Abstract
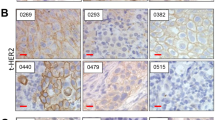
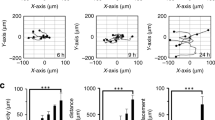
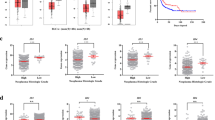
We sought to evaluate the biological function of the receptor tyrosine kinase EphB4 in bladder cancer. All of the nine bladder cancer cell lines examined express EphB4 and the receptor could be phosphorylated following stimulation with its cognate ligand, EphrinB2. Out of the 15 fresh bladder cancer specimens examined, 14 expressed EphB4 with a mean sevenfold higher level of expression compared to adjacent normal urothelium. EphB4 expression was regulated by several mechanisms: EPHB4 gene locus was amplified in 27% tumor specimens and 33% cell lines studied; inhibition of EGFR signaling downregulated EphB4 levels; and forced expression of wild-type p53 reduced EphB4 expression. EphB4 knockdown using specific siRNA and antisense oligodeoxynucleotides molecules led to a profound inhibition in cell viability associated with apoptosis via activation of caspase-8 pathway and downregulation of antiapoptotic factor, bcl-xl. Furthermore, EphB4 knockdown significantly inhibited tumor cell migration and invasion. EphB4 knockdown in an in vivo murine tumor xenograft model led to a nearly 80% reduction in tumor volume associated with reduced tumor proliferation, increased apoptosis and reduced tumor microvasculature. EphB4 is thus a potential candidate as a predictor of disease outcome in bladder cancer and as target for novel therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams RH, Wilkinson GA, Weiss C . (1999). Genes Dev 13: 295–306.
Andres AC, Zuercher G, Djonov V, Flueck M, Ziemiecki A . (1995). Int J Cancer 63: 288–296.
Battle E, Bacani J, Begthel H, Jonkeer S, Gregorieff A, van de Born M et al. (2005). Nature 435: 1126–1130.
Berclaz G, Andres AC, Albrecht D . (1996). Biochem Biophys Res 226: 869–875.
Berclaz G, Karamitopoulou E, Mazzucchelli L . (2003). Ann Oncol 14: 220–226.
Buscarini M, Quek ML, Gill P, Xia G, Quinn DI, Stein JP . (2005). BJU Int 95: 739–742.
Chatterjee SJ, Datar R, Youssefzadeh D, George B, Goebell PJ, Stein JP et al. (2004). J Clin Oncol 22: 1007–1013.
Chow NH, Chan SH, Tzai TS, Ho CL, Liu HS . (2001). Clin Cancer Res 7: 1957–1962.
Cooper MJ, Haluschak JJ, Johnson D, Schwartz S, Morrison LJ, Lippa M et al. (1994). Oncol Res 6: 569–579.
Cutler SJ, Heney NM, Friedell GH . (1982) In: Bonney WW, Prout Jr GR (eds). Bladder Cancer, vol. 1. Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, pp 35–46.
Di Fiore PP, Segatto O, Taylor WG, Aaronson SA, Pierce JH . (1990). Science 248: 79–83.
Esrig D, Elmajian D, Groshen S, Freeman JA, Stein JP, Chen SC et al. (1994). N Engl J Med 331: 1259–1264.
Gerety SS, Wang HU, Chen ZF, Anderson DJ . (1999). Mol Cell 4: 403–413.
Gontero P, Banisadr S, Frea B, Brausi M . (2004). Eur Urol 46: 296–311.
Hara I, Miyake H, Hara S, Arakawa S, Kamidono S . (2001). J Urol 165: 1769–1772.
Hasson P, Egoz N, Winkler C, Volohonsky G, Jia S, Dinur T et al. (2004). Nat Genet 37: 101–105.
Holder N, Klein R . (1999). Development 126: 2033–2044.
Koss LG . (1979). Hum Pathol 10: 533–548.
Lawson ND, Scheer N, Pham VN, Kim CH, Chitnis AB, Campos-Ortega JA et al. (2001). Development 128: 3675–3683.
Loehrer PJ, Einhorn LH, Elson PJ, Crawford ED, Kuebler P, Tannock I et al. (1992). J Clin Oncol 10: 1066–1073.
Logothetis CJ, Dexeus FH, Finn L, Sella A, Amato RJ, Ayala AG et al. (1990). J Clin Oncol 8: 1050–1055.
Lutzeyer W, Rubben H, Dahm H . (1982). J Urol 127: 250–252.
Mao W, Luis E, Ross S, Silva J, Tan C, Crowley C et al. (2004). Cancer Res 64: 781–788.
Masood R, Kundra A, Zhu S, Xia G, Scalia P, Smith DL et al. (2003). Int J Cancer 104: 603–610.
Masood R, Xia G, Smith DL, Scalia P, Still JG, Tulpule A et al. (2005). Blood 105: 1310–1318.
Munarini N, Jager R, Abderhalden S, Zuercher G, Rohrbach V, Loercher S et al. (2002). J Cell Sci 115: 25–37.
Noren NK, Lu M, Freeman AL, Koolpe M, Pasquale EB . (2004). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 5583–5588.
O’Leary DD, Wilkinson DG . (1999). Curr Opin Neurobiol 9: 65–73.
Oates AC, Lackmann M, Power MA . (1999). Mech Dev 83: 77–94.
Pasquale EB . (1997). Curr Opin Cell Biol 9: 608–615.
Rieger KM, Little AF, Swart JM, Kastrinakis WV, Fitzgerald JM, Hess DT et al. (1995). Br J Cancer 72: 683–690.
Stein JP, Lieskovsky G, Cote R, Groshen S, Feng AC, Boyd S et al. (2001). J Clin Oncol 19: 666–675.
Steinle JJ, Meininger CJ, Forough R, Wu G, Wu MH, Granger HJ . (2002). J Biol Chem 277: 43830–43835.
Stephenson SA, Slomka S, Douglas EL, Hewett PJ, Hardingham JE . 2001)). BMC Mol Biol 2: 15–23.
Sternberg CN, Calabro F, Pizzocaro G . (2001). Cancer 92: 2993–2998.
Takai N, Miyazaki T, Fujisawa K, Nasu K, Miyakawa I . (2001). Oncol Rep 8: 567–573.
Tickle C, Altabef M . (1999). Curr Opin Genet Dev 9: 455–460.
Vasala K, Paakko P, Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T . (2003). Urology 62: 952–957.
von der Maase H, Hansen SW, Roberts JT, Dogliotti L, Oliver T, Moore MJ et al. (2000). J Clin Oncol 18: 3068–3077.
Wu W, Shu X, Hovsepyan H, Mosteller RD, Broek D . (2003). Oncogene 22: 3361–3370.
Xia G, Kumar SR, Masood R, Koss M, Templeman C, Quinn D et al. (2005a). Clin Cancer Res 11: 4305–4315.
Xia G, Kumar SR, Masood R, Zhu S, Reddy R, Krasnoperov V et al. (2005b). Cancer Res 65: 4623–4632.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants from Whittier Foundation and NIH R01CA72918 to PSG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, G., Kumar, S., Stein, J. et al. EphB4 receptor tyrosine kinase is expressed in bladder cancer and provides signals for cell survival. Oncogene 25, 769–780 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209108
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209108
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Eph receptors and ephrins in cancer progression
Nature Reviews Cancer (2024)
-
Transcriptome-guided resolution of tumor microenvironment interactions in pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma subtypes
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation (2022)
-
Role of tyrosine kinases in bladder cancer progression: an overview
Cell Communication and Signaling (2020)
-
Dying to communicate: apoptotic functions of Eph/Ephrin proteins
Apoptosis (2018)
-
Eph/ephrin signaling in the kidney and lower urinary tract
Pediatric Nephrology (2016)