Abstract
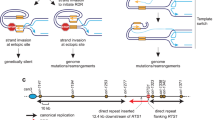
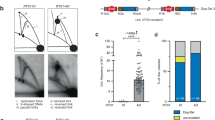
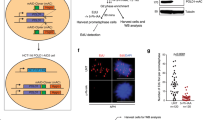
The mechanisms through which the oncoprotein c-Myc initiates locus-specific gene amplification are not understood. When analysing the initiation mechanism of c-Myc-dependent amplification of the mouse ribonucleotide reductase R2 (R2) gene, we observe c-Myc-dependent initiation of illegitimate DNA replication of the R2 gene. We demonstrate multiple simultaneous c-Myc-induced R2 replication forks, whereas R2 normally replicates with a single fork. In contrast, cyclin C replicates with only a single replication fork irrespective of c-Myc deregulation. In addition to de novo replication forks, c-Myc also initiates bi-allelic replication of R2, abrogating its normal mono-allelic replication pattern. Moreover, several chromosomal regions also display c-Myc-induced illegitimate replication profiles. Thus, c-Myc can act as an illegitimate replication-licensing factor that promotes de novo replication initiation and illegitimate replication timing that adversely impacts upon genomic stability.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blackwell TK, Huang J, Ma A, Kretzner L, Alt FW, Eisenmann RN, Weintraub H . 1993 Mol. Cell Biol. 9: 5216–5224
Brown PC, Tlsty TD, Schimke RT . 1983 Mol. Cell Biol. 3: 1097–1107
Butler DK, Yasuda LE, Yao MC . 1996 Cell 87: 1115–1122
Carroll SM, DeRose ML, Gaudray P, Moore CM, Needham-Vandevanter DR, Von Hoff DD, Wahl GM . 1988 Mol. Cell. Biol. 8: 1525–1533
Classon M, Henriksson M, Sumegi J, Klein G, Hammaskjold ML . 1987 Nature 330: 272–274
Denis N, Kitzis A, Kruh J, Dautry F, Crocos D . 1991 Oncogene 6: 1453–1457
Dijkwel PA, Vaughn JP, Hamlin JL . 1991 Mol. Cell. Biol. 11: 3850–3859
Felsher DW, Bishop JM . 1999a Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96: 3940–3944
Felsher DW, Bishop JM . 1999b Mol. Cell. 4: 199–207
Gandarillas A, Davies D, Blanchard J-M . 2000 Oncogene 19: 3278–3289
Hamlin JL, Ma C . 1990 Bioch. Biophys. Acta 1087: 107–125
Hamlin JL, Leu TH, Vaughn JP, Ma C, Dijkwel PA . 1991 Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 41: 203–239
Henriksson M, Classon M, Hammarskjold ML, Klein G, Sumegi J . 1988 Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 141: 202–207
Johnston RN, Beverley SM, Schimke RT . 1983 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80: 3711–3715
Kitsberg D, Selig S, Brandeis M, Simon I, Keshet I, Driscoll DJ, Nicholls RD, Cedar H . 1993 Nature 29: 459–463
Khan F, Clarke V, D'Eustachio P . 1994 Genomics 21: 128–137
Knudson Jr AG . 1986 Annu. Rev. Genet. 20: 231–251
Kuschak TI, Taylor C, McMillan-Ward E, Israels S, Henderson DW, Mushinski JF, Wright JA, Mai S . 1999 Gene 238: 351–365
Leonhardt H, Page AW, Weier HU, Bestor TH . 1992 Cell 71: 865–873
Li H, Lahti JM, Valentine M, Saito M, Reed SI, Look AT, Kidd VJ . 1996 Genomics 32: 253–259
Li Q, Dang CV . 1999 Mol. Cell. Biol. 19: 5339–5351
Littlewood TD, Hancock DC, Danielian PS, Parker MG, Evan GI . 1995 Nucleic Acids Res. 23: 1686–1690
Ma C, Martin S, Trask B, Hamlin JL . 1993 Genes Dev. 7: 605–620
Mai S, Jalava A . 1994 Nucl. Acids Res. 22: 2264–2273
Mai S, Mårtensson I-L . 1995 Nucl. Acids. Res. 23: 1–9
Mai S, Fluri M, Hanley-Hyde J . 1994 ‘Cyclin D2, a target for c-Myc-mediated gene amplification’. Basel Institute for Immunology Annual Report 1994 Basel, Switzerland 1994 p 53
Mai S, Fluri M, Siwarski D, Huppi K . 1996b Chromosome Res. 4: 365–371
Mai S, Hanley-Hyde J, Fluri M . 1996a Oncogene 12: 277–
Mai S, Hanley-Hyde J, Rainey GJ, Kuschak TI, Paul JT, Littlewood TD, Mischak H, Stevens LM, Henderson DW, Mushinski JF . 1999 Neoplasia 1: 241–252
Mai S . 1994 Gene 148: 253–260
Meinkoth J, Killary AM, Fournier RE, Wahl GM . 1987 Mol. Cell. Biol. 7: 1415–1424
Morris T, Thacker J . 1993 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 1392–1396
Pipiras E, Coquelle A, Bieth A, Debatisse M . 1998 EMBO J. 17: 325–333
Poupon M-F, Smith KA, Chernova OB, Gilbert C, Stark GR . 1996 Mol. Biol. Cell. 7: 345–354
Ruiz JC, Wahl GM . 1988 Mol. Cell. Biol. 8: 4302–4313
Schimke RT . 1988 J. Biol. Chem. 263: 5989–5992
Simon I, Tenzen T, Reubinoff BE, Hillman D, McCarrey JR, Cedar H . 1999 Nature 401: 929–932
Singer MJ, Mesner LD, Friedman CL, Trask BJ, Hamlin JL . 2000 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 7921–7926
Smith KA, Gorman PA, Stark MB, Groves RP, Stark GR . 1990 Cell 63: 1219–1227
Smith KA, Stark MB, Gorman PA, Stark GR . 1992 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 5427–5431
Spradling AC . 1981 Cell 27: 193–201
Stark GR . 1993 Adv. Cancer Res. 61: 87–113
Statsoft Electronic Statistics Textbook, /Nonparametric Statistics, http://www.statsoft.com/textbook/stnonpar.html
Thelander L, Berg P . 1986 Mol. Cell. Biol. 6: 3433–3442
Tlsty TD, Margolin BH, Lum K . 1989 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86: 9441–9445
Wahl GM, Padgett RA, Stark GR . 1979 J. Biol. Chem. 254: 8679–8689
Wang S, Dijkwel PA, Hamlin JL . 1998 Mol. Cell. Biol. 18: 39–50
Wells J, Held P, Illeye S, Heintz NH . 1996 Mol. Cell. Biol. 16: 634–647
Wiener F, Mai S . 2000 Technical Tips Online, 1:88:TO1884
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mrs Mary Cheang (Biostatistical Consulting Unit, Department of Community Health Services, Faculty of Medicine, University of Manitoba) for statistical analysis. We thank our colleagues, Drs A Begleiter, GG Hicks, T Fest and JF Mushinski, for critical reading of this manuscript. TI Kuschak was supported by a GH Sellers Graduate studentship awarded through CancerCare Manitoba. S Mai and JA Wright were funded through the National Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada (S Mai NSERC grant # 311-3135-03; JA Wright NSERC grant # 311-1735-05), and the Medical Research Council (JA Wright MRC grant # 321-3119-70, S Mai CIHR grant # 321-3135-19).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuschak, T., Kuschak, B., Taylor, C. et al. c-Myc initiates illegitimate replication of the ribonucleotide reductase R2 gene. Oncogene 21, 909–920 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205145
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205145
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Global regulation of genome duplication in eukaryotes: an overview from the epifluorescence microscope
Chromosoma (2008)
-
Telomeric aggregates and end-to-end chromosomal fusions require myc box II
Oncogene (2007)
-
Inhibitory effect of c-Myc on p53-induced apoptosis in leukemia cells. Microarray analysis reveals defective induction of p53 target genes and upregulation of chaperone genes
Oncogene (2005)