Abstract
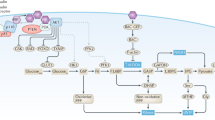
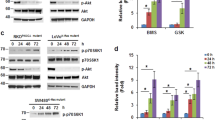
The insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) is crucial for growth and survival of malignant cells. Experience in targeting IGF-1R in cancer models has shown that strategies promoting downregulation of the receptor are much more efficient in inducing apoptosis than those inhibiting the IGF-1R activity. Recently, we found that the cyclolignan picropodophyllin (PPP) inhibits phosphorylation of IGF-1R and activation of downstream signaling without interfering with the highly homologous insulin receptor (IR). Furthermore, PPP treatment caused strong regression of tumor grafts and prolonged survival of animals with systemic tumor disease. Here we demonstrate that PPP also downregulates the IGF-1R, whereas the IR and several other receptors were not affected. PPP-induced IGF-1R downregulation required expression of the MDM2 E3 ligase, which recently was found to ubiquitinate and cause degradation of the IGF-1R. In addition knockdown of β-arrestin1, the adaptor molecule known to bridges MDM2 and IGF-1R, prevented downregulation of the receptor and significantly decreased PPP-induced cell death. All together these data suggest that PPP downregulates IGF-1R by interfering with the action of β-arrestin1/MDM2 as well as the achieved receptor downregulation contributes to the apoptotic effect of PPP.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
07 December 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02556-8
References
Adams TE, Epa VC, Garrett TP, Ward CW . (2000). Structure and function of the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor. Cell Mol Life Sci 57: 1050–1093.
All-Ericsson C, Girnita L, Seregard S, Bartolazzi A, Jager MJ, Larsson O . (2002). Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in uveal melanoma: a predictor for metastatic disease and a potential therapeutic target. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43: 1–8.
Baserga R . (1995). The insulin-like growth factor I receptor: a key to tumor growth? Cancer Res 55: 249–252.
Baserga R . (2000). The contradictions of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Oncogene 19: 5574–5581.
Baserga R . (2004). Targeting the IGF-1 receptor: from rags to riches. Eur J Cancer 40: 2013–2015.
Baserga R . (2005). The insulin-like growth factor-I receptor as a target for cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets 9: 753–768.
Baserga R, Hongo A, Rubini M, Prisco M, Valentinis B . (1997). The IGF-I receptor in cell growth, transformation and apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1332: F105–F126.
Buchardt O, Jensen RB, Hansen HF, Nielsen PE, Andersen D, Chinoin I . (1986). Thermal chemistry of podophyllotoxin in ethanol and a comparison of the cytostatic activity of the thermolysis products. J Pharm Sci 75: 1076–1080.
Catrina SB, Lewitt M, Massambu C, Dricu A, Grunler J, Axelson M et al. (2005). Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor activity is essential for Kaposi's sarcoma growth and survival. Br J Cancer 92: 1467–1474.
Colon E, Zaman F, Axelson M, Larsson O, Carlsson-Skwirut C, Svechnikov KV et al. (2007). Insulin-like growth factor-I is an important antiapoptotic factor for rat Leydig cells during postnatal development. Endocrinology 148: 128–139.
Conti L, Regis G, Longo A, Bernabei P, Chiarle R, Giovarelli M et al. (2007). In the absence of IGF-1 signaling, IFN-{gamma} suppresses human malignant T cell growth. Blood 109: 2496–2504.
Ghosh RN, Gelman DL, Maxfield FR . (1994). Quantification of low density lipoprotein and transferrin endocytic sorting HEp2 cells using confocal microscopy. J Cell Sci 107 (Pt 8): 2177–2189.
Girnita A, All-Ericsson C, Economou MA, Astrom K, Axelson M, Seregard S et al. (2006). The insulin-like growth factor-I receptor inhibitor picropodophyllin causes tumor regression and attenuates mechanisms involved in invasion of uveal melanoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 12: 1383–1391.
Girnita A, Girnita L, del Prete F, Bartolazzi A, Larsson O, Axelson M . (2004). Cyclolignans as inhibitors of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and malignant cell growth. Cancer Res 64: 236–242.
Girnita L, Girnita A, Brodin B, Xie Y, Nilsson G, Dricu A et al. (2000a). Increased expression of insulin-like growth factor I receptor in malignant cells expressing aberrant p53: functional impact. Cancer Res 60: 5278–5283.
Girnita L, Girnita A, Larsson O . (2003). Mdm2-dependent ubiquitination and degradation of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 8247–8252.
Girnita L, Shenoy SK, Sehat B, Vasilcanu R, Girnita A, Lefkowitz RJ et al. (2005). {beta}-Arrestin is crucial for ubiquitination and down-regulation of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor by acting as adaptor for the MDM2 E3 ligase. J Biol Chem 280: 24412–24419.
Girnita L, Shenoy SK, Sehat B, Vasilcanu R, Vasilcanu D, Girnita A et al. (2007). beta-Arrestin and Mdm2 mediate IGF-1 receptor-stimulated ERK activation and cell cycle progression. J Biol Chem 282: 11329–11338.
Girnita L, Wang M, Xie Y, Nilsson G, Dricu A, Wejde J et al. (2000b). Inhibition of N-linked glycosylation down-regulates insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor at the cell surface and kills Ewing's sarcoma cells: therapeutic implications. Anticancer Drug Des 15: 67–72.
Larsson O, Girnita A, Girnita L . (2005). Role of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor signalling in cancer. Br J Cancer 92: 2097–2101.
Lee CT, Wu S, Gabrilovich D, Chen H, Nadaf-Rahrov S, Ciernik IF et al. (1996). Antitumor effects of an adenovirus expressing antisense insulin-like growth factor I receptor on human lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 56: 3038–3041.
LeRoith D, Roberts Jr CT . (2003). The insulin-like growth factor system and cancer. Cancer Lett 195: 127–137.
Loughran G, Huigsloot M, Kiely PA, Smith LM, Floyd S, Ayllon V et al. (2005). Gene expression profiles in cells transformed by overexpression of the IGF-I receptor. Oncogene 24: 6185–6193.
McGraw TE, Maxfield FR . (1990). Human transferrin receptor internalization is partially dependent upon an aromatic amino acid on the cytoplasmic domain. Cell Regul 1: 369–377.
Menu E, Jernberg-Wiklund H, De Raeve H, De Leenheer E, Coulton L, Gallagher O et al. (2007). Targeting the IGF-1R using picropodophyllin in the therapeutical 5T2MM mouse model of multiple myeloma: beneficial effects on tumor growth, angiogenesis, bone disease and survival. Int J Cancer 121: 1857–1861.
Menu E, Jernberg-Wiklund H, Stromberg T, De Raeve H, Girnita L, Larsson O et al. (2006). Inhibiting the IGF-1 receptor tyrosine kinase with the cyclolignan PPP: an in vitro and in vivo study in the 5T33MM mouse model. Blood 107: 655–660.
Moffat J, Grueneberg DA, Yang X, Kim SY, Kloepfer AM, Hinkle G et al. (2006). A lentiviral RNAi library for human and mouse genes applied to an arrayed viral high-content screen. Cell 124: 1283–1298.
Razuvaev A, Henderson B, Girnita L, Larsson O, Axelson M, Hedin U et al. (2007). The cyclolignan picropodophyllin attenuates intimal hyperplasia after rat carotid balloon injury by blocking insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor signaling. J Vasc Surg 46: 108–115.
Resnicoff M, Coppola D, Sell C, Rubin R, Ferrone S, Baserga R . (1994). Growth inhibition of human melanoma cells in nude mice by antisense strategies to the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor. Cancer Res 54: 4848–4850.
Rubini M, Hongo A, D'Ambrosio C, Baserga R . (1997). The IGF-I receptor in mitogenesis and transformation of mouse embryo cells: role of receptor number. Exp Cell Res 230: 284–292.
Samani AA, Yakar S, Leroith D, Brodt P . (2007). The role of the IGF system in cancer growth and metastasis: overview and recent insights. Endocr Rev 28: 20–47.
Sehat B, Andersson S, Vasilcanu R, Girnita L, Larsson O . (2007). Role of ubiquitination in IGF-1 receptor signaling and degradation. PLoS ONE 2: E340.
Shapiro DN, Jones BG, Shapiro LH, Dias P, Houghton PJ . (1994). Antisense-mediated reduction in insulin-like growth factor-I receptor expression suppresses the malignant phenotype of a human alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. J Clin Invest 94: 1235–1242.
Shenoy SK, McDonald PH, Kohout TA, Lefkowitz RJ . (2001). Regulation of receptor fate by ubiquitination of activated beta 2-adrenergic receptor and beta-arrestin. Science 294: 1307–1313.
Stromberg T, Ekman S, Girnita L, Dimberg LY, Larsson O, Axelson M et al. (2006). IGF-1 receptor tyrosine kinase inhibition by the cyclolignan PPP induces G2/M-phase accumulation and apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells. Blood 107: 669–678.
Tomizawa M, Saisho H . (2006). Signaling pathway of insulin-like growth factor-II as a target of molecular therapy for hepatoblastoma. World J Gastroenterol 12: 6531–6535.
Ulfarsson E, Karstrom A, Yin S, Girnita A, Vasilcanu D, Thoren M et al. (2005). Expression and growth dependency of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor in craniopharyngioma cells: a novel therapeutic approach. Clin Cancer Res 11: 4674–4680.
Vasilcanu D, Girnita A, Girnita L, Vasilcanu R, Axelson M, Larsson O . (2004). The cyclolignan PPP induces activation loop-specific inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor. Link to the phosphatidyl inositol-3 kinase/Akt apoptotic pathway. Oncogene 23: 7854–7862.
Vasilcanu D, Weng WH, Girnita A, Lui WO, Vasilcanu R, Axelson M et al. (2006). The insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor inhibitor PPP produces only very limited resistance in tumor cells exposed to long-term selection. Oncogene 25: 3186–3195.
Vecchione A, Marchese A, Henry P, Rotin D, Morrione A . (2003). The Grb10/Nedd4 complex regulates ligand-induced ubiquitination and stability of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor. Mol Cell Biol 23: 3363–3372.
Xie Y, Skytting B, Nilsson G, Brodin B, Larsson O . (1999). Expression of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in synovial sarcoma: association with an aggressive phenotype. Cancer Res 59: 3588–3591.
Yu H, Rohan T . (2000). Role of the insulin-like growth factor family in cancer development and progression. J Natl Cancer Inst 92: 1472–1489.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the Swedish Cancer Society, the Cancer Society in Stockholm, the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Children Cancer Society, Ingabritt and Arne Lundberg's research foundation, the King Gustaf V's research foundation, Alex and Eva Wallström's foundation and the Karolinska Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vasilcanu, R., Vasilcanu, D., Rosengren, L. et al. Picropodophyllin induces downregulation of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor: potential mechanistic involvement of Mdm2 and β-arrestin1. Oncogene 27, 1629–1638 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210797
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210797
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
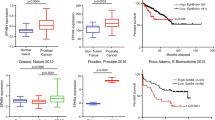
IGF-1R is a molecular determinant for response to p53 reactivation therapy in conjunctival melanoma
Oncogene (2022)
-
Regulation of Hippo-YAP signaling by insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in the tumorigenesis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2020)
-
The association of TP53 mutations with the resistance of colorectal carcinoma to the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor inhibitor picropodophyllin
BMC Cancer (2013)
-
Enhancement of doxorubicin cytotoxicity of human cancer cells by tyrosine kinase inhibition of insulin receptor and type I IGF receptor
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2012)
-
Targeting insulin-like growth factor axis in hepatocellular carcinoma
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2011)