Abstract
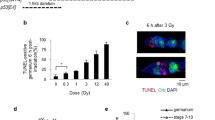
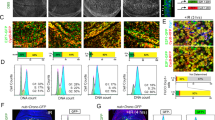
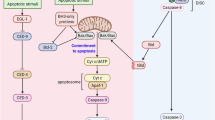
In mammalian cells, the p53 protein is a key regulator of the cell cycle following DNA damage. In the present study, we investigated the function of p53 in the A6 amphibian cell line. Using various specific Xenopus p53 monoclonal antibodies, we showed that Xenopus p53 accumulates after DNA damage, including gamma and UV irradiation or treatment with adriamycin. Such accumulation is accompanied by an increase in the apparent molecular weight of the protein. This change was shown to be the result of a phosphorylation event that occurs after DNA damage. Accumulation of Xenopus p53 is parallel to a drastic change in the cell cycle distribution. Brief exposure to adriamycin or gamma irradiation induces reversible growth arrest, whereas long-term exposure to adriamycin leads to apoptosis. Taken together, these results indicate that p53 has a similar behaviour in frog cells and mammalian cells, and that it conserves two activities, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amariglio F, Tchang F, Prioleau MN, Soussi T, Cibert C, Mechali M . 1997 Oncogene 15: 2191–2199
Andrews NC, Faller DV . 1991 Nucleic Acids Res. 19: 2499
Bisbee CA, Baker MA, Wilson AC, Haji-Azimi I, Fischberg M . 1977 Science 195: 785–787
Brodsky MH, Nordstrom W, Tsang G, Kwan E, Rubin GM, Abrams JM . 2000 Cell 101: 103–113
Bunz F, Dutriaux A, Lengauer C, Waldman T, Zhou S, Brown JP, Sedivy JM, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B . 1998 Science 282: 1497–1501
Chen XB, Ko LJ, Jayaraman L, Prives C . 1996 Gene Dev. 10: 2438–2451
Dequiedt F, Kettmann R, Burny A, Willems L . 1995 Virology 209: 676–683
Dileonardo A, Linke SP, Clarkin K, Wahl GM . 1994 Gene Dev. 8: 2540–2551
El-Deiry WS, Kern SE, Pientenpol JA, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B . 1992 Nature Gen. 1: 45–49
Halazonetis TD, Davis LJ, Kandil AN . 1993 EMBO J. 12: 1021–1028
Hansen S, Hupp TR, Lane DP . 1996 J. Biol. Chem. 271: 3917–3924
Hardy-Bessard AC, Garay E, Lacronique V, Legros Y, Demarquay C, Houque A, Portefaix JM, Granier C, Soussi T . 1998 Oncogene 16: 883–890
Hupp TR, Meek DW, Midgley CA, Lane DP . 1992 Cell 71: 875–886
Jin S, Martinek S, Joo WS, Wortman JR, Mirkovic N, Sali A, Yandell MD, Pavletich NP, Young MW, Levine AJ . 2000 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 97: 7301–7306
Kuerbitz SJ, Plunkett BS, Walsh WV, Kastan MB . 1992 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 89: 7491 7495
Kussie PH, Gorina S, Marechal V, Elenbaas B, Moreau J, Levine AJ, Pavletich NP . 1996 Science 274: 948–953
Levine AJ . 1997 Cell 88: 323–331
Marechal V, Elenbaas B, Taneyhill L, Piette J, Mechali M, Nicolas JC, Levine AJ, Moreau J . 1997 Oncogene 14: 1427–1433
Mayr B, Blauensteiner J, Edlinger A, Reifinger M, Alton K, Schaffner G, Brem G . 2000 Res. Vet. Sci. 68: 63–70
Meek DW . 1998 Cell Signal 10: 159–166
Nicol CJ, Harrison ML, Laposa RR, Gimelshtein IL, Wells PG . 1995 Nat. Genet. 10: 181–187
Nigro JM, Sikorski R, Reed SI, Vogelstein B . 1992 Mol. Cell Biol. 12: 1357–1365
Norimura T, Nomoto S, Katsuke M, Gondo Y, Kondo S . 1996 Nature Med. 2: 577–580
Ory K, Legros Y, Auguin C, Soussi T . 1994 EMBO J. 13: 3496–3504
Rafferty K . 1969 Biology of Amphibian Tumors. Mirzell M. (ed) Springer Verlag: Berlin pp. 52–81
Ridgway PJ, Soussi T, Braithwaite AW . 1994 J. Virol. 68: 7178–7187
Shieh SY, Ikeda M, Taya Y, Prives C . 1997 Cell 91: 325–334
Soussi T, Caron de Fromentel C, Méchali M, May P, Kress M . 1987 Oncogene 1: 71–78
Soussi T, Caron de Fromentel C, Stürzbecher HW, Ullrich S, Jenkins J, May P . 1989 J. Virol. 63: 3894–3901
Soussi T, Dehouche K, Béroud C . 2000 Hum. Mutat. 15: 105–113
Soussi T, May P . 1996 J. Mol. Biol. 260: 623–637
Tchang F, Mechali M . 1999 Exp. Cell. Res. 251: 46–56
Tokino T, Nakamura Y . 2000 Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 33: 1–6
Veldhoen N, Stewart J, Brown R, Milner J . 1998 Oncogene 16: 249–255
Wang Y, Farmer G, Soussi T, Prives C . 1995 Oncogene 10: 779–784
Wilson GD, McNally NJ, Dunphy E, Karcher H, Pfragner R . 1985 Cytometry 6: 641–647
Woo RA, McLure KG, Lees-Miller SP, Rancourt DE, Lee PWK . 1998 Nature 394: 700–704
Acknowledgements
We thank J Bram, M Le Bras, Z Macïorowski and G Zalcman for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by grants from the Ligue Nationale contre le Cancer (Comité de Paris) and the Association pour la Recherche contre le Cancer (ARC). K Bensaad is supported by a fellowship from the Ligue Nationale contre le Cancer (Comité National).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bensaad, K., Rouillard, D. & Soussi, T. Regulation of the cell cycle by p53 after DNA damage in an amphibian cell line. Oncogene 20, 3766–3775 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204492
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204492
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
p53 induction and cell viability modulation by genotoxic individual chemicals and mixtures
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2018)
-
Cytotoxic properties of the nitrosyl iron complex with phenylthiyl
Russian Chemical Bulletin (2011)
-
Lack of p53 induction in fish cells by model chemotherapeutics
Oncogene (2006)
-
The proline-rich region of mouse p53 influences transactivation and apoptosis but is largely dispensable for these functions
Oncogene (2003)
-
Data mining the p53 pathway in the Fugu genome: evidence for strong conservation of the apoptotic pathway
Oncogene (2003)