Abstract
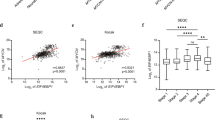
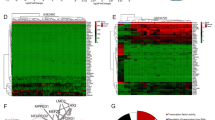
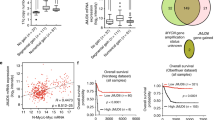
Differential screening of the genes obtained from cDNA libraries of primary neuroblastomas (NBLs) between the favorable and unfavorable subsets has identified a novel gene BCH motif-containing molecule at the carboxyl terminal region 1 (BMCC1). Its 350 kDa protein product possessed a Bcl2-/adenovirus E1B nineteen kDa-interacting protein 2 (BNIP2) and Cdc42GAP homology domain in the COOH-terminus in addition to P-loop and a coiled-coil region near the NH2-terminus. High levels of BMCC1 expression were detected in the human nervous system as well as spinal cord, brain and dorsal root ganglion in mouse embryo. The immunohistochemical study revealed that BMCC1 was positively stained in the cytoplasm of favorable NBL cells but not in unfavorable ones with MYCN amplification. The quantitative real-time reverse transcription–PCR using 98 primary NBLs showed that high expression of BMCC1 was a significant indicator of favorable NBL. In primary culture of newborn mice superior cervical ganglion (SCG) neurons, mBMCC1 expression was downregulated after nerve growth factor (NGF)-induced differentiation, and upregulated during the NGF-depletion-induced apoptosis. Furthermore, the proapoptotic function of BMCC1 was also suggested by increased expression in CHP134 NBL cells undergoing apoptosis after treatment with retinoic acid, and by an enhanced apoptosis after depletion of NGF in the SCG neurons obtained from newborn mice transgenic with BMCC1 in primary culture. Thus, BMCC1 is a new member of prognostic factors for NBL and may play an important role in regulating differentiation, survival and aggressiveness of the tumor cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagrodia S, Derijard B, Davis RJ, Cerione RA . (1995). J Biol Chem 270: 27995–27998.
Bazenet CE, Mota MA, Rubin LL . (1998). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 3984–3989.
Boyd JM, Malstrom S, Subramanian T, Venkatesh LK, Schaeper U, Elangovan B et al. (1994). Cell 79: 341–351.
Brodeur GM, Pritchard J, Berthold F, Carlsen NL, Castel V, Castelberry RP et al. (1993). J Clin Oncol 11: 1466–1477.
Brodeur GM, Seeger RC, Schwab M, Varmus HE, Bishop JM . (1984). Science 224: 1121–1124.
Burge C, Karlin S . (1997). J Mol Biol 268: 78–94.
Burge CB, Karlin S . (1998). Curr Opin Struct Biol 8: 346–354.
Cahill MA, Peter ME, Kischkel FC, Chinnaiyan AM, Dixit VM, Krammer PH et al. (1996). Oncogene 13: 2087–2096.
Caron H . (1995). Med Pediatr Oncol 24: 215–221.
Chuang TH, Hahn KM, Lee JD, Danley DE, Bokoch GM . (1997). Mol Biol Cell 8: 1687–1698.
Coso OA, Chiariello M, Yu JC, Teramoto H, Crespo P, Xu N et al. (1995). Cell 81: 1137–1146.
Evans AE, Gerson J, Schnaufer L . (1976). Natl Cancer Inst Monogr 44: 49–54.
Favrot MC, Combaret V, Lasset C . (1993). N Engl J Med 329: 1965.
Garcia I, Martinou I, Tsujimoto Y, Martinou JC . (1992). Science 258: 302–304.
Garnier M, Di Lorenzo D, Albertini A, Maggi A . (1997). J Neurosci 17: 4591–4599.
Gjoerup O, Lukas J, Bartek J, Willumsen BM . (1998). J Biol Chem 273: 18812–18818.
Gooding LR, Aquino L, Duerksen-Hughes PJ, Day D, Horton TM, Yei SP et al. (1991). J Virol 65: 3083–3094.
Hashimoto S, Ishii A, Yonehara S . (1991). Int Immunol 3: 343–351.
Hockenbery D, Nunez G, Milliman C, Schreiber RD, Korsmeyer SJ . (1990). Nature 348: 334–336.
Horton P, Nakai K . (1996). Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol 4: 109–115.
Islam A, Kageyama H, Takada N, Kawamoto T, Takayasu H, Isogai E et al. (2000). Oncogene 19: 617–623.
Juo P, Kuo CJ, Reynolds SE, Konz RF, Raingeaud J, Davis RJ et al. (1997). Mol Cell Biol 17: 24–35.
Kaneko M, Nishihira H, Mugishima H, Ohnuma N, Nakada K, Kawa K et al. (1998). Med Pediatr Oncol 31: 1–7.
Kozak M . (1987). Nucl Acids Res 15: 8125–8148.
Larisch S, Yi Y, Lotan R, Kerner H, Eimerl S, Tony Parks W et al. (2000). Nat Cell Biol 2: 915–921.
Lee VM, Shelanski ML, Greene LA . (1980). Neuroscience 5: 2239–2245.
Lenczowski JM, Dominguez L, Eder AM, King LB, Zacharchuk CM, Ashwell JD . (1997). Mol Cell Biol 17: 170–181.
Low BC, Seow KT, Guy GR . (2000). J Biol Chem 275: 37742–37751.
Moasser MM, Khoo KS, Maerz WJ, Zelenetz A, Dmitrovsky E . (1996). Differentiation 60: 251–257.
Nagai M, Ichimiya S, Ozaki T, Seki N, Mihara M, Furuta S et al. (2000). Int J Oncol 16: 907–916.
Nakagawara A . (1998). Hum Cell 11: 115–124.
Nakagawara A . (2001). Cancer Lett 169: 107–114.
Nakagawara A, Arima-Nakagawara M, Scavarda NJ, Azar CG, Cantor AB, Brodeur GM . (1993). N Engl J Med 328: 847–854.
Nakagawara A, Azar CG, Scavarda NJ, Brodeur GM . (1994). Mol Cell Biol 14: 759–767.
Nakagawara A, Milbrandt J, Muramatsu T, Deuel TF, Zhao H, Cnaan A et al. (1995). Cancer Res 55: 1792–1797.
Nakamura Y, Ozaki T, Ichimiya S, Nakagawara A, Sakiyama S . (1998). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 243: 722–726.
Ohira M, Morohashi A, Inuzuka H, Shishikura T, Kawamoto T, Kageyama H et al. (2003a). Oncogene 22: 5525–5536.
Ohira M, Morohashi A, Nakamura Y, Isogai E, Furuya K, Hamano S et al. (2003b). Cancer Lett 197: 63–68.
Olson MF, Ashworth A, Hall A . (1995). Science 269: 1270–1272.
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL, Korsmeyer SJ . (1993). Cell 74: 609–619.
Seimiya H, Mashima T, Toho M, Tsuruo T . (1997). J Biol Chem 272: 4631–4636.
Shimada H, Chatten J, Newton Jr WA, Sachs N, Hamoudi AB, Chiba T et al. (1984). J Natl Cancer Inst 73: 405–416.
Solovyev VV, Salamov AA . (1999). Nucl Acids Res 27: 248–250.
Subramanian T, Boyd JM, Chinnadurai G . (1995). Oncogene 11: 2403–2409.
Takihara Y, Tomotsune D, Shirai M, Katoh-Fukui Y, Nishii K, Motaleb MA et al. (1997). Development 124: 3673–3682.
Tanaka T, Sugimoto T, Sawada T . (1998). Cancer 83: 1626–1633.
Vegeto E, Pollio G, Pellicciari C, Maggi A . (1999). FASEB J 13: 793–803.
White E, Sabbatini P, Debbas M, Wold WS, Kusher DI, Gooding LR . (1992). Mol Cell Biol 12: 2570–2580.
Whitfield J, Neame SJ, Paquet L, Bernard O, Ham J . (2001). Neuron 29: 629–643.
Yamamoto M, Marui N, Sakai T, Morii N, Kozaki S, Ikai K et al. (1993). Oncogene 8: 1449–1455.
Yuan J, Horvitz HR . (1992). Development 116: 309–320.
Zhang B, Zhang Y, Collins CC, Johnson DI, Zheng Y . (1999). J Biol Chem 274: 2609–2612.
Zhang B, Zheng Y . (1998). J Biol Chem 273: 25728–25733.
Zhang S, Han J, Sells MA, Chernoff J, Knaus UG, Ulevitch RJ et al. (1995). J Biol Chem 270: 23934–23936.
Zhou YT, Soh UJ, Shang X, Guy GR, Low BC . (2002). J Biol Chem 277: 7483–7492.
Zou H, Henzel WJ, Liu X, Lutschg A, Wang X . (1997). Cell 90: 405–413.
Acknowledgements
We thank Shigeyuki Furuta, Shiho Hamano, Hiroyuki Inuzuka, Aiko Morohashi for technical assistance, Masayuki Fukumura, Toshihide Kanamori and Mika Kimura for helping full-length cDNA cloning, and Shigeru Sakiyama for encouragement. This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for the 2nd Term Comprehensive 10-Year Strategy for Cancer Control from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan (AN), and by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) (AN) and for Scientific Research on Priority Areas (2) ‘Medical Genome Science’ (MO, EI, AN) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, and by a fund from Hisamitsu Pharmaceutical Co. Inc. (AN). We also thank following hospitals and departments for providing surgical samples: First Department of Surgery, Hokkaido University School of Medicine; Department of Pediatrics, National Sapporo Hospital; Department of Pediatric Surgery, Tohoku University School of Medicine; Department of Surgery, Gunma Children's Medical Center; Department of Pediatrics, Pediatric Surgery and General Surgery, Jichi Medical University; Department of Hematology and Oncology, Saitama Children's Medical Center; Department of Pediatrics, Juntendo University School of Medicine; Department of Surgery, Kiyose Metropolitan Children's Hospital; Department of Surgery and Pathology, Chiba Children's Hospital; Department of Pediatric Surgery, Chiba University School of Medicine; Department of Pediatric Surgery, Kimitsu Central Hospital; Department of Pediatric Surgery, Niigata University School of Medicine; Department of Pediatrics and Pediatric Surgery, Aichi Medical University; Department of Pediatrics, Kyoto Prefectural Medical University; Tumor Board, Hyogo Children's Hospital; Department of Pediatrics and Pediatric Surgery, Kagoshima University School of Medicine; Department of Pediatric Surgery, Showa University School of Medicine; Department of Pediatrics, Oita University School of Medicine; Department of Pediatric Surgery, Ohta General Hospital; Department of Pediatrics, Ichinomiya City Hospital; Department of Pediatric Surgery, Osaka City General Hospital; Department of Pediatrics, Nihon University School of Medicine Itabashi Hospital; Department of Pediatric Surgery, University of Tsukuba School of Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Machida, T., Fujita, T., Ooo, M. et al. Increased expression of proapoptotic BMCC1, a novel gene with the BNIP2 and Cdc42GAP homology (BCH) domain, is associated with favorable prognosis in human neuroblastomas. Oncogene 25, 1931–1942 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209225
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209225
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Prune homolog 2 with BCH domain (PRUNE2) gene expression is associated with feed efficiency-related traits in Nelore steers
Mammalian Genome (2022)
-
Programmed expression of pro-apoptotic BMCC1 during apoptosis, triggered by DNA damage in neuroblastoma cells
BMC Cancer (2019)
-
BMCC1, which is an interacting partner of BCL2, attenuates AKT activity, accompanied by apoptosis
Cell Death & Disease (2015)
-
High expression of MACC1 predicts poor prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma
Tumor Biology (2014)
-
Cancer-Related PRUNE2 Protein Is Associated with Nucleotides and Is Highly Expressed in Mature Nerve Tissues
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2011)