Abstract
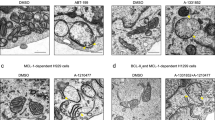
Deleted in breast cancer-1 (DBC-1) was initially cloned from a homozygously deleted region in breast and other cancers on human chromosome 8p21, although no function is known for the protein product it encodes. We identified the generation of amino-terminally truncated versions of DBC-1 during tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α-mediated apoptosis. Full-length 150 kDa DBC-1 underwent caspase-dependent processing during TNF-α-mediated death signaling, to produce p120 DBC-1 and p66 DBC-1 carboxy-terminal fragments. Endogenous DBC-1 localized to the nucleus in healthy cells, but localized to the cytoplasm during TNF-α-mediated apoptosis, consistent with the loss of the amino-terminus containing the nuclear localization signal. Overexpression of an amino-terminal truncated DBC-1, resembling p120 DBC-1, caused mitochondrial clustering, mitochondrial matrix condensation, and sensitized cells to TNF-α-mediated apoptosis. The carboxy-terminal coiled-coil domain of DBC-1 was responsible for the cytoplasmic and mitochondrial localization, and for the death-promoting activity of DBC-1. Thus, caspase-dependent processing of DBC-1 may act as a feed-forward mechanism to promote apoptosis and possibly also tumor suppression. DBC-1, like its homolog cell cycle and apoptosis regulatory protein-1 (CARP-1), may function in the regulation of apoptosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JM . (2003). Genes Dev., 17, 2481–2495.
Aravind L and Koonin EV . (2000). Trends Biochem. Sci., 25, 112–114.
Baffa R, Santoro R, Bullrich F, Mandes B, Ishii H and Croce CM . (2000). Clin. Cancer Res., 6, 1372–1377.
Baud V and Karin M . (2001). Trends Cell Biol., 11, 372–377.
Chen H, Detmer SA, Ewald AJ, Griffin EE, Fraser SE and Chan D . (2003). J. Cell Biol., 160, 189–200.
Chiu R, Novikov L, Mukherjee S and Shields D . (2002). J. Cell Biol., 159, 637–648.
Cryns V and Yuan J . (1998). Genes Dev., 12, 1551–1570.
Cuconati A and White E . (2002). Genes Dev., 16, 2465–2478.
Dai W, Li Y, Ouyang B, Pan H, Reissmann P, Li J, Wiest J, Stambrook P, Gluckman JL, Noffsinger A and Bejarano P . (2000). Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 27, 332–336.
Danial NN and Korsmeyer SJ . (2004). Cell, 116, 205–219.
Desagher S and Martinou JC . (2000). Trends Cell Biol., 10, 369–377.
De Vos K, Goossens V, Boone E, Vancompernolle K, Vandenabeele P, Haegeman G, Fiers W and Grooten J . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 9673–9680.
De Vos K, Severin F, Van Herreweghe F, Vancompernolle K, Goosens V, Hyman A and Grooten J . (2000). J. Cell Biol., 149, 1207–1214.
Dong JT . (2001). Cancer Metast. Rev., 20, 173–193.
Fischer U, Janicke RU and Schulze-Osthoff K . (2003). Cell Death Differ., 10, 76–100.
Fujiwara Y, Ohata H, Emi M, Okui K, Koyama K, Tsuchiya E, Nakajima T, Monden M, Mori T, Kurimasa A, Oshimura M and Nakamura Y . (1994). Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 10, 7–14.
Gohring F, Schwab BL, Nicotera P, Leist M and Fackelmayer FO . (1997). EMBO J., 16, 7361–7371.
Gottlieb E, Armour SM, Harris MH and Thompson CB . (2003). Cell Death Differ., 10, 709–717.
Hackenbrock CR . (1966). J. Cell Biol., 30, 269–297.
Hackenbrock CR . (1968). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 61, 598–605.
Hamaguchi M, Meth JL, von Klitzing C, Wei W, Esposito D, Rodgers L, Walsh T, Welcsh P, King MC and Wigler MH . (2002). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 99, 13647–13652.
Han J, Sabbatini P, Perez D, Rao L, Modha D and White E . (1996). Genes Dev., 10, 461–477.
He WW, Sciavolino PJ, Wing J, Augustus M, Hudson P, Meissner PS, Curtis RT, Shell BK, Bostwock DG, Tindall DJ, Gelmann EP, Abate-Shen C and Carter KC . (1997). Genomics, 43, 69–77.
Igney FH and Krammer PH . (2002). Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2, 277–288.
Kahng YS, Lee YS, Kim BK, Park WS, Lee JY and Kang CS . (2003). J. Gastroenterol Hepatol., 18, 430–436.
Karbowski M and Youle RJ . (2003). Cell Death Differ., 10, 870–880.
Kim KW, Kim BJ, Chung CW, Jo DG, Kim IK, Song YH, Kwon YK, Woo HN and Jung YK . (2002). J. Cell Biochem., 85, 334–345.
Kipp M, Schwab BL, Przbylski M, Nicotera P and Fackelmayer FO . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 5031–5036.
Knosel T, Petersen S, Schwabe H, Schluns K, Stein U, Schlag PM, Dietel M and Petersen I . (2002). Virchows arch., 440, 187–194.
Kothakota S, Azuma T, Reinhard C, Klippel A, Tang J, Ch K, McGarry TJ, Kirschne MW, Koths K, Kwiatkowski DJ and Williams LT . (1997). Science, 278, 294–298.
Kucharczak J, Simmons MJ, Fan Y and Gelinas C . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 8961–8982.
Kurimoto F, Gemma A, Hosoya Y, Seike M, Takenaka K, Uematsu K, Yoshimura A, Shibuya M and Kudoh S . (2001). Int. J. Mol. Med., 8, 89–93.
Lai J, Flanagan J, Philips WA, Chenevix-Trench G and Arnold J . (2003). Br. J. Cancer, 88, 270–276.
Lassus H, Laitinen MP, Anttonen M, Heikinheimo M, Aaltonen LA, Ritvos O and Butzow R . (2001). Lab. Invest., 81, 517–526.
Legros F, Lombes A, Frachon P and Rojo M . (2002). Mol. Biol. Cell, 13, 4343–4354.
Mancini M, Anderson BO, Caldwell E, Sedghinasab M, Paty PB and Hockenbery DM . (1997). J. Cell Biol., 138, 449–469.
Martinez-Climent JA, Vizcarra E, Sanchez D, Blesa D, Marugan IIB, Sole F, Rubio-Moscardo F, Terol MJ, Climent J, Sarsotti E, Tormo M, Andreu E, Salido M, Ruiz MA, Prosper F, Siebert R, Dyer MJ and Garcia-Conde J . (2001). Blood, 98, 3479–3482.
Martinou I, Desagher S, Eskes R, Antonsson B, Andre E, Fakan S and Martinou JC . (1999). J. Cell Biol., 144, 883–889.
Nachmias B, Ashhab Y, Bucholtz V, Drize O, Kadouri L, Lotem M, Peretz T, Mandelboim O and Ben-Yehuda D . (2003). Cancer Res., 63, 6340–6349.
Nagata S . (1999). Annu. Rev. Genet., 33, 29–55.
Perez D and White E . (2000). Mol. Cell, 6, 53–63.
Plaumann M, Seitz S, Frege R, Estevez-Schwarz L and Scherneck S . (2003). J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol., 129, 349–354.
Rishi AK, Zhang B, Boyanapalli M, Wali A, Mohammad RM, Yu Y, Fontana JA, Hatfield JS, Dawson MI, Majumdar AP and Reichert U . (2003). J. Biol. Chem., 278, 33422–33435.
Rojo M, Legros F, Chateau D and Lombes A . (2002). J. Cell Sci., 115, 1663–1674.
Sahara S, Aoto M, Eguchi Y, Imamoto N, Yoneda Y and Tsujimoto Y . (1999). Nature, 401, 168–173.
Santel A and Fuller MT . (2000). J. Cell Sci., 114, 867–874.
Scorrano L, Ashiya MKB, Weiler S, Oakes SA, Mannella CA and Korsmeyer SJ . (2002). Dev. Cell, 2, 55–67.
Sundararajan R, Cuconati A, Nelson D and White E . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 45120–45127.
Sundararajan R and White E . (2001). J. Virol., 75, 7506–7516.
Sunwoo JB, Holt MS, Radford DM, Deeker C and Scholnick SB . (1996). Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 16, 164–169.
Swalwell JI, Vocke CD, Yang Y and Walker . (2002). Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 33, 201–205.
Thomas WD, Zhang XD, Franco AW, Nguyen T and Hersey P . (2000). J. Immunol., 165, 5612–5620.
Thor AD, Eng C, Devries S, Paterakos M, Watkin WG, Edgerton S, Moore DH, Etzell J and Waldman FM . (2002). Hum. Pathol., 33, 628–631.
White E, Sabbatini P, Debbas M, Wold WSM, Kusher DI and Gooding L . (1992). Mol. Cell. Biol., 12, 2570–2580.
Xu Z, Liang L, Wang H, Li T and Zhao M . (2003). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 311, 1057–1066.
Zamzami N and Kroemer G . (1999). Nature, 401, 127–128.
Zhuang J, Dinsdale D and Cohen GM . (1998). Cell Death Differ., 5, 953–962.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Kyriakos Economides for help with confocal microscopy. We also thank Dr Deirdre Nelson for critical reading, and Thomasina Sharkey for assistance with preparation of the manuscript. This work has been supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (CA53370) to EW and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sundararajan, R., Chen, G., Mukherjee, C. et al. Caspase-dependent processing activates the proapoptotic activity of deleted in breast cancer-1 during tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated death signaling. Oncogene 24, 4908–4920 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208681
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208681
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A novel form of Deleted in breast cancer 1 (DBC1) lacking the N-terminal domain does not bind SIRT1 and is dynamically regulated in vivo
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
DBC1/CCAR2 is involved in the stabilization of androgen receptor and the progression of osteosarcoma
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
CCAR2 deficiency augments genotoxic stress-induced apoptosis in the presence of melatonin in non-small cell lung cancer cells
Tumor Biology (2014)
-
DBC1 is over-expressed and associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer
International Journal of Clinical Oncology (2014)
-
Role of multifunctional transcription factor TFII-I and putative tumour suppressor DBC1 in cell cycle and DNA double strand damage repair
British Journal of Cancer (2013)