Abstract
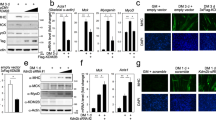
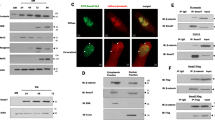
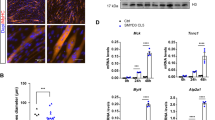
Smad proteins transduce signals from transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) superfamily ligands to regulate the expression of target genes. In order to identify novel partners of Smad proteins in transcriptional regulation, we performed a two-hybrid screen using Smad5, a protein that is activated predominantly by bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling. We identified an interaction between Smad5 and suppressor of variegation 3-9 homolog 2 (Suv39h2), a chromatin modifier enzyme. Suv39h proteins are histone methyltransferases that methylate histone H3 on lysine 9, resulting in transcriptional repression or silencing of target genes. Biochemical studies in mammalian cells demonstrated that Smad5 binds to both known mammalian isoforms of Suv39h proteins, and that Smad proteins activated by the TGF-β signaling pathway, Smad2 and Smad3, do not bind with significant affinity. Functional studies using the muscle creatine kinase (MCK) promoter, which is suppressed by BMP signaling, demonstrate that Suv39h proteins and Smads cooperate to repress promoter activity. These data suggest a model where association of Smad proteins with Suv39h methyltransferases can repress or silence genes involved in developmental processes, and argues that inefficient gene repression may result in the alteration of the differentiated phenotype. Thus, examination of the Smad–Suv interaction may provide insight into the mechanism of phenotypic determination mediated by BMP signaling.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aagaard L, Laible G, Selenko P, Schmid M, Dorn R, Schotta G, Kuhfittig S, Wolf A, Lebersorger A, Singh PB, Reuter G and Jenuwein T . (1999). EMBO J., 18, 1923–1938.
Akiyama S, Katagiri T, Namiki M, Yamaji N, Yamamoto N, Miyama K, Shibuya H, Ueno N, Wozney JM and Suda T . (1997). Exp. Cell Res., 235, 362–369.
Bannister AJ, Zegerman P, Partridge JF, Miska EA, Thomas JO, Allshire RC and Kouzarides T . (2001). Nature, 410, 120–124.
Brubaker KD, Corey E, Brown LG and Vessella RL . (2004). J. Cell Biochem., 91, 151–160.
Caestecker MD and Meyrick B . (2001). Respir. Res., 2, 193–197.
Chakraborty S, Sinha KK, Senyuk V and Nucifora G . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 5229–5237.
Cong YS and Bacchetti S . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 35665–35668.
Davey C, Fraser R, Smolle M, Simmen MW and Allan J . (2003). J. Mol. Biol., 325, 873–887.
de Caestecker MP, Hemmati P, Larisch-Bloch S, Ajmera R, Roberts AB and Lechleider RJ . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 13690–13696.
de Caestecker MP, Parks WT, Frank CJ, Castagnino P, Bottaro DP, Roberts AB and Lechleider RJ . (1998). Genes Dev., 12, 1587–1592.
Feng XH, Zhang Y, Wu RY and Derynck R . (1998). Genes Dev., 12, 2153–2163.
Firestein R, Cui X, Huie P and Cleary ML . (2000). Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 4900–4909.
Fujii M, Takeda K, Imamura T, Aoki H, Sampath TK, Enomoto S, Kawabata M, Kato M, Ichijo H and Miyazono K . (1999). Mol. Cell. Biol., 10, 3801–3813.
Hogan BL . (1996). Genes Dev., 10, 1580–1594.
Howe JR, Bair JL, Sayed MG, Anderson ME, Mitros FA, Petersen GM, Velculescu VE, Traverso G and Vogelstein B . (2001). Nat. Genet., 28, 184–187.
Itoh S, Ericsson J, Nishikawa J, Heldin CH and ten Dijke P . (2000). Nucleic Acids Res., 28, 4291–4298.
Janknecht R, Wells NJ and Hunter T . (1998). Genes Dev., 12, 2114–2119.
Jenuwein T and Allis CD . (2001). Science, 293, 1074–1080.
Keeton EK, Fletcher TM, Baumann CT, Hager GL and Smith CL . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 28247–28255.
Kouzarides T . (2002). Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 12, 198–209.
Lachner M, O’Carroll D, Rea S, Mechtler K and Jenuwein T . (2001). Nature, 410, 116–120.
Li J, Lin Q, Yoon HG, Huang ZQ, Strahl BD, Allis CD and Wong J . (2002). Mol. Cell. Biol., 22, 5688–5697.
Liberati NT, Moniwa M, Borton AJ, Davie JR and Wang XF . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 22595–22603.
Liu D, Black BL and Derynck R . (2001). Genes Dev., 15, 2950–2966.
Luo K, Stroschein SL, Wang W, Chen D, Martens E, Zhou S and Zhou Q . (1999). Genes Dev., 13, 2196–2206.
Macaluso M, Cinti C, Russo G, Russo A and Giordano A . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 3511–3517.
Macias-Silva M, Hoodless PA, Tang SJ, Buchwald M and Wrana JL . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 25628–25636.
Massague J and Wotton D . (2000). EMBO J., 19, 1745–1754.
Melcher M, Schmid M, Aagaard L, Selenko P, Laible G and Jenuwein T . (2000). Mol. Cell. Biol., 20, 3728–3741.
Melhuish TA and Wotton D . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 39762–39766.
Moustakas A, Souchelnytskyi S and Heldin CH . (2001). J. Cell Sci., 114, 4359–4369.
Nielsen SJ, Schneider R, Bauer UM, Bannister AJ, Morrison A, O’Carroll D, Firestein R, Cleary M, Jenuwein T, Herrera RE and Kouzarides T . (2001). Nature, 412, 561–565.
Peters AH, O’Carroll D, Scherthan H, Mechtler K, Sauer S, Schofer C, Weipoltshammer K, Pagani M, Lachner M, Kohlmaier A, Opravil S, Doyle M, Sibilia M and Jenuwein T . (2001). Cell, 107, 323–337.
Pouliot F and Labrie C . (2002). J. Endocrinol., 172, 187–198.
Rea S, Eisenhaber F, O’Carroll D, Strahl BD, Sun ZW, Schmid M, Opravil S, Mechtler K, Ponting CP, Allis CD and Jenuwein T . (2000). Nature, 406, 593–599.
Reeves R, Gorman CM and Howard B . (1985). Nucleic Acids Res., 13, 3599–3615.
Remacle JE, Kraft H, Lerchner W, Wuytens G, Collart C, Verschueren K, Smith JC and Huylebroeck D . (1999). EMBO J., 18, 5073–5084.
Snowden AW, Gregory PD, Case CC and Pabo CO . (2002). Curr. Biol., 12, 2159–2166.
Strahl BD and Allis CD . (2000). Nature, 403, 41–45.
Vandel L, Nicolas E, Vaute O, Ferreira R, Ait-Si-Ali S and Trouche D . (2001). Mol. Cell. Biol., 21, 6484–6494.
Vaute O, Nicolas E, Vandel L and Trouche D . (2002). Nucleic Acids Res., 30, 475–481.
von Bubnoff A and Cho KW . (2001). Dev. Biol., 239, 1–14.
Whitman M . (1998). Genes Dev., 12, 2445–2462.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by HL65681 and CA102660 to RJL. PF was a recipient of a Post-Doctoral Fellowship by American Heart Association. We thank T Jenuwein, T Kouzarides, J Wrana, L Attisano, D Trouche, E Olson, A Lassar, R Derynck and P ten Dijke for constructs. We would like to thank AB Roberts and CS Hill for helpful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frontelo, P., Leader, J., Yoo, N. et al. Suv39h histone methyltransferases interact with Smads and cooperate in BMP-induced repression. Oncogene 23, 5242–5251 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207660
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207660
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
H3K9 methylation is a barrier during somatic cell reprogramming into iPSCs
Nature Genetics (2013)
-
An in vivo reporter of BMP signaling in organogenesis reveals targets in the developing kidney
BMC Developmental Biology (2008)
-
The contradictory definitions of heterochromatin: transcription and silencing
Chromosoma (2006)