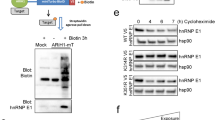
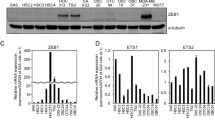
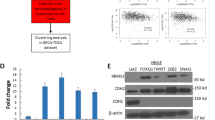
Abstract
Ets proteins constitute a family of conserved sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins and function as transcription factors. ETS1 plays important roles in differentiation, lymphoid cell development, invasiveness and angiogenesis. Such diverse roles of ETS1 are likely to be dependent on its associated proteins. A yeast two-hybrid screen was conducted and here we describe a novel ETS1 interacting protein designated as ETS1-associated protein II (EAPII). EAPII protein interacts with ETS1 and other Ets proteins (ETS2 and FLI1) both in vitro and in vivo. Indirect immunofluorescence demonstrated that EAPII is predominately localized to the nucleus of mammalian cells. EAPII negatively modulates ETS1 transcriptional activity and attenuates synergistic transactivation by ETS1 and AP-1. Significantly, re-expression of EAPII inhibits the migration of epithelial cancer cells, but does not affect cell viability. Therefore, EAPII is a novel ETS1 modulator that regulates specific aspects of the ETS1 functions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassuk AG and Leiden JM . (1995). Immunity, 3, 223–237.
Chen Z, Fisher RJ, Riggs CW, Rhim JS and Lautenberger JA . (1997). Cancer Res., 57, 2013–2019.
Davidson B, Reich R, Goldberg I, Gotlieb WH, Kopolovic J, Berner A, Ben-Baruch G, Bryne M and Nesland JM . (2001). Clin. Cancer Res., 7, 551–557.
de Nigris F, Mega T, Berger N, Barone MV, Santoro M, Viglietto G, Verde P and Fusco A . (2001). Cancer Res., 61, 2267–2275.
Delannoy-Courdent A, Mattot V, Fafeur V, Fauquette W, Pollet I, Calmels T, Vercamer C, Boilly B, Vandenbunder B and Desbiens X . (1998). J. Cell. Sci., 111,1521–1534.
Fisher RJ, Mavrothalassitis G, Kondoh A and Papas TS . (1991). Oncogene, 6, 2249–2254.
Fitzsimmons D, Hodsdon W, Wheat W, Maira SM, Wasylyk B and Hagman J . (1996). Genes Dev., 10, 2198–2211.
Ghysdael J and Boureux A . (1997). The ETS family of Transcriptional Regulators. Birkhauser Verlag: Basel, Switzerland.
Graves B and Petersen J . (1998). Advances in Cancer Research, Vol. 75. Academic Press: San Diego, CA, pp. 1–55.
Gri G, Savio D, Trinchieri G and Ma X . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 6431–6438.
Gyuris J, Golemis E, Chertkov H and Brent R . (1993). Cell, 75, 791–803.
He TC, Zhou S, da Costa LT, Yu J, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B . (1998). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 2509–2514.
Holzmeister J, Ludewig B, Pauli G and Simon D . (1993). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 197, 1229–1233.
Ito Y, Miyoshi E, Takeda T, Sakon M, Noda K, Tsujimoto M, Monden M, Taniguchi N and Matsuura N . (2000). Am. J. Clin. Pathol., 114, 719–725.
Iwasaka C, Tamaka K, Abe M and Sato Y . (1996). J. Cell. Physiol., 169, 522–531.
Koizumi S, Fisher RJ, Fujiwara S, Jorcyk C, Bhat NK, Seth A. and Papas TS . (1990). Oncogene, 5, 675–681.
Kramer B, Wiegmann K and Kronke M . (1995). J. Biol. Chem., 270, 6577–6583.
Li R, Pei H and Papas T . (1999). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 96, 3876–3881.
Li R, Pei H and Watson DK . (2000a). Oncogene, 19, 6514–6523.
Li R, Pei H, Watson DK and Papas TS . (2000b). Oncogene, 19, 745–753.
Maroulakou IG and Bowe DB . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 6432–6442.
Narayan VA, Kriwacki RW and Caradonna JP . (1997). J.Biol. Chem., 272, 7801–7809.
Nimer S, Zhang J, Avraham H and Miyazaki Y . (1996). Blood, 88, 66–74.
Oda N, Abe M and Sato Y . (1999). J. Cell. Physiol., 178, 121–132.
Ozaki I, Mizum T, Zhao G, Yotsumoto H, Hara T, Kajihara S, Hisatomi A, Sakai T and Yamamoto K . (2000). Cancer Res., 60, 6519–6525.
Pype S, Declercq W, Ibrahimi A, Michiels C, Van Rietschoten JG, Dewulf N, de Boer M, Vandenabeele P, Huylebroeck D and Remacle JE . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 18586–18593.
Remy P and Baltzinger M . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 6417–6431.
Rutter JL, Mitchel TI, Buttice G, Meyers J, Gusella JF, Ozelius LJ and Brinckerhoff CE . (1998). Cancer Res., 58, 5321–5325.
Seidel JJ and Graves BJ . (2002). Genes Dev., 16, 127–137.
Sementchenko VI, Sehweinfest CW, Papas TS and Watson DK . (1998). Oncogene, 17, 2883–2888.
Sementchenko VI and Watson DK . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 6533–6548.
Seth A, Hodge DR, Thompson DM, Robinson L, Panayiotakis A, Watson DK and Papas TS . (1993). AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses, 9, 1017–1023.
Sharrocks AD . (2001). Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol., 2, 827–837.
Skalicky JJ, Donaldson LW, Petersen JM, Graves BJ and McIntosh LP . (1996). Protein sci., 5, 296–309.
Thomas RS, Yymms MJ, McKinlay LH, Shannon MF, Seth A and Kola I . (1997). Oncogens, 14, 2845–2855.
Verger A and Duterque-Coquillaud M . (2002). Bioessays, 24, 362–370.
Wasylyk B, Wasylyk C, Flores P, Begue A, Leprince D and Stehelin D . (1990). Nature, 346, 191–193.
Watson DK, Li R, Sementchenko VI, Mavrothalassitis G and Seth A . (2002). Encyclopedia of Cancer, Vol. 2. Bertino JR (ed). Academic Press: New York, pp. 751–758.
Westermarck J and Kahari VM . (1999). FASEB J., 13, 781–792.
Wheat W, Fit/simmons D, Lennox H, Krautkramer SR, Gentile LN, McIntosh LP and Lagman J . (1999). Mol. Cell. Biol., 19, 2231–2241.
Yang X, Khossavi-Far R, Chang HY and Baltimore D . (1997). Cell, 89, 1067–1076.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr R Brent (The Molecular Sciences Institute, Berkely, CA, USA) for generously providing the yeast two-hybrid reagents, Dr R Tjian (University of California, Berkeley) for the pCMV-c-fos and pCMV-c-jun plasmids, and Drs J Rutter and C Brinckerhoff (Dartmouth Medical School, NH) for the pGL3-MMP1 plasmid. We thank Dr T Hsu for critical review of the manuscript. The GenBank accession number for the sequence of EAPII reported in this paper is AF201687, jointly deposited with Dr Takis S Papas. This study is dedicated to the memory of Dr Takis S Papas, a mentor, scientific colleague and friend. This work was supported in part by American Cancer Society Grant IRG97-151 and Start-up fund from Medical University of South Carolina (RL) and a National Institutes of Health Grant P01CA78582 (DKW).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pei, H., Yordy, J., Leng, Q. et al. EAPII interacts with ETS1 and modulates its transcriptional function. Oncogene 22, 2699–2709 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206374
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206374
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The PML nuclear bodies-associated protein TTRAP regulates ribosome biogenesis in nucleolar cavities upon proteasome inhibition
Cell Death & Differentiation (2012)
-
Structural basis for recognition of 5′-phosphotyrosine adducts by Tdp2
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2012)
-
Tyrosyl DNA phosphodiesterase 2, an enzyme fit for purpose
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2012)
-
Oncogenic role of EAPII in lung cancer development and its activation of the MAPK–ERK pathway
Oncogene (2011)
-
ΦC31 integrase interacts with TTRAP and inhibits NFκB activation
Molecular Biology Reports (2010)