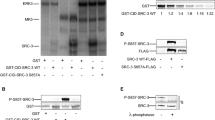
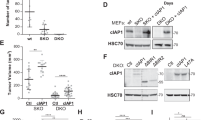
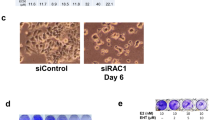
Abstract
The p160 nuclear receptor co-activators represent a family of molecules, which are recruited by steroid nuclear receptors as well as other transcription factors that are overexpressed in several tumors. We investigated the role of one member of this family on the sensitivity of cells to apoptosis. We observed that overexpression of the RAC3 (receptor-associated co-activator-3) p160 co-activator inhibits hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death in human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK293) cells. The mechanism involves the activation of anti-apoptotic pathways mediated through enhanced nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) activity, inhibition of caspase-9 activation, diminished apoptotic-inducing factor (AIF) nuclear localization and a change in the activation pattern of several kinases, including an increase in both AKT and p38 kinase activities, and inhibition of ERK2. Moreover, RAC3 has been found associated with a protein complex containing AIF, Hsp90 and dynein, suggesting a role for the co-activator in the cytoplasmatic nuclear transport of these proteins associated with cytoskeleton. These results demonstrate that there are several molecular pathways that could be affected by their overexpression, including those not restricted to steroid regulation or the nuclear action of co-activators, which results in diminished sensitivity to apoptosis. Furthermore, this could represent one mechanism by which co-activators contribute to tumor development.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AIF:
-
apoptotic-inducing factor
- CBP:
-
CREB-binding protein
- IκB:
-
inhibitor of NF-κB
- p53:
-
tumor-suppressor protein
- RAC3:
-
receptor-associated co-activator-3
- SRC-1:
-
steroid receptor co-activator-1
- TIF-2:
-
transcriptional intermediary factor-2
- TNF-α:
-
tumor necrosis factor-α
References
Anzick S, Kononen J, Walker R, Azorsa D, Tanner M, Guan X et al. (1997). AIB1, a steroid receptor coactivator amplified in breast and ovarian cancer. Science 277: 965–968.
Arnoult D, Parone P, Martinou J-C, Antonsson B, Estaquier J, Ameisen JC . (2002). Mitochondrial release of apoptosis-inducing factor occurs downstream of cytochrome c release in response to several proapoptotic stimuli. J Cell Biol 159: 923–929.
Beg A, Baltimore D . (1996). An essential role for NFκB in preventing TNF-α-induced cell death. Science 274: 782–784.
Cavarretta ITR, Mukopadhyay R, Lonard DM, Cowsert LM, BENNETT CF, O'Malley BW et al. (2002). Reduction of coactivator expression by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides inhibits ERa transcriptional activity and MCF-7 proliferation. Mol Endocrinol 16: 253–270.
Chen D, Ma H, Hong H, Koh S, Huang S, Schurter B et al. (1999). Regulation of transcription by a protein methyltransferase. Science 284: 2174–2177.
Cobb MH, Robbins DJ, Boulton TG . (1991). ERKs, extracellular signal-regulated MAP-2 kinases. Curr Opin Cell Biol 3: 1025–1032.
Costas MA, Muller Igaz L, Holsboer F, Arzt E . (2000). Transrepression of NF-κB is not required for glucocorticoid-mediated protection of TNF-αinduced apoptosis on fibroblast. Biochem Biophys Acta 1499: 122–129.
Coste A, Antal MC, Chan S, Kastner P, Mark M, O'Malley BW et al. (2006). Absence of the steroid receptor coactivator-3 induces B-cell lymphoma. EMBO J 25: 2453–2464.
Downward J . (1998). Ras signalling and apoptosis. Curr Opin Genet Dev 8: 49–54.
Franco DL, Nojek IM, Molinero L, Coso OA, Costas MA . (2002). Osmotic stress sensitizes naturally resistant cells to TNF-α-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 9: 1090–1098.
Galigniana MD, Harrell JM, O'Hagen HM, Ljungman M, Pratt WB . (2004). Hsp90-binding immunophilins link p53 to dynein during p53 transport to the nucleus. J Biol Chem 279: 22483–22489.
Ghosh S, Karin M . (2002). Missing pieces in the NF-κB puzzle. Cell 109: 81–96.
Glaeser M, Floetotto T, Hanstein B, Beckmann MW, Niederacher D . (2001). Gene amplification and expression of the steroid receptor coactivator SRC3 (AIB1) in sporadic breast and endometrial carcinomas. Horm Metab Res 33: 121–126.
Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG . (2000). The coregulator exchange in transcriptional functions of nuclear receptors. Genes Dev 14: 121–141.
Gnanapragasam VJ, Leung HY, Pulimood AS, Neal DE, Robson CN . (2001). Expression of RAC 3, a steroid hormone receptor co-activator in prostate cancer. Br J Cancer 85: 1928–1936.
Gross A, McDonnell J, Korsmeyer S . (1999). BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev 13: 1899–1911.
Gurbuxani S, Schmitt E, Cande C, Parcellier A, Hammann A, Daugas E et al. (2003). Heat shock protein 70 binding inhibits the nuclear import of apoptosis-inducing factor. Oncogene 22: 6669–6678.
Guttridge DC, Albanese C, Reuther JY, Pestell RG, Baldwin Jr AS . (1999). NF-κB controls cell growth and differentiation through transcriptional regulation of cyclin D1. Mol Cell Biol 19: 5785–5799.
Hengartner MO . (2000). The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 407: 770–776.
Hinz M, Krappmann D, Eichten A, Heder A, Scheidereit C, Strauss M . (1999). NF-κB function in growth control: regulation of cyclin D1 expression and G0/G1-to-S-phase transition. Mol Cell Biol 19: 2690–2698.
Iwase H, Omoto Y, Toyama T, Yamashita H, Hara Y, Sugiura H et al. (2003). Clinical significance of AIB1 expression in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 80: 339–345.
Katoh I, Tomimori Y, Ikawa Y, Kurata S . (2004). Dimerization and processing of procaspase-9 by redox stress in mitochondria. J Biol Chem 279: 15515–15523.
Kultz D, Burg M . (1998). Evolution of osmotic stress signaling via MAP kinase cascades. J Exp Biol 201: 3015–3021.
Li H, Gomes PJ, Chen JD . (1997). RAC3, a steroid/nuclear receptor-associated coactivator that is related to SRC-1 and TIF2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 8479–8484.
List HJ, Reiter R, Singh B, Wellstein A, Riegel AT . (2001). Expression of the nuclear coactivator AIB1 in normal and malignant breast tissue. Breast Cancer Res Treat 68: 21–28.
Martelli AM, Nyakern M, Tabellini G, Bortul R, Tazzari PL, Evangelisti C et al. (2006). Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway and its therapeutical implications for human acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 20: 911–928.
Na S, Lee S, Han S, Choi H, Im S, Lee J . (1998). SRC-1 interacts with the p50 subunit and coactivates the NFκB-mediated transactivations. J Biol Chem 273: 10831–10834.
Onate S, Tsai S, Tsai M, O'Malley B . (1995). Sequence and characterization of a coactivator for the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science 270: 1354–1357.
Ono K, Han J . (2000). The p38 signal transduction pathway: activation and function. Cell Signal 12: 1–13.
Park BG, Yoo CI, Kim HT, Kwon CH, Kim YK . (2005). Role of mitogen-activated protein kinases in hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death in osteoblastic cells. Toxicology 215: 115–125.
Peterson C, Logie C . (2000). Recruitment of chromatin remodeling machines. J Cell Biochem 78: 179–185.
Pratt WB, Toft DO . (2003). Regulation of signaling protein function and trafficking by the hsp90/hsp70-based chaperone machinery. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 228: 111–133.
Ravagnan L, Gurbuxani S, Susin SA, Maisse C, Daugas E, Zamzami N et al. (2001). Heat-shock protein 70 antagonizes apoptosis-inducing factor. Nat Cell Biol 3: 839–843.
Rubio MF, Werbajh S, Cafferata EG, Quaglino A, Colo GP, Nojek IM et al. (2006). TNF-alpha enhances estrogen-induced cell proliferation of estrogen-dependent breast tumor cells through a complex containing nuclear factor-kappa B. Oncogene 25: 1367–1377.
Sakakura C, Hagiwara A, Yasuoka R, Fujita Y, Nakanishi M, Masuda K et al. (2000). Amplification and over-expression of the AIB1 nuclear receptor co-activator gene in primary gastric cancers. Int J Cancer 89: 217–223.
Sheppard K, Rose D, Haque Z, Kurokawa R, McInerney E, Westin S et al. (1999). Transcriptional activation by NF-kappaB requires multiple coactivators. Mol Cell Biol 19: 6367–6378.
Sheppard KA, Phelps KM, Williams AJ, Thanos D, Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG et al. (1998). Nuclear integration of glucocorticoid receptor and nuclear factor-kappaB signaling by CREB-binding protein and steroid receptor coactivator-1. J Biol Chem 273: 29291–29294.
Spencer TE, Jenster G, Burcin MM, Allis CD, Zhou J, Mizzen CA et al. (1997). Steroid receptor coactivator-1 is a histone acetyltransferase. Nature 389: 194–198.
Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamzami N, Marzo I, Snow BE, Brothers GM et al. (1999). Molecular characterization of mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor. Nature 397: 441–446.
Takahashi A, Ohtani N, Yamakoshi K, Iida S, Tahara H, Nakayama K et al. (2006). Mitogenic signalling and the p16INK4a-Rb pathway cooperate to enforce irreversible cellular senescence. Nat Cell Biol 8: 1291–1297.
Torchia J, Rose DW, Inostroza J, Kamei Y, Westin S, Glass CK et al. (1997). The transcriptional co-activator p/CIP binds CBP and mediates nuclear-receptor function. Nature 387: 677–684.
Torres-Arzayus MI, Font de Mora J, Yuan J, Vazquez F, Bronson R, Rue M et al. (2004). High tumor incidence and activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway in transgenic mice define AIB1 as an oncogene. Cancer Cell 6: 263–274.
Wang H, Huang Z, Xia L, Feng Q, Erdjument-Bromage H, Strahl B et al. (2001). Methylation of histone H4 at arginine 3 facilitating transcriptional activation by nuclear hormone receptor. Science 293: 853–857.
Wang Z, Rose DW, Hermanson O, Liu F, Herman T, Wu W et al. (2000). Regulation of somatic growth by the p160 coactivator p/CIP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 13549–13554.
Werbajh S, Nojek I, Lanz R, Costas MA . (2000). RAC-3 is a NF-κB coactivator. FEBS Lett 485: 195–199.
Xu J, Qingtian L . (2003). Review of the in vivo functions of the p160 steroid receptor coactivator family. Mol Endocrinol 17: 1681–1692.
Xu J, Liao L, Ning G, Yoshida-Komiya H, Deng C, O'Malley BW . (2000). The steroid receptor coactivator SRC-3 (p/CIP/RAC3/AIB1/ACTR/TRAM-1) is required for normal growth, puberty, female reproductive function, and mammary gland development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 6379–6384.
Yan J, Tsai SY, Tsai MJ . (2006). SRC-3/AIB1: transcriptional coactivator in oncogenesis. Acta Pharmacol Sin 27: 387–394.
Zhang L, Himi T, Morita I, Murota S . (2001). Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt or mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling sensitizes endothelial cells to TNF-alpha cytotoxicity. Cell Death Differ 8: 528–536.
Zhou G, Hashimoto Y, Kwak I, Tsai SY, Tsai M-J . (2003). Role of the steroid receptor coactivator SRC-3 in cell growth. Mol Cell Biol 23: 7742–7755.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Roberto Rosato and Dr Steven Grant for comments about the manuscript and Dr Fernanda Ceriani for help and support. This work has been supported by grants from the Argentine National Research Council (CONICET), Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica and Fundación Antorchas, Argentina and the NIH Fogarty International Center Grant R03TW007162-01A2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colo, G., Rubio, M., Nojek, I. et al. The p160 nuclear receptor co-activator RAC3 exerts an anti-apoptotic role through a cytoplasmatic action. Oncogene 27, 2430–2444 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210900
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210900
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Functional relationship between CFTR and RAC3 expression for maintaining cancer cell stemness in human colorectal cancer
Cellular Oncology (2021)
-
Role of RAC3 coactivator in the adipocyte differentiation
Cell Death Discovery (2018)
-
RAC3 influences the chemoresistance of colon cancer cells through autophagy and apoptosis inhibition
Cancer Cell International (2017)
-
RAC3 more than a nuclear receptor coactivator: a key inhibitor of senescence that is downregulated in aging
Cell Death & Disease (2015)
-
Overexpression of AIB1 correlates inversely with E-cadherin expression in pancreatic adenocarcinoma and may promote lymph node metastasis
International Journal of Clinical Oncology (2014)