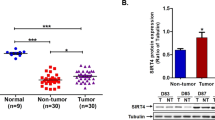
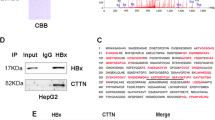
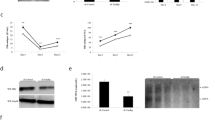
Abstract
Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) is a pleiotropic cytokine implicated as a pathogenic mediator in various liver diseases. Enhanced TGF-β production and lack of TGF-β responses are often observed during hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. In this study, we demonstrate that TGF-β-mediated transactivation is decreased in cells exogenously expressing the intact HCV polyprotein. Among 10 viral products of HCV, only core and nonstructural protein 3 (NS3) physically interact with the MH1 (Mad homology 1) region of the Smad3 and block TGF-β/Smad3-mediated transcriptional activation through interference with the DNA-binding ability of Smad3, not the nuclear translocation. However, the interactive domain of NS3 extends to the MH2 (Mad homology 2) region of Smad3 and a distinction is found between effects mediated, respectively, by these two viral proteins. HCV core, in the presence or absence of TGF-β, has a stronger suppressive effect on the DNA-binding and transactivation ability of Smad3 than NS3. Although HCV core, NS3, and the HCV subgenomic replicon all attenuate TGF-β/Smad3-mediated apoptosis, only HCV core represses TGF-β-induced G1 phase arrest through downregulation of the TGF-β-induced p21 promoter activation. Along with this, HCV core, rather than NS3, exhibits a significant inhibitory effect on the binding of Smad3/Sp1 complex to the proximal p21 promoter in response to TGF-β. In conclusion, HCV viral proteins interact with the TGF-β signaling mediator Smad3 and differentially impair TGF-β/Smad3-mediated transactivation and growth inhibition. This functional counteraction of TGF-β responses provides insights into possible mechanisms, whereby the HCV oncogenic proteins antagonize the host defenses during hepatocarcinogenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe M, Harpel JG, Metz CN, Nunes L, Loskutoff DJ and Rigkin DB . (1994). Anal. Biochem., 216, 276–284.
Blight KJ, Kolykhalov AA and Rice CM . (2000). Science, 290, 1972–1974.
Chen CM, You LR, Hwang LH and Lee YHW . (1997). J. Virol., 71, 9417–9426.
Chen SY, Kao CF, Chen CM, Shih CM, Hsu MJ, Chao CH, Wang SH, You LR and Lee YHW . (2003). J. Biol. Chem., 278, 591–607.
Datto MB, Li Y, Panus JF, Howe DJ, Xiong Y and Wang XF . (1995). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 92, 5545–5549.
De Bleser PJ, Niki T, Rogiers V and Geerts A . (1997). J. Hepatol., 26, 886–893.
De Francesco R and Steinkuhler C . (2000). Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol., 242, 149–169.
Dennler S, Itoh S, Vivien D, Dijke PT, Huet S and Gauthier JM . (1998). EMBO J., 17, 3091–3100.
Derynck R, Akhurst RJ and Balmain A . (2001). Nat. Genet., 29, 117–129.
Dey A, Atcha IA and Bagchi S . (1997). Virology, 228, 190–199.
Dubordeau M, Miyamura T, Matsuura Y, Alric L, Pipy B and Rousseau D . (2002). J. Hepatol., 37, 486–492.
El-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, Lin D, Mercer WE, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B . (1993). Cell, 75, 817–825.
Fujita T, Ishido S, Muramatsu S, Itoh M and Hotta H . (1996). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 229, 825–831.
Graham FL and van der Eb AJ . (1973). Virology, 52, 456–467.
Hata A, Lo RS, Wotton D, Lagna G and Massague J . (1997). Nature, 388, 82–87.
Ito N, Kawata S, Tamura S, Takaishi K, Shirai Y, Kiso S, Yabuuchi I, Matsuda Y, Nishioka M and Tarui S . (1991). Cancer Res., 51, 4080–4083.
Jang CW, Chen CH, Chen CC, Chen JY, Su YH and Chen RH . (2002). Nat. Cell Biol., 4, 51–58.
Jayaraman L and Massague J . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 40710–40717.
Kim DH, Chang JH, Lee KH, Lee HY and Kim SJ . (1996). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 688–694.
Kolykhalov AA, Agapov EV, Blight KJ, Mihalik K, Feinstone SM and Rice CM . (1997). Science, 277, 570–574.
Kwong AD, Kim JL and Lin C . (2000). Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol., 242, 171–196.
Lai MM and Ware CF . (2000). Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol., 242, 117–134.
Lauer GM and Walker BD . (2001). N. Engl. J. Med., 345, 41–52.
Lee DK, Kim BC, Brady JN, Jeang KT and Kim SJ . (2002a). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 33766–33775.
Lee DK, Kim BC, Kim IY, Cho EA, Satterwhite DJ and Kim SJ . (2002b). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 38557–38564.
Lee DK, Park SH, Yi Y, Choi SG, Lee C, Parks WT, Cho H, de Caestecker MP, Shaul Y, Roberts AB and Kim SJ . (2001). Genes Dev., 15, 455–466.
Lee MN, Jung EY, Kwun HJ, Jun HK, Yu DY, Choi YH and Jang KL . (2002c). J. Gen. Virol., 83, 2145–2151.
Massague J . (2000). Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol., 1, 169–178.
Matsuzaki K, Date M, Furukawa F, Tahashi Y, Matsushita M, Sakitani K, Yamashiki N, Seki T, Saito H, Nishizawa M, Fujisawa J and Inoue K . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 1394–1402.
Moriya K, Fujie H, Shintani Y, Yotsuyanagi H, Tsutsumi T, Ishibashi K, Matsuura Y, Kimura S, Miyamura T and Koike K . (1998). Nat. Med., 4, 1065–1067.
Moriya K, Yotsuyanagi H, Shintani Y, Fujie H, Ishibashi K, Matsuura Y, Miyamura T and Koike K . (1997). J. Gen. Virol., 78, 1527–1531.
Nakao A, Imamura T, Souchelnytskyi S, Kawabata M, Ishisaki A, Oeda E, Tamaki K, Hanai J, Heldin CH, Miyazono K and ten Dijke P . (1997). EMBO J., 16, 5353–5362.
Nishihara A, Hanai JI, Imamura T, Miyazono K and Kawabata M . (1999). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 28716–28723.
Oberhammer FA, Pavelka M, Sharma S, Tiefenbacher R, Purchio AF, Bursch W and Schulte-Hermann R . (1992). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 89, 5408–5412.
Pardali K, Kurisaki A, Moren A, ten Dijke P, Kardassis D and Moustakas A . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 29244–29256.
Prokova V, Mosialos G and Karassis D . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 9342–9350.
Ray RB, Steele R, Meyer K and Ray R . (1998). Gene, 208, 331–336.
Ray S, Broor SL, Vaishnav Y, Sarkar C, Girish R, Dar L, Seth P and Broor S . (2003). J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol., 18, 393–403.
Reed KE and Rice CM . (2000). Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol., 242, 55–84.
Sakamuro D, Furukawa T and Takegami T . (1995). J. Virol., 69, 3893–3896.
Seeff LB . (2002). Hepatology, 36, S35–S46.
Shih CM, Lo SJ, Miyamura T, Chen SY and Lee YHW . (1993). J. Virol., 67, 5823–5832.
Shih WL, Kuo ML, Chuang SE, Cheng AL and Doong SL . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 25858–25864.
Tellinghuisen TL and Rice CM . (2002). Curr. Opin. Microbiol., 5, 419–427.
Wrana JL, Attisano L, Carcamo J, Zentella A, Doody J, Laiho M, Wang XF and Massague J . (1992). Cell, 71, 1003–1014.
You LR, Chen CM, Yeh TS, Tsai TY, Mai RT, Lin CH and Lee YHW . (1999). J. Virol., 73, 2841–2853.
Zemel R, Gerechet S, Greif H, Bachmatove L, Birk Y, Golan-Goldhirsh A, Kunin M, Berdichevsky Y, Benhar I and Tur-Kaspa R . (2001). J. Viral Hepatitis., 8, 96–102.
Zhang Y, Feng XH and Derynck R . (1998). Nature, 394, 909–913.
Zhang Y, Feng XH, We RY and Derynck R . (1996). Nature, 383, 168–172.
Acknowledgements
We thank CM Rice and Apath (St Louis, MO, USA) for generously providing the Ava.5 cells and p90/HCVFLlongpU plasmid. We also thank L-H Hwang, R-H Chen, C-K Chou, K-H Lan, K Tokushige and K Miyazono for providing plasmids used in this study. We are grateful to R Kirby for critical reading and comments on this manuscript. This work was supported by the following grants to Y-HW Lee: NSC 89-2315-B-010-006-MH, NSC 89-2320-B-010-121, NSC 90-2320-B-010-077, NSC 91-2320-B-010-040, and NSC 92-2320-B-010-064 from National Science Council; and in part by grants NHRI-EX91-9002BL, NHRI-EX92-9002BL, and NHRI-EX93-9002BL from the National Health Research Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, PL., Chang, MH., Chao, CH. et al. Hepatitis C viral proteins interact with Smad3 and differentially regulate TGF-β/Smad3-mediated transcriptional activation. Oncogene 23, 7821–7838 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208066
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208066
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Model of the adaptive immune response system against HCV infection reveals potential immunomodulatory agents for combination therapy
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
TRAF6 is a novel NS3-interacting protein that inhibits classical swine fever virus replication
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
An integrative approach for a network based meta-analysis of viral RNAi screens
Algorithms for Molecular Biology (2015)
-
Cytokine/chemokine patterns connect host and viral characteristics with clinics during chronic hepatitis C
European Journal of Medical Research (2012)
-
Virus-specific mechanisms of carcinogenesis in hepatitis C virus associated liver cancer
Oncogene (2011)