Abstract
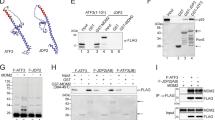
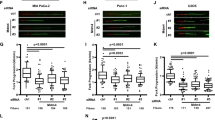
A common mechanism by which the tumor suppressor p53 accumulates in the nucleus following cellular stress is through the attenuation of its interaction with MDM2, a protein involved in the nuclear export and degradation of p53. This is accomplished by induced modifications of p53, MDM2 or both. We have previously found that the kinase and mRNA synthesis inhibitor DRB (5,6-dichloro-1-b-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole) induces the nuclear accumulation of p53 without concomitant phosphorylation of the ser15 site of p53, which is thought to be a modification important for the attenuation of p53–MDM2 interaction. It has been proposed that the mechanism by which p53 accumulates following blockage of transcription involves the downregulation of MDM2 expression. In this study, we tested this hypothesis and found that after DRB treatment, p53 accumulated despite the fact that MDM2 levels remained high in human cells. Furthermore, over expression of MDM2 did not prevent the accumulation of p53 following DRB treatment. In, addition, p53 accumulating in the nucleus after DRB treatment was able to interact with MDM2 and was ubiquitylated. These findings suggest that blockage of transcription induce the nuclear accumulation of p53 without breaking the p53–MDM2 regulation loop.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arriola EL, Lopez AR and Chresta CM . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 1081–1091.
Ashcroft M, Kubbutat MH and Vousden KH . (1999). Mol. Cell. Biol., 19, 1751–1758.
Ashcroft M, Taya Y and Vousden KH . (2000). Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 3224–3233.
Banin S, Moyal L, Shieh S, Taya Y, Anderson CW, Chessa L, Smorodinsky NI, Prives C, Reiss Y, Shiloh Y and Ziv Y . (1998). Science, 281, 1674–1677.
Bean LJH and Stark GR . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 1076–1084.
Blattner C, Sparks A and Lane D . (1999a). Mol. Cell. Biol., 19, 3704–3713.
Blattner C, Tobiasch E, Litfen M, Rahmsdorf HJ and Herrlich P . (1999b). Oncogene, 18, 1723–1732.
Boyd SD, Tsai KY and Jacks T . (2000). Nat. Cell Biol., 2, 563–568.
Canman CE, Lim DS, Cimprich KA, Taya Y, Tamai K, Sakaguchi K, Appella E, Kastan MB and Siliciano JD . (1998). Science, 281, 1677–1679.
Chen L, Lu W, Agrawal S, Zhou W, Zhang R and Chen J . (1999). Mol. Med., 5, 21–34.
Craig AL, Burch L, Vojtesek B, Mikutowska J, Thompson A and Hupp TR . (1999). Biochem. J., 342, 133–141.
David-Pfeuty T, Nouvian-Dooghe Y, Sirri V, Roussel P and Hernandez-Verdun D . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 5951–5963.
Dubois MF, Nguyen VT, Bellier S and Bensaude O . (1994). J. Biol. Chem., 269, 13331–13336.
Dulic V, Kaufmann WK, Wilson SJ, Tlsty TD, Lees E, Harper JW, Elledge SJ and Reed SI . (1994). Cell, 76, 1013–1023.
Dumaz N and Meek DW . (1999). EMBO J., 18, 7002–7010.
Geyer RK, Yu ZK and Maki CG . (2000). Nat. Cell Biol., 2, 569–573.
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A and Oren M . (1997). Nature, 387, 296–299.
Honda R, Tanaka H and Yasuda H . (1997). FEBS Lett., 420, 25–27.
Inoue T, Geyer RK, Yu ZK and Maki CG . (2001). FEBS Lett., 490, 196–201.
Joseph TW, Zaika A and Moll UM . (2003). FASEB J., 17, 1622–1630.
Kapoor M, Hamm R, Yan W, Taya Y and Lozano G . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 358–364.
Kastan MB, Onyekwere O, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B and Craig RW . (1991). Cancer Res., 51, 6304–6311.
Khanna KK, Keating KE, Kozlov S, Scott S, Gatei M, Hobson K, Taya Y, Gabrielli B, Chan D, Lees-Miller SP and Lavin MF . (1998). Nat. Genet., 20, 398–400.
Khosravi R, Maya R, Gottlieb T, Oren M, Shiloh Y and Shkedy D . (1999). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 96, 14973–14977.
Klibanov SA, O'Hagan HM and Ljungman M . (2001). J. Cell Sci., 114, 1867–1873.
Kubbutat MH, Jones SN and Vousden KH . (1997). Nature, 387, 299–303.
Latonen L, Kurki S, Pitkanen K and Laiho M . (2003). Cell Signal., 15, 95–102.
Leach FS, Tokino T, Meltzer P, Burrell M, Oliner JD, Smith S, Hill DE, Sidransky D, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B . (1993). Cancer Res., 53, 2231–2234.
Ljungman M . (2000). Neoplasia, 2, 208–225.
Ljungman M, O'Hagan HM and Paulsen MT . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 5964–5971.
Ljungman M and Zhang F . (1996). Oncogene, 13, 823–831.
Ljungman M, Zhang F, Chen F, Rainbow AJ and McKay BC . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 583–592.
Lopes UG, Erhardt P, Yao R and Cooper GM . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 12893–12896.
Lowe SW and Ruley HE . (1993). Genes Dev., 7, 535–545.
Maki CG and Howley PM . (1997). Mol. Cell. Biol., 17, 355–363.
Maki CG, Huibregtse JM and Howley PM . (1996). Cancer Res., 56, 2649–2654.
Maltzman W and Czyzyk L . (1984). Mol. Cell. Biol., 4, 1689–1694.
Maya R, Balass M, Kim ST, Shkedy D, Leal JF, Shifman O, Moas M, Buschmann T, Ronai Z, Shiloh Y, Kastan MB, Katzir E and Oren M . (2001). Genes Dev., 15, 1067–1077.
Nakamura S, Roth JA and Mukhopadhyay T . (2000). Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 9391–9398.
O'Hagan HM and Ljungman M . (2004). Mutat. Res., 546, 7–15.
O'Hagan HM and Ljungman M . Exp. Cell. Res., (in press).
Rodriguez MS, Desterro JM, Lain S, Lane DP and Hay RT . (2000). Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 8458–8467.
Rotter V, Abutbul H and Ben-Ze'ev A . (1983). EMBO J., 2, 1041–1047.
Rubbi CP and Milner J . (2003). EMBO J., 22, 6068–6077.
Scheer U and Benavente R . (1990). BioEssays, 12, 14–21.
Scheer U, Hugle B, Hazan R and Rose KM . (1984). J. Cell Biol., 99, 672–679.
Schneiderhan N, Budde A, Zhang Y and Brune B . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 2857–2868.
Shaulsky G, Goldfinger N, Ben-Ze'ev A and Rotter V . (1990). Mol. Cell. Biol., 10, 6565–6577.
Sherr CJ and Weber JD . (2000). Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 10, 94–99.
Shieh SY, Ikeda M, Taya Y and Prives C . (1997). Cell, 91, 325–334.
Shieh SY, Taya Y and Prives C . (1999). EMBO J., 18, 1815–1823.
Shinozaki T, Nota A, Taya Y and Okamoto K . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 8870–8880.
Siliciano JD, Canman CE, Taya Y, Sakaguchi K, Appella E and Kastan MB . (1997). Genes Dev., 11, 3471–3481.
Stommel JM, Marchenko ND, Jimenez GS, Moll UM, Hope TJ and Wahl GM . (1999). EMBO J., 18, 1660–1672.
Symonds H, Krall L, Remington L, Saenz-Robles M, Lowe S, Jacks T and Van Dyke T . (1994). Cell, 78, 703–711.
Tao W and Levine AJ . (1999). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 96, 6937–6941.
Unger T, Juven-Gershon T, Moallem E, Berger M, Vogt Sionov R, Lozano G, Oren M and Haupt Y . (1999). EMBO J., 18, 1805–1814.
Wang W, Takimoto R, Rastinejad F and El-Deiry WS . (2003). Mol. Cell. Biol., 23, 2171–2181.
Wang X, Michael D, de Murcia G and Oren M . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 15697–15702.
Wu L and Levine AJ . (1997). Mol. Med., 3, 441–451.
Wu X, Bayle JH, Olson D and Levine AJ . (1993). Genes Dev., 7, 1126–1132.
Xirodimas DP, Stephen CW and Lane DP . (2001). Exp. Cell Res., 270, 66–77.
Yu ZK, Geyer RK and Maki CG . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 5892–5897.
Zhang Y and Xiong Y . (2001). Science, 292, 1910–1915.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (CA-82376) and from funds from the University of Michigan Cancer Biology Training Program and Rackham Graduate School.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O'Hagan, H., Ljungman, M. Nuclear accumulation of p53 following inhibition of transcription is not due to diminished levels of MDM2. Oncogene 23, 5505–5512 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207709
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207709
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
CDK9 activity is critical for maintaining MDM4 overexpression in tumor cells
Cell Death & Disease (2020)
-
Nucleolar control of p53: a cellular Achilles’ heel and a target for cancer therapy
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2014)
-
Small-molecule multi-targeted kinase inhibitor RGB-286638 triggers P53-dependent and -independent anti-multiple myeloma activity through inhibition of transcriptional CDKs
Leukemia (2013)
-
R-Roscovitine simultaneously targets both the p53 and NF-κB pathways and causes potentiation of apoptosis: implications in cancer therapy
Cell Death & Differentiation (2008)
-
The ubiquitin–proteasome system regulates p53-mediated transcription at p21waf1 promoter
Oncogene (2007)