Abstract
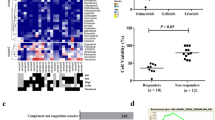
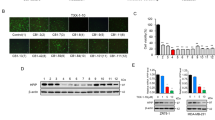
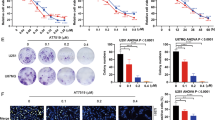
Despite many efforts to alter the relentlessly aggressive progression of tumors of neural origin, individuals bearing these tumors exhibit poor prognosis for long-term survival. In an attempt to find an effective treatment, we examined the efficacy of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, flurbiprofen, to suppress the growth of tumor cell lines derived from medulloblastoma and glioblastoma multiforme. Results from cell proliferation assays have revealed that flurbiprofen effectively inhibits the growth of various tumor cells in a dose-dependent manner and causes a noticeable change in the progression of cells through cell cycle stages. Treatment of tumor cells with flurbiprofen reduced the number of cells in G1 and G2, and significantly increased their numbers in S phase, suggesting that, flurbiprofen accelerates G1/S entry, and/or delays cell exit from S to G2/M stages. Results from RNase protection assay and Western blot analysis showed that while treatment of cells with flurbiprofen causes a minor change in the RNA level of different cyclins, there is a significant decrease in the level of cyclin B protein upon flurbiprofen treatment. Examination of tumor suppressors by RNase protection technique showed a subtle increase in the levels of several tumor suppressors upon flurbiprofen treatment. Interestingly, at the protein level, p53 tumor suppressor was substantially increased upon flurbiprofen treatment, yet the level of p21, a downstream target for p53 remained unchanged. Curiously, treatment of the cells with flurbiprofen enhanced the level of COX-2 expression. Results from co-immunoprecipitation showed association of COX-2 with p53 in tumor cells. These observations suggest that the interaction of COX-2 with p53 may cause p21-independent suppression of tumor cell growth upon flurbiprofen treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deininger MH, Weller M, Streffer J, Mittelbronn M, Meyermann R . 1999 Acta Neuropathol. 98: 240–244
DuBois RN, Abramson SB, Crofford L, Gupta RA, Simon LS, Van DePutte LBA, Lipsky PE . 1998 FASEB J. 12: 1063–1073
Fung K-M, Trojanowski JQ . 1995 J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 54: 285–296
Goldberg Y, Nassif II, Pittas A, Tsai LL, Dynlacht BD, Rigas B, Shiff SJ . 1996 Oncogene 12: 893–901
Gottifredi V, Peschiaroli A, Fimia GM, Malone R . 1999 J. Cell. Sci. 112: 2397–2407
Grubbs CJ, Lubet RA, Koki AT, Leahy KM, Masferrer JL, Steele VE, Kelloff GJ, Hill DL, Seibert K . 2000 Cancer Res. 60: 5599–5602
Hart MN, Earle KM . 1973 Cancer 32: 890–897
Joki T, Heese O, Nikas DC, Bello B, Zhang J, Kraeft S-K, Seyfried NT, Abe T, Chen LB, Carroll RS, Black PM . 2000 Cancer Res. 60: 4926–4931
Keller JJ, Offerhaus GJA, Polak M, Goodman SN, Zahurak ML, Hylind LM, Hamilton SR, Giardiello FM . 1999 Gut 45: 822–828
Kleihues P, Cavanee WK . 2000 Pathology and Genetics of Tumors of the Nervous System TARC Press
Kohn KW, Jackman J, O'Connor PM . 1994 J. Cell. Biochem. 54: 440–452
Matsuhashi N, Nakajima A, Fukushima Y, Yazaki Y, Oka T . 1997 Gut 40: 344–349
Molenaar WM, Trojanowski JQ . 1994 Crit. Rev. Oncology/Hematology 17: 1–25
Smith WL, Marnett LJ . 1991 Biochem. Biophys, Acta. 1083: 1–17
Souza RF, Shewmake K, Beer DG, Cryer B, Spechler SJ . 2000 Cancer Res. 60: 5767–5772
Taylor MT, Lawson KR, Ignatenko NA, Marek SE, Stringer DE, Skovan BA, Gerner EW . 2000 Cancer Res. 60: 6607–6610
Tegeder I, Niederberger E, Israr E, Gühring H, Brüne K, Euchenhofer C, Grösch S, Geisslinger G . 2001 FASEB J. 15: 595–597
von Knethen A, Callsen D,, Brüne B . 1999 Immunol. 163: 2858–2866
Warner TD, Giuliano F, Vojnovic I, Bukasa A, Mitchell JA, Vane JR . 1999 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96: 7563–7568
Wechter WJ, Murray Jr ED, Kantoci D, Quiggle DD, Leipold DD, Gibson KM, McCracken JD . 2000a Life Sciences 66: 745–753
Wechter WJ, Leipold DD, Murray Jr ED, Quiggle DD, McCracken JD, Barrios RS, Greenberg NM . 2000b Cancer Res. 60: 2203–2208
Williams CS, DuBois RN . 1996 Am. J. Physiol. 270: G393–G400
Williams CS, Watson AJM, Sheng H, Helou R, Shao J, DuBois RN . 2000 Cancer Res. 60: 6045–6051
Zhang X, Morham SG, Langenbach R, Young DA . 1999 J. Exp. Med. 190: 451–459
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the contributions of Dr Reiner Class for performing FACs analysis, and Dr William J Wechter for a conversation which sparked this research. We would like to thank past and present members of the Center for Neurovirology and Cancer Biology for insightful discussion, and sharing of ideas and reagents, Dr Kris Reiss for his editorial contributions and discussions, Dr J Gordon for statistical analysis, and C Schriver for preparation of the manuscript. This work was made possible by grants awarded by NIH to K Khalili.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
King, Jr, J., Khalili, K. Inhibition of human brain tumor cell growth by the anti-inflammatory drug, flurbiprofen. Oncogene 20, 6864–6870 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204907
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204907
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Flurbiprofen inhibits cell proliferation in thyroid cancer through interrupting HIP1R-induced endocytosis of PTEN
European Journal of Medical Research (2022)
-
Drug Repurposing in Medulloblastoma: Challenges and Recommendations
Current Treatment Options in Oncology (2021)
-
Anticancer activity of tolfenamic acid in medulloblastoma: a preclinical study
Tumor Biology (2013)
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug use and brain tumour risk: a case–control study within the Clinical Practice Research Datalink
Cancer Causes & Control (2013)
-
R-flurbiprofen, a novel nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, decreases cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in pituitary adenoma cells in vitro
Journal of Neuro-Oncology (2012)