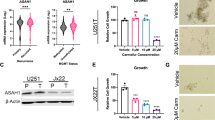
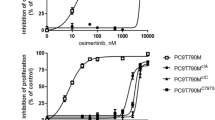
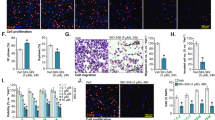
Abstract
Choline kinase (ChoK, E.C. 2.7.1.32) is involved in the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine (PC), and has been found to be increased in human tumors and tumor-derived cell lines. Furthermore, ChoK inhibitors have been reported to show a potent and selective antitumoral activity both in vitro and in vivo. Here, we provide the basis for a rational understanding of the antitumoral activity of ChoK inhibitors. In normal cells, blockage of de novo phosphorylcholine (PCho) synthesis by inhibition of ChoK promotes the dephosphorylation of pRb, resulting in a reversible cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 phase. In contrast, ChoK inhibition in tumor cells renders cells unable to arrest in G0/G1 as manifested by a lack of pRb dephosphorylation. Furthermore, tumor cells specifically suffer a drastic wobble in the metabolism of main membrane lipids PC and sphingomyelin (SM). This lipid disruption results in the enlargement of the intracellular levels of ceramides. As a consequence, normal cells remain unaffected, but tumor cells are promoted to apoptosis. Thus, we provide in this study the rationale for the potential clinical use of ChoK inhibitors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bielawska A, Linardic CM and Hannun YA . (1992). FEBS Lett., 307, 211–214.
Billah MM and Anthes JC . (1990). Biochem. J., 269, 281–291.
Brennan P, Babbage JW, Thomas G and Cantrell D . (1999). Mol. Cell. Biol., 19, 4729–4738.
Brindley DN, Abousalham A, Kikuchi Y, Wang CN and Waggoner DW . (1996). Biochem. Cell Biol., 74, 469–476.
Cui Z and Houweling M . (2002). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1585, 87–96.
Cui Z, Houweling M, Chen MH, Record M, Chap H, Vance DE and Terce F . (1996). J. Biol. Chem., 271, 14668–14671.
Davies SM, Epand RM, Kraayenhof R and Cornell RB . (2001). Biochemistry, 40, 10522–10531.
Dbaibo GS, Pushkavera MY, Jayadev S, Schwarz JK, Horowitz JM, Obeid LM and Hannun YA . (1995). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 92, 1347–1351.
DeLong CJ, Shen YJ, Thomas MJ and Cui Z . (1999). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 29683–29688.
Dressler KA, Mathias S and Kolesnick RN . (1992). Science, 255, 1715–1718.
Esko JD, Nishijima M and Raetz CR . (1982). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 79, 1698–1702.
Esko JD, Wermuth MM and Raetz CR . (1981). J. Biol. Chem., 256, 7388–7393.
Fernandez-Tome MC, Speziale EH and Sterin-Speziale NB . (2002). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1583, 185–194.
Finney RE, Nudelman E, White T, Bursten S, Klein P, Leer LL, Wang N, Waggoner D, Singer JW and Lewis RA . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 5204–5213.
Flores I, Jones DR, Cipres A, Diaz-Flores E, Sanjuan MA and Merida I . (1999). J. Immunol., 163, 708–714.
Flores I, Martinez AC, Hannun YA and Merida I . (1998). J. Immunol., 160, 3528–3533.
Foster DA and Xu L . (2003). Mol. Cancer Res., 1, 789–800.
Golfman LS, Bakovic M and Vance DE . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 43688–43692.
Green DR . (2000). Cell, 102, 1–4.
Hannun YA . (1996). Science, 274, 1855–1859.
Henneberry AL and McMaster CR . (1999). Biochem. J., 339 (Part 2), 291–298.
Hernández-Alcoceba R, Fernández F and Lacal JC . (1999). Cancer Res., 59, 3112–3118.
Hernández-Alcoceba R, Saniger L, Campos J, Núñez MC, Khaless F, Gallo MA, Espinosa A and Lacal JC . (1997). Oncogene, 15, 2289–2301.
Holmes-McNary MQ, Loy R, Mar MH, Albright CD and Zeisel SH . (1997). Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res., 101, 9–16.
Houweling M, Cui Z and Vance DE . (1995). J. Biol. Chem., 270, 16277–16282.
Hudson JM, Frade R and Bar-Eli M . (1995). DNA Cell Biol., 14, 759–766.
Hundertmark S, Lorenz U, Weitzel HK and Ragosch V . (1999). Horm. Metab. Res., 31, 8–13.
Janicke RU, Sprengart ML, Wati MR and Porter AG . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 9357–9360.
Jarvis WD, Fornari Jr FA, Browning JL, Gewirtz DA, Kolesnick RN and Grant S . (1994). J. Biol. Chem., 269, 31685–31692.
Jiménez B, del Peso L, Montaner S, Esteve P and Lacal JC . (1995). J. Cell Biochem., 57, 141–149.
Kim KH and Carman GM . (1999). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 9531–9538.
Kolesnick R . (2002). J. Clin. Invest., 110, 3–8.
Kuge O, Nishijima M and Akamatsu Y . (1986). J. Biol. Chem., 261, 5795–5798.
Lacal JC . (1997). FEBS Lett., 410, 73–77.
Lacal JC . (2001). Int. Drugs, 4, 419–426.
Lykidis A and Jackowski S . (2001). Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol., 65, 361–393.
Man AS, Lee E and Choy PC . (1994). Lipids, 29, 15–19.
Moolenaar WH, Kruijer W, Tilly BC, Verlaan I, Bierman AJ and de Laat SW . (1986). Nature, 323, 171–173.
Nishizuka Y . (1992). Science, 258, 607–614.
Nourse J, Firpo E, Flanagan WM, Coats S, Polyak K, Lee MH, Massague J, Crabtree GR and Roberts JM . (1994). Nature, 372, 570–573.
Ostrander DB, Sparagna GC, Amoscato AA, McMillin JB and Dowhan W . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 38061–38067.
Pelech SL and Vance DE . (1984). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 779, 217–251.
Ramirez de Molina A, Bȧn̄ez-Coronel M, Gutiérrez R, Rodríguez-González A, Megías D, Olmeda D and Lacal JC . Cancer Res. (in press).
Rodríguez-González A, Ramírez de Molina A, Fernández F, Ramos MA, Nuñez MC, Campos JM and Lacal JC . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 8803–8812.
Ruiz-Ruiz CaAL-R . (2002). Biochem. J., 825–832.
Ruvolo PP . (2003). Pharmacol. Res., 47, 383–392.
Sheaff RJ, Groudine M, Gordon M, Roberts JM and Clurman BE . (1997). Genes Dev., 11, 1464–1478.
Sherr CjaRJM . (1999). Genes Dev., 13, 1501–1512.
Sillence DJ and Allan D . (1998). Biochem. J., 331 (Part 1), 251–256.
Spiegel S and Kolesnick R . (2002). Leukemia, 16, 1596–1602.
Takahashi K, Avissar N, Whitin J and Cohen H . (1987). Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 256, 677–686.
Tsukiyama T, Ishida N, Shirane M, Minamishima YA, Hatakeyama S, Kitagawa M and Nakayama K . (2001). J. Immunol., 166, 304–312.
Uchida T . (1994). J. Biochem. (Tokyo), 116, 508–518.
Uchida T . (1996). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1304, 89–104.
Ursini F, Maiorino M and Gregolin C . (1985). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 839, 62–70.
Vance DE, Walkey CJ and Cui Z . (1997). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1348, 142–150.
Wang X . (2001). Genes Dev., 15, 2922–2933.
Warden CH and Friedkin M . (1985). J. Biol. Chem., 260, 6006–6011.
Weinberg RA . (1995). Cell, 81, 323–330.
Weinhold PA, Rounsifer ME, Charles L and Feldman DA . (1989). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1006, 299–310.
Wieder T, Orfanos CE and Geilen CC . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 11025–11031.
Wieprecht M, Wieder T and Geilen CC . (1994). Biochem. J., 297 (Part 1), 241–247.
Wittenberg J and Kornberg A. . (1953). J. Biol. Chem., 202, 431–444.
Yen CL, Mar MH and Zeisel SH . (1999). FASEB J., 13, 135–142.
Yen CL, Mar MH, Meeker RB, Fernandes A and Zeisel SH . (2001). FASEB J., 15, 1704–1710.
Zeisel SH . (1993). FASEB J., 7, 551–557.
Zeisel SH, DaCosta K-H, Franklin PD, Alexander EA, Lamont JT, Sheard NF and Beiser A . (1991). FASEB J., 5, 2093–2098.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grant SAF2001-2042 from MCyT, and by Grants FIS C03-08 and C03-10 from MSyC. ARG was a fellow from Departamento de Educación (Universidades e Investigación del Gobierno Vasco), Grant [Ref. BFI (98.124)]. ARM was a fellow from FIS (Instituto de Salud Carlos III), Grant BEFI 99/9125 (Ref. CPC/CLC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodríguez-González, A., Ramirez de Molina, A., Fernández, F. et al. Choline kinase inhibition induces the increase in ceramides resulting in a highly specific and selective cytotoxic antitumoral strategy as a potential mechanism of action. Oncogene 23, 8247–8259 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208045
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208045
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A new family of choline kinase inhibitors with antiproliferative and antitumor activity derived from natural products
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2015)
-
A non-catalytic role of choline kinase alpha is important in promoting cancer cell survival
Oncogenesis (2013)
-
Choline kinase inhibition induces exacerbated endoplasmic reticulum stress and triggers apoptosis via CHOP in cancer cells
Cell Death & Disease (2013)
-
Choline metabolism in malignant transformation
Nature Reviews Cancer (2011)
-
The choC gene encoding a putative phospholipid methyltransferase is essential for growth and development in Aspergillus nidulans
Current Genetics (2010)