. Nat Med 12: 114–121.
Bentires-Alj M, Paez JG, David FS, Keilhack H, Halmos B, Naoki K et al. (2004). Activating mutations of the Noonan syndrome-associated SHP2/PTPN11 gene in human solid tumors and adult acute myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Res 64: 8816–8820.
Chen Y, Takita J, Hiwatari M, Igarashi T, Hanada R, Kikuchi A et al. (2006). Mutations of the PTPN11 and RAS genes in rhabdomyosarcoma and pediatric hematological malignancies. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 45: 583–591.
Choong K, Freedman MH, Chitayat D, Kelly EN, Taylor G, Zipursky A . (1999). Juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia and Noonan syndrome. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 21: 523–527.
Clark GJ, Cox AD, Graham SM, Der CJ . (1995). Biological assays for Ras transformation. Methods Enzymol 255: 395–412.
Digilio MC, Conti E, Sarkozy A, Mingarelli R, Dottorini T, Marino B et al. (2002). Grouping of multiple-lentigines/LEOPARD and Noonan syndromes on the PTPN11 gene. Am J Hum Genet 71: 389–394.
Gelb BD, Tartaglia M . (2006). Noonan syndrome and related disorders: dysregulated RAS-mitogen activated protein kinase signal transduction. Hum Mol Genet 15: R220–R226.
Guex N, Peitsch MC . (1997). SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: an environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis 18: 2714–2723.
Hatakeyama M . (2004). Oncogenic mechanisms of the Helicobacter pylori CagA protein. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 688–694.
Higashi H, Nakaya A, Tsutsumi R, Yokoyama K, Fujii Y, Ishikawa S et al. (2004). Helicobacter pylori CagA induces Ras-independent morphogenetic response through SHP-2 recruitment and activation. J Biol Chem 279: 17205–17216.
Higashi H, Tsutsumi R, Muto S, Sugiyama T, Azuma T, Asaka M et al. (2002). SHP-2 tyrosine phosphatase as an intracellular target of Helicobacter pylori CagA protein. Science 295: 683–686.
Hof P, Pluskey S, Dhe-Paganon S, Eck MJ, Shoelson SE . (1998). Crystal structure of the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2. Cell 92: 441–450.
Keilhack H, David FS, McGregor M, Cantley LC, Neel BG . (2005). Diverse biochemical properties of Shp2 mutants. Implications for disease phenotypes. J Biol Chem 280: 30984–30993.
Keilhack H, Tenev T, Nyakatura E, Godovac-Zimmermann J, Nielsen L, Seedorf K et al. (1998). Phosphotyrosine 1173 mediates binding of the protein-tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 to the epidermal growth factor receptor and attenuation of receptor signaling. J Biol Chem 273: 24839–24846.
Kosaki K, Suzuki T, Muroya K, Hasegawa T, Sato S, Matsuo N et al. (2002). PTPN11 (protein-tyrosine phosphatase, nonreceptor-type 11) mutations in seven Japanese patients with Noonan syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87: 3529–3533.
Lauchle JO, Braun BS, Loh ML, Shannon K . (2006). Inherited predispositions and hyperactive Ras in myeloid leukemogenesis. Pediatr Blood Cancer 46: 579–585.
Loh ML, Vattikuti S, Schubbert S, Reynolds MG, Carlson E, Lieuw KH et al. (2004). Mutations in PTPN11 implicate the SHP-2 phosphatase in leukemogenesis. Blood 103: 2325–2331.
Mansour SJ, Matten WT, Hermann AS, Candia JM, Rong S, Fukasawa K et al. (1994). Transformation of mammalian cells by constitutively active MAP kinase. Science 265: 966–970.
Martinelli S, Carta C, Flex E, Binni F, Cordisco EL, Moretti S et al. (2006). Activating PTPN11 mutations play a minor role in pediatric and adult solid tumors. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 166: 124–129.
Mohi MG, Neel BG . (2007). The role of Shp2 (PTPN11) in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 17: 23–30.
Neel BG, Gu H, Pao L . (2003). The ‘Shp’ing news: SH2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatases in cell signaling. Trends Biochem Sci 28: 284–293.
Niihori T, Aoki Y, Narumi Y, Neri G, Cave H, Verloes A et al. (2006). Germline KRAS and BRAF mutations in cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome. Nat Genet 38: 294–296.
Noguchi T, Matozaki T, Horita K, Fujioka Y, Kasuga M . (1994). Role of SH-PTP2, a protein-tyrosine phosphatase with Src homology 2 domains, in insulin-stimulated Ras activation. Mol Cell Biol 14: 6674–6682.
Orita M, Iwahana H, Kanazawa H, Hayashi K, Sekiya T . (1989). Detection of polymorphisms of human DNA by gel electrophoresis as single-strand conformation polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 2766–2770.
Roberts AE, Araki T, Swanson KD, Montgomery KT, Schiripo TA, Joshi VA et al. (2007). Germline gain-of-function mutations in SOS1 cause Noonan syndrome. Nat Genet 39: 70–74.
Rodriguez-Viciana P, Tetsu O, Tidyman WE, Estep AL, Conger BA, Cruz MS et al. (2006). Germline mutations in genes within the MAPK pathway cause cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome. Science 311: 1287–1290.
Schubbert S, Zenker M, Rowe SL, Boll S, Klein C, Bollag G et al. (2006). Germline KRAS mutations cause Noonan syndrome. Nat Genet 38: 331–336.
Tabin CJ, Bradley SM, Bargmann CI, Weinberg RA, Papageorge AG, Scolnick EM et al. (1982). Mechanism of activation of a human oncogene. Nature 300: 143–149.
Tartaglia M, Martinelli S, Cazzaniga G, Cordeddu V, Iavarone I, Spinelli M et al. (2004). Genetic evidence for lineage-related and differentiation stage-related contribution of somatic PTPN11 mutations to leukemogenesis in childhood acute leukemia. Blood 104: 307–313.
Tartaglia M, Martinelli S, Stella L, Bocchinfuso G, Flex E, Cordeddu V et al. (2006). Diversity and functional consequences of germline and somatic PTPN11 mutations in human disease. Am J Hum Genet 78: 279–290.
Tartaglia M, Mehler EL, Goldberg R, Zampino G, Brunner HG, Kremer H et al. (2001). Mutations in PTPN11, encoding the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2, cause Noonan syndrome. Nat Genet 29: 465–468.
Tartaglia M, Niemeyer CM, Fragale A, Song X, Buechner J, Jung A et al. (2003). Somatic mutations in PTPN11 in juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia, myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Genet 34: 148–150.
Tartaglia M, Pennacchio LA, Zhao C, Yadav KK, Fodale V, Sarkozy A et al. (2007). Gain-of-function SOS1 mutations cause a distinctive form of Noonan syndrome. Nat Genet 39: 75–79.
Tsutsumi R, Takahashi A, Azuma T, Higashi H, Hatakeyama M . (2006). Focal adhesion kinase is a substrate and downstream effector of SHP-2 complexed with Helicobacter pylori CagA. Mol Cell Biol 26: 261–276.
Acknowledgements
We thank many physicians who cared for patients at the affiliated hospitals of the Division of Surgical Oncology, Graduate School of Medicine, Hokkaido University. We also thank Drs Miyuki Kida, Ryouhei Tsutsumi and Naoko Murata-Kamiya for technical support and valuable discussion. This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) of Japan and by a research grant from Takeda Science Foundation (MH).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyamoto, D., Miyamoto, M., Takahashi, A. et al. Isolation of a distinct class of gain-of-function SHP-2 mutants with oncogenic RAS-like transforming activity from solid tumors. Oncogene 27, 3508–3515 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1211019
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1211019
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A comprehensive review of SHP2 and its role in cancer
Cellular Oncology (2022)
-
Molecular anatomy and pathogenic actions of Helicobacter pylori CagA that underpin gastric carcinogenesis
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2020)
-
Probing the Dynamic Mechanism of Uncommon Allosteric Inhibitors Optimized to Enhance Drug Selectivity of SHP2 with Therapeutic Potential for Cancer Treatment
Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (2019)
-
Discovery of a Novel Inhibitor of the Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Shp2
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatases as potential therapeutic targets
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2014)