Abstract
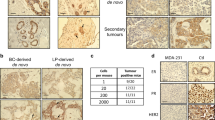
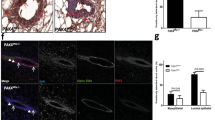
Aurora-A/STK15/BTAK, which encodes a centrosome-associated kinase, is amplified and overexpressed in multiple types of human tumors, including breast cancer. However, the causal relationship between overexpression of Aurora-A and tumorigenesis has not been fully established due to contradictory data obtained from different experimental systems. To investigate this, we generated a mouse strain that carries an MMTV-Aurora-A transgene. We showed that all the MMTV-Aurora-A mice displayed enhanced branch morphogenesis in the mammary gland and about 40% developed mammary tumors at 20 months of age. The tumor incidence was significantly increased in a p53+/− mutation background with about 70% MMTV-Aurora-A;p53+/− animals developed tumors at 18 months of age. Of note, overexpression of Aurora-A led to genetic instability, characterized by centrosome amplification, chromosome tetraploidization and premature sister chromatid segregation, at stages prior to tumor formation. Most notably, the severe chromosomal abnormality did not cause cell death owing to the activation of AKT pathway, including elevated levels of phosphorylated AKT and mammalian target of rapamycin, and nuclear accumulation of cyclin D1, which enabled continuous proliferation of the tetraploid cells. These data establish Aurora-A as an oncogene that causes malignant transformation through inducing genetic instability and activating oncogenic pathways such as AKT and its downstream signaling.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amon A . (1999). Curr Opin Genet Dev 9: 69–75.
Anand S, Penrhyn-Lowe S, Venkitaraman AR . (2003). Cancer Cell 3: 51–62.
Andreassen PR, Lohez OD, Margolis RL . (2003). Mutat Res 532: 245–253.
Aust DE, Muders M, Kohler A, Schmidt M, Diebold J, Muller C et al. (2004). Scand J Gastroenterol 39: 766–772.
Berdnik D, Knoblich JA . (2002). Curr Biol 12: 640–647.
Bischoff JR, Plowman GD . (1999). Trends Cell Biol 9: 454–459.
Bischoff JR, Anderson L, Zhu Y, Mossie K, Ng L, Souza B et al. (1998). EMBO J 17: 3052–3065.
Chiba S, Okuda M, Mussman JG, Fukasawa K . (2000). Exp Cell Res 258: 310–321.
Colditz GA . (1998). J Natl Cancer Inst 90: 814–823.
Crane R, Gadea B, Littlepage L, Wu H, Ruderman JV . (2004). Biol Cell 96: 215–229.
Deng CX, Xu X . (2004). Methods Mol Biol 280: 185–200.
Diehl JA, Cheng M, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ . (1998). Genes Dev 12: 3499–3511.
Downward J . (1998). Curr Opin Cell Biol 10: 262–267.
Ducat D, Zheng Y . (2004). Exp Cell Res 301: 60–67.
Fang G . (2002). Mol Biol Cell 13: 755–766.
Gadducci A, Biglia N, Sismondi P, Genazzani AR . (2005). Gynecol Endocrinol 20: 343–360.
Giet R, McLean D, Descamps S, Lee MJ, Raff JW, Prigent C et al. (2002). J Cell Biol 156: 437–451.
Giet R, Petretti C, Prigent C . (2005). Trends Cell Biol 15: 241–250.
Gotoh J, Obata M, Yoshie M, Kasai S, Ogawa K . (2003). Carcinogenesis 24: 435–442.
Hannak E, Kirkham M, Hyman AA, Oegema K . (2001). J Cell Biol 155: 1109–1116.
Hirota T, Kunitoku N, Sasayama T, Marumoto T, Zhang D, Nitta M et al. (2003). Cell 114: 585–598.
Hu W, Kavanagh JJ, Deaver M, Johnston DA, Freedman RS, Verschraegen CF et al. (2005). Oncol Res 15: 49–57.
Kamada K, Yamada Y, Hirao T, Fujimoto H, Takahama Y, Ueno M et al. (2004). Oncol Rep 12: 593–599.
Katayama H, Brinkley WR, Sen S . (2003). Cancer Metastasis Rev 22: 451–464.
Katayama H, Sasai K, Kawai H, Yuan ZM, Bondaruk J, Suzuki F et al. (2004). Nat Genet 36: 55–62.
Kufer TA, Nigg EA, Sillje HH . (2003). Chromosoma 112: 159–163.
Liu Q, Kaneko S, Yang L, Feldman RI, Nicosia SV, Chen J et al. (2004). J Biol Chem 279: 52175–52182.
Marumoto T, Hirota T, Morisaki T, Kunitoku N, Zhang D, Ichikawa Y et al. (2002). Genes Cells 7: 1173–1182.
Meraldi P, Honda R, Nigg EA . (2002). EMBO J 21: 483–492.
Meraldi P, Honda R, Nigg EA . (2004). Curr Opin Genet Dev 14: 29–36.
Michel LS, Liberal V, Chatterjee A, Kirchwegger R, Pasche B, Gerald W et al. (2001). Nature 409: 355–359.
Mita MM, Mita A, Rowinsky EK . (2003). Clin Breast Cancer 4: 126–137.
Morgan SE, Kastan MB . (1997). Adv Cancer Res 71: 1–25.
Oikawa T, Okuda M, Ma Z, Goorha R, Tsujimoto H, Inokuma H et al. (2005). Mol Cell Biol 25: 4046–4061.
Ouchi M, Fujiuchi N, Sasai K, Katayama H, Minamishima YA, Ongusaha PP et al. (2004). J Biol Chem 279: 19643–19648.
Prall OW, Rogan EM, Sutherland RL . (1998). J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 65: 169–174.
Satyamoorthy K, Li G, Vaidya B, Patel D, Herlyn M . (2001). Cancer Res 61: 7318–7324.
Sen S, Zhou H, Zhang RD, Yoon DS, Vakar-Lopez F, Ito S et al. (2002). J Natl Cancer Inst 94: 1320–1329.
Shah A, Swain WA, Richardson D, Edwards J, Stewart DJ, Richardson CM et al. (2005). Clin Cancer Res 11: 2930–2936.
Stenoien DL, Sen S, Mancini MA, Brinkley BR . (2003). Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 55: 134–146.
Sudakin V, Chan GK, Yen TJ . (2001). J Cell Biol 154: 925–936.
Tanaka T, Kimura M, Matsunaga K, Fukada D, Mori H, Okano Y . (1999). Cancer Res 59: 2041–2044.
Tanaka E, Hashimoto Y, Ito T, Okumura T, Kan T, Watanabe G et al. (2005). Clin Cancer Res 11: 1827–1834.
Tang Z, Bharadwaj R, Li B, Yu H . (2001). Dev Cell 1: 227–237.
Wang RH, Yu H, Deng CX . (2004). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 17108–17113.
Xu X, Wagner KU, Larson D, Weaver Z, Li C, Ried T et al. (1999a). Mol Cell 3: 389–395.
Xu X, Weaver Z, Linke SP, Li C, Gotay J, Wang XW et al. (1999b). Nat Genet 22: 37–43.
Xu B, Kim S, Kastan MB . (2001). Mol Cell Biol 21: 3445–3450.
Yoon DS, Wersto RP, Zhou W, Chrest FJ, Garrett ES, Kwon TK et al. (2002). Am J Pathol 161: 391–397.
Zhang D, Hirota T, Marumoto T, Shimizu M, Kunitoku N, Sasayama T et al. (2004). Oncogene 23: 8720–8730.
Zhou H, Kuang J, Zhong L, Kuo WL, Gray JW, Sahin A et al. (1998). Nat Genet 20: 189–193.
Acknowledgements
We thank members of Deng laboratory for critically reading this manuscript and discussion of this project. This research was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institutes of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, NIH, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Zhou, YX., Qiao, W. et al. Overexpression of aurora kinase A in mouse mammary epithelium induces genetic instability preceding mammary tumor formation. Oncogene 25, 7148–7158 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209707
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209707
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Removing the association of random gene sets and survival time in cancers with positive random bias using fixed-point gene set
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Bora phosphorylation substitutes in trans for T-loop phosphorylation in Aurora A to promote mitotic entry
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Reciprocal interaction between SIRT6 and APC/C regulates genomic stability
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
PROTAC-mediated degradation reveals a non-catalytic function of AURORA-A kinase
Nature Chemical Biology (2020)
-
Characterization and risk association of polymorphisms in Aurora kinases A, B and C with genetic susceptibility to gastric cancer development
BMC Cancer (2019)