Abstract
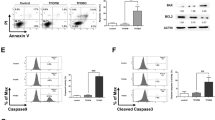
In this work, we describe the process of cell death induced by a series of new benzo(b)thiophenesulphonamide 1,1-dioxide derivatives (BTS) that have been selected as candidate antineoplastic drugs. Human leukaemic CCRF-CEM cells incubated with BTS undergo a typical apoptotic process that includes cell shrinkage, phosphatidylserine translocation to the cell surface, mitochondrial dysfunction, caspase activation, chromatin condensation and internucleosomal DNA degradation. Mitochondrial alterations included dissipation of the mitochondrial membrane potential, oxidation of the phospholipid cardiolipin, release of cytochrome c and uncoupling of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, leading to a decrease of the intracellular ATP pool. Activation of caspase-8, -9 and -3 takes place during BTS-induced apoptosis. Either the addition of the specific caspase-8 inhibitor Z-IETD-fmk, or the overexpression of the antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 significantly prevented BTS-induced apoptosis, suggesting the involvement of both caspase-8-regulated and mitochondria-dependent signalling pathways in this process. BTS induce a significant increase in the production and accumulation of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) that can be observed within minutes after drug addition. Moreover, cytochrome c release, caspase-3 activation and cell death can be completely abrogated by a previous incubation with the antioxidant N-acetyl-cysteine. These results suggest that ROS are essential mediators in BTS-induced apoptosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso MM, Encio I, Martinez-Merino V, Gil M and Migliaccio M . (2001). Br. J. Cancer, 85, 1400–1402.
Boutonnat J, Barbier M, Muirhead K, Mousseau M, Grunwald D, Ronot X and Seigneurin D . (2000). Cytometry, 42, 50–60.
Bozolla JJ and Russell LD . (1992). Electron Microscopy. Jones, Bartlett (ed). Boston, MA.
Buttke TM and Sandstrom PA . (1995). Free Radic. Res., 22, 389–397.
Costantini P, Jacotot E, Decaudin D and Kroemer G . (2000). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 92, 1042–1053.
Cotter TG, Glynn JM, Echeverri F and Green DR . (1992). Anticancer Res., 12, 773–779.
Ferreira CG, Span SW, Peters GJ, Kruyt FA and Giaccone G . (2000) Cancer Res., 60, 7133–7141.
Green DR, Bissonnette RP and Cotter TG . (1994). Important Adv. Oncol., 37–52.
Green DR and Reed JC . (1998). Science, 281, 1309–1312.
Hartmann BL, Geley S, Loffler M, Hattmannstorfer R, Strasser-Wozak EM, Auer B and Kofler R . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 713–719.
Howbert JJ, Grossman CS, Crowell TA, Rieder BJ, Harper RW, Kramer KE, Tao EV, Aikins J, Poore GA, Rinzel SM, Grindey GB, Shaw WN and Todd GC . (1990). J. Med. Chem., 33, 2393–2407.
Huschtscha LI, Bartier WA, Ross CE and Tattersall MH . (1996). Br. J. Cancer, 73, 54–60.
Keller JN, Kindy MS, Holtsberg FW, St Clair DK, Yen HC, Germeyer A, Steiner SM, Bruce-Keller AJ, Hutchins JB and Mattson MP . (1998). J. Neurosci., 18, 687–697.
Kim PKM, Mahidhara R and Seol DW . (2001). Drug Res. Update, 4, 293–296.
Koren R, Rocker D, Kotestiano O, Liberman UA and Ravid A . (2000). J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol., 73, 105–112.
Kroemer G and Reed JC . (2000). Nat. Med., 6, 513–519.
Li PF, Dietz R and von Harsdorf R . (1999). EMBO J., 18, 6027–6036.
Martin SJ, Green DR and Cotter TG . (1994). Trends Biochem. Sci., 19, 26–30.
Martinez-Merino V, Gri MS, Encio I, Migliaccio H and Arteaga C (2000). Benzo(b)tiophere Sulphonamid 1,1-dioxide derivatives and their use as antineoplastic agents, Patent No WO 00/63202.
Mossmann T . (1983). J. Immunol. Method, 65, 55–59.
Nomura K, Imai H, Koumura T and Nakagawa Y . (2001). Biol. Signals Recept., 10, 81–92.
Oridate N, Higuchi M, Suzuki S, Shroot B, Hong WK and Lotan R . (1997a). Int. J. Cancer, 70, 484–487.
Oridate N, Lotan D, Mitchell MF, Hong WK and Lotan R . (1995). J. Cell. Biochem. Suppl., 23, 80–86.
Oridate N, Suzuki S, Higuchi M, Mitchell MF, Hong WK and Lotan R . (1997b). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 89, 1191–1198.
Phillips AC, Bates S, Ryan KM, Helin K and Vousden KH . (1997). Genes Dev., 11, 1853–1863.
Reed JC and Kroemer G . (2000). Cell Death Differ., 7, 1145.
Scudiero DA, Shoemaker RH, Paull KD, Monks A, Tierney S, Nofziger TH, Currens MJ, Seniff D and Boyd MR . (1988). Cancer Res., 48, 4827–4833.
Seki K, Yoshikawa H, Shiiki K, Hamada Y, Akamatsu N and Tasaka K . (2000). Chemother. Pharmacol., 45, 199–206.
Shapiro HM . (2000). Methods, 21, 271–279.
Skulachev VP . (1998). FEBS Lett., 423(3), 275–280.
Sosinski J, Thakar JH, Germain GS, Harwood FC and Houghton PJ . (1993). Biochem. Pharmacol., 45, 2135–2142.
Susin SA, Zamzami N and Kroemer G . (1998). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1366, 151–165.
Suzuki S, Higuchi M, Proske RJ, Oridate N, Hong WK and Lotan R . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 6380–6387.
Tang D, Lahti JM and Kidd VJ . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 9303–9307.
Taylor WR and Stark GR . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 35–43.
Umansky V, Ratter F, Lampel S, Bucur M, Schirrmacher V and Ushmorov A . (2001). Exp. Cell Res., 265, 274–282.
Umansky V, Rocha M, Breitkreutz R, Hehner S, Bucur M, Erbe N, Droge W and Ushmorov A . (2000). J. Cell Biochem., 78, 578–587.
Zamai L, Canonico B, Luchetti F, Ferri P, Melloni E, Guidotti L, Cappellini A, Cutroneo G, Vitale M and Papa S . (2001). Cytometry, 44, 57–64.
Zamzami N and Kroemer G . (2001). Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol., 2, 67–71.
Zamzami N, Marchetti P, Castedo M, Decaudin D, Macho A, Hirsch T, Susin SA, Petit PX, Mignotte B and Kroemer G . (1995). J. Exp. Med., 182, 367–377.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alonso, M., Asumendi, A., Villar, J. et al. New benzo(b)thiophenesulphonamide 1,1-dioxide derivatives induce a reactive oxygen species-mediated process of apoptosis in tumour cells. Oncogene 22, 3759–3769 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206435
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206435
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Oxidation of protein-bound methionine in Photofrin-photodynamic therapy-treated human tumor cells explored by methionine-containing peptide enrichment and quantitative proteomics approach
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Discovery of monocarbonyl curcumin-BTP hybrids as STAT3 inhibitors for drug-sensitive and drug-resistant breast cancer therapy
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
ROS-induced cleavage of NHLRC2 by caspase-8 leads to apoptotic cell death in the HCT116 human colon cancer cell line
Cell Death & Disease (2017)
-
Benzo[b]thiophenesulphonamide 1,1-dioxide derivatives inhibit tNOX activity in a redox state-dependent manner
British Journal of Cancer (2005)