Abstract
Bcl-xL and Bcl-2 are phosphorylated in response to microtubule inhibitors, but the kinase(s) responsible and the functional significance have remained unclear. In this study, we investigated the characteristics of Bcl-xL and Bcl-2 phosphorylation in KB-3 carcinoma cells treated with vinblastine. In both asynchronous and synchronous cell cultures, Bcl-xL and Bcl-2 underwent a well-defined and coordinated cycle of phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, with a lengthy period of phosphorylation preceding apoptosis induction, and with dephosphorylation closely correlated with initiation of apoptosis. Internally, validated inhibitors of JNK, ERK, p38MAPK, or CDK1 failed to inhibit vinblastine-induced phosphorylation of Bcl-xL or Bcl-2. In vitro, Bcl-xL and Bcl-2 were poor substrates relative to c-Jun and ATF2 for active recombinant JNK1. Both Bcl-xL and Bcl-2 were localized primarily to the mitochondrial fraction in both control and vinblastine-treated cells, indicating that phosphorylation did not promote subcellular redistribution. Bcl-xL kinase activity was demonstrated in mitochondrial extracts from vinblastine-treated, but not control, cells. These findings suggest that phosphorylation of these key antiapoptotic proteins may be catalysed by a novel or unsuspected kinase that is activated or induced in response to microtubule damage. Furthermore, the same kinase and phosphatase system may be operating in tandem on both proteins, and phosphorylation appears to maintain their antiapoptotic function, whereas dephosphorylation may trigger apoptosis. These results provide evidence for a novel signaling pathway connecting microtubule damage to apoptosis induction, and help to clarify some of the controversy concerning the role of Bcl-2 phosphorylation in microtubule inhibitor-induced apoptosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams J and Cory S . (2001). Trends Biochem. Sci., 26, 61–66.
Amundson SA, Myers TG, Scudiero D, Kitada S, Reed JC and Fornace Jr AJ . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 6101–6110.
Bain J, McLauchlan H, Elliott M and Cohen P . (2003). Biochem. J., 371, 199–204.
Basu A and Haldar S . (2003). FEBS Lett., 538, 41–47.
Bennett BL, Sasaki DT, Murray BW, O'Leary EC, Sakata ST, Xu W, Leisten JC, Motiwala A, Pierce S, Satoh Y, Bhagwat SS, Manning AM and Anderson DW . (2001). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 98, 13681–13686.
Blagosklonny MV, Giannakakou P, El-Deiry WS, Kingston DGI, Higgs PI, Neckers L and Fojo T . (1997). Cancer Res., 57, 130–135.
Brichese L, Barboule N, Heliez C and Valette A . (2002). Exp. Cell. Res., 278, 101–111.
Calastretti A, Bevilacqua A, Ceriani C, Vigano S, Zancai P, Capaccioli S and Nicolin A . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 6172–6180.
Chang BS, Minn AJ, Muchmore SW, Fesik SW and Thompson CB . (1997). EMBO J., 16, 968–977.
Du L, Lyle CS, Hall-Obey T, Gaarde WA, Muir JA, Bennett BL and Chambers TC . (2004). J. Biol. Chem., 279, 11957–11966.
Fan M, Du L, Stone AA, Gilbert KM and Chambers TC . (2000a). Cancer Res., 60, 6403–6407.
Fan M, Goodwin M, Vu T, Brantley-Finley C, Gaarde WA and Chambers TC . (2000b). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 29980–29985.
Fang G, Chang BS, Kim CN, Perkins C, Thompson CB and Bhalla KN . (1998). Cancer Res., 58, 3202–3208.
Furukawa Y, Iwase S, Kikuchi J, Terui Y, Nakamura M, Yamada H, Kano Y and Matsuda M . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 21661–21667.
Huang DCS and Strasser A . (2000). Cell, 103, 839–842.
Ito T, Deng X, Carr B and May WS . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 11671–11673.
Kharbanda S, Saxena S, Yoshida K, Pandey P, Kaneki M, Wang Q, Cheng K, Chen YN, Campbell A, Sudha T, Yuan ZM, Narula J, Weichselbaum R, Nalin C and Kufe D . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 322–327.
Ling YH, Tornos C and Perez-Soler R . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 18984–18991.
Maundrell K, Antonsson B, Magnenat E, Camps M, Muda M, Chabert C, Gillierson C, Boschert U, Vial-Knecht E, Martinou JC and Arkinstall S . (1997). J. Biol Chem, 272, 25238–25242.
Newmeyer DD and Ferguson-Miller S . (2003). Cell, 112, 481–490.
Osborn MT, Berry A, Ruberu MS, Ning B, Bell LM and Chambers TC . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 5756–5764.
Pathan N, Aime-Sempe C, Kitada S, Basu A, Haldar S and Reed JC . (2001). Neoplasia, 3, 550–559.
Poruchynsky MS, Wand EE, Rudin CM, Blagosklonny MV and Fojo T . (1998). Cancer Res., 58, 3331–3338.
Potapova O, Gorospe M, Bost F, Dean NM, Gaarde WA, Mercola D and Holbrook NJ . (2000a). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 24767–24775.
Potapova O, Gorospe M, Dougherty RH, Dean NM, Gaarde WA and Holbrook NJ . (2000b). Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 1713–1722.
Ruvolo PP, Deng X and May WS . (2001). Leukemia, 15, 515–522.
Scorrano L and Korsmeyer SJ . (2003). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 304, 437–444.
Srivastava RK, Mi QS, Hardwick JM and Longo DL . (1999). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 96, 3775–3780.
Srivastava RK, Srivastava AR, Korsmeyer SJ, Nesterova M, Cho-Chung YS and Longo DL . (1998). Mol. Cell. Biol., 18, 3509–3517.
Stone AA and Chambers TC . (2000). Exp. Cell Res., 254, 110–119.
Tsujimoto Y . (2003). J. Cell. Physiol., 195, 158–167.
Wang S, Wang Z, Boise L, Dent P and Grant S . (1999). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 259, 67–72.
Yamamoto K, Ichijo H and Korsmeyer SJ . (1999). Mol. Cell. Biol., 19, 8469–8478.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grants CA75577 and CA10982 from the National Cancer Institute and in part by a grant from the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences Graduate Student Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, L., Lyle, C. & Chambers, T. Characterization of vinblastine-induced Bcl-xL and Bcl-2 phosphorylation: evidence for a novel protein kinase and a coordinated phosphorylation/dephosphorylation cycle associated with apoptosis induction. Oncogene 24, 107–117 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208189
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208189
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
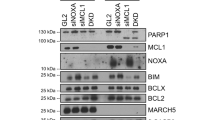
MARCH5-dependent degradation of MCL1/NOXA complexes defines susceptibility to antimitotic drug treatment
Cell Death & Differentiation (2020)
-
Regulation of apoptosis by an intrinsically disordered region of Bcl-xL
Nature Chemical Biology (2018)
-
Cdk2 phosphorylation of Bcl-xL after stress converts it to a pro-apoptotic protein mimicking Bax/Bak
Cell Death Discovery (2016)
-
Mesenchymal stem cells for treating ocular surface diseases
BMC Ophthalmology (2015)
-
Critical role of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein phosphorylation in mitotic death
Cell Death & Disease (2013)