Abstract
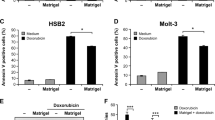
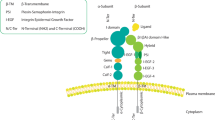
Integrin-mediated adhesion to extracellular matrix proteins confers resistance to radiation- or drug-induced genotoxic injury. To analyse the underlying mechanisms specific for β1-integrins, wild-type β1A-integrin-expressing GD25β1A cells were compared to GD25β1B cells, which express signaling-incompetent β1B variants. Cells grown on fibronectin, collagen-III, β1-integrin-IgG or poly-l-lysine were exposed to 0–6 Gy X-rays in presence or depletion of growth factors and phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K) inhibitors (LY294002, wortmannin). In order to test the relevance of these findings in tumor cells, human A-172 glioma cells were examined under the same conditions after siRNA-mediated silencing of β1-integrins. We found that β1A-integrin-mediated adhesion to fibronectin, collagen-III or β1-IgG was essential for cell survival after radiation-induced genotoxic injury. Mediated by PI3K, pro-survival β1A-integrin/Akt signaling was critically involved in this process. Additionally, the β1-integrin downstream targets p130Cas and paxillin-impaired survival-regulating PI3K-dependent JNK. In A-172 glioma cells, β1-integrin knockdown and PI3K inhibition confirmed the central role of β1-integrins in Akt- and p130Cas/paxillin-mediated prosurvival signaling. These findings suggest β1-integrins as critical regulators of cell survival after radiation-induced genotoxic injury. Elucidation of the molecular circuitry of prosurvival β1-integrin-mediated signaling in tumor cells may promote the development of innovative molecular-targeted therapeutic antitumor strategies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ECM:
-
extracellular matrix
- FAK:
-
focal adhesion kinase
- ILK:
-
integrin-linked kinase
- p130Cas:
-
Crk-associated substrate
- Akt:
-
protein kinase B/Akt
- PI3K:
-
phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- JNK:
-
c-Jun N2-terminal kinase
- FN:
-
fibronectin
- ColIII:
-
collagen-III
- β1-IgG:
-
anti-β1-integrin-IgG
- PLL:
-
poly-l-lysine
References
Almeida EA, Hie D, Han Q, Hauck CR, Jin F, Kawakatsu H et al. (2000). J Cell Biol 149: 741–754.
Armulik A, Svineng G, Wennerberg K, Fässler R, Johansson S . (2000). Exp Cell Res 254: 55–63.
Armulik A . (2002). Front Biosci 7: d219–d227.
Barcellos-Hoff MH . (2001). J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 6: 213–221.
Beinke C, van Beuningen D, Cordes N . (2003). Int J Radiat Biol 79: 721–731.
Brakebusch C, Fässler R . (2003). EMBO J 22: 2324–2333.
Cook JA, Gius D, Wink DA, Krishna MC, Russo A, Mitchell JB . (2004). Semin Radiat Oncol 14: 259–266.
Cordes N . (2004). Cancer Res 64: 5683–5692.
Cordes N, van Beuningen D . (2003). Brit J Cancer 88: 1470–1479.
Cordes N, Hansmeier B, Beinke C, Meineke V, van Beuningen D . (2003). Brit J Cancer 89: 2122–2132.
Cordes N, Meineke V . (2003). Strahlenther Onkol 179: 337–344.
Damiano JS, Cress AE, Hazlehurst LA, Shtil AA, Dalton WS . (1999). Blood 93: 1658–1667.
Dedhar S, Hannigan GE . (1997). Curr Opin Cell Biol 8: 657–669.
Dent P, Yacoub A, Fisher PB, Hagan MP, Grant S . (2003). Oncogene 22: 5885–5896.
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Weber K, Tuchl T . (2002). Methods 26: 199–213.
Fässler R, Pfaff M, Murphy J, Noegel AA, Johansson S, Timpl R et al. (1995). J Cell Biol 128: 979–988.
Fornaro M, Steger CA, Bennett AM, Wu JJ, Languino LR . (2000). Mol Biol Cell 11: 2235–2249.
Giancotti FG, Ruoslahti E . (1999). Science 285: 1028–1032.
Hanks SK, Polte TR . (1997). Bioessays 19: 137–145.
Hanks SK, Ryzhova L, Shin NY, Brabek J . (2003). Front Biosci 8: d982–d996.
Hannigan GE, Leung-Hagesteijn C, Fitz-Gibbon L, Coppolino MG, Radeva G, Filmus J et al. (1996). Nature 379: 91–96.
Hynes RO . (2002). Cell 110: 673–687.
Kasahara T, Koguchi E, Funakoshi M, Aizu-Yokota E, Sonoda Y . (2002). Antioxid Redox Signal 4: 491–499.
Khwaja A, Rodriguez-Viciana P, Wennström S, Warne HP, Downward J . (1997). EMBO J 16: 2783–2793.
Kinbara K, Goldfinger LE, Hansen M, Chou FL, Ginsberg MH . (2003). Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4: 767–776.
King WG, Mattaliano MD, Chan TO, Tsichlis PN, Brugge JS . (1997). Mol Cell Biol 17: 4406–4418.
Martin SS, Vuori K . (2004). Biochim Biophys Acta 1692: 145–157.
Oguey D, George PW, Ruegg C . (2000). Gene Ther 7: 1292–1303.
Owen JD, Ruest PJ, Fry DW, Hanks SK . (1999). Mol Cell Biol 19: 4806–4818.
Park CC, Bissell MJ, Barcellos-Hoff MH . (2000). Mol Med Today 6: 324–329.
Parsons JT . (2003). J Cell Sci 116: 1409–1416.
Pfaff M, Liu S, Erle DJ, Ginsberg MH . (1998). J Biol Chem 273: 6104–6109.
Sakai T, Zhang Q, Fässler R, Mosher DF . (1998). J Cell Biol 141: 527–538.
Schaller MD, Hildebrand JD, Parsons JT . (1999). Mol Biol Cell 10: 3489–3505.
Schaller MD . (2001). Biochem Biophys Acta 1540: 1–21.
Schwartz MA . (1997). J Cell Biol 139: 575–578.
Schwartz MA, Assoian RK . (2001). J Cell Sci 114: 2553–2560.
Sethi T, Rintoul RC, Moore SM, MacKinnon AC, Salter D, Choo C et al. (1999). Nat Med 5: 662–668.
Shen Y, Schaller MD . (1999). Mol Biol Cell 10: 2507–2518.
Shimaoka M, Takagi J, Springer TA . (2002). Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 31: 485–516.
Tadokoro S, Shattil SJ, Eto K, Tai V, Liddington RC, de Pereda JM et al. (2003). Science 302: 103–106.
Unger M, Weaver VM . (2003). Methods Mol Biol 223: 315–347.
Velling T, Nilsson S, Stefansson A, Johansson S . (2004). EMBO Rep 5: 901–905.
Vlodavsky I, Lui GM, Gospodarowicz D . (1980). Cell 19: 607–616.
Watt FM . (2002). EMBO J 21: 19–26.
Wennerberg K, Armulik A, Sakai T, Karlsson M, Fassler R, Schaefer EM et al. (2000). Mol Cell Biol 20: 5758–5765.
Yamada KM, Even-Ram S . (2002). Nat Cell Biol 4: E75–E76.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr Fässler (Department of Molecular Medicine, Max-Planck Institute of Biochemistry, Martinsried, Germany) and Dr Velling (Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology, The Biomedical Center, Uppsala University, Sweden) for kindly providing the cell lines. We also thank Ms Bärbel Reincke and Mr Ralph Hartmann for excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cordes, N., Seidler, J., Durzok, R. et al. β1-integrin-mediated signaling essentially contributes to cell survival after radiation-induced genotoxic injury. Oncogene 25, 1378–1390 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209164
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209164
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Advances in molecular targeted therapies to increase efficacy of (chemo)radiation therapy
Strahlentherapie und Onkologie (2023)
-
The extracellular matrix alteration, implication in modulation of drug resistance mechanism: friends or foes?
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2022)
-
Growth factor receptor and β1 integrin signaling differentially regulate basal clonogenicity and radiation survival of fibroblasts via a modulation of cell cycling
In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Animal (2022)
-
Extracellular matrix and its therapeutic potential for cancer treatment
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2021)
-
Targeting the tumour stroma to improve cancer therapy
Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology (2018)