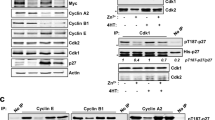
Abstract
MYC transcription factors are potent stimulators of cell proliferation. It has been suggested that the CDK-inhibitor p27kip1 is a critical G1 phase cell cycle target of c-MYC. We show here that mouse embryo fibroblasts deficient for both p27kip1 and the related p21cip1 are still responsive to stimulation by c-MYC and can be arrested in G1 by a dominant negative mutant of c-MYC. This growth arrest can be overruled by ectopic expression of E2F or adenovirus E1A, but not by a mutant of E1A defective for binding to retinoblastoma family proteins. We show that fibroblasts with a genetic disruption of all three retinoblastoma family members (pRb, p107 and p130) are unresponsive to a dominant negative c-MYC mutant. These data indicate that p27kip1 is not the only rate limiting cell cycle target of c-MYC and suggest that regulation of E2F is also essential for c-MYC's mitogenic activity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berns A, van der Lugt N, Alkema M, van Lohuizen M, Domen J, Acton D, Allen J, Laird PW and Jonkers J. . 1994 Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 59: 435–447.
Berns K, Hijmans EM and Bernards R. . 1997 Oncogene 15: 1347–1356.
Berns K, Hijmans EM, Koh E, Daley GQ and Bernards R. . 2000 Oncogene 19: 3330–3334.
Bouchard C, Thieke K, Maier A, Saffrich R, Hanley HJ, Ansorge W, Reed S, Sicinski P, Bartek J and Eilers M. . 1999 EMBO J. 18: 5321–5333.
Deng C, Zhang P, Harper JW, Elledge SJ and Leder P. . 1995 Cell 82: 675–684.
Dulic V, Lees E and Reed SI. . 1992 Science 257: 1958–1961.
Eilers M, Picard D, Yamamoto KR and Bishop JM. . 1989 Nature 340: 66–68.
Eilers M, Schirm S and Bishop JM. . 1991 EMBO J. 10: 133–141.
Fero ML, Rivkin M, Tasch M, Porter P, Carow CE, Firpo E, Polyak K, Tsai LH, Broudy V, Perlmutter RM, Kaushansky K and Roberts JM. . 1996 Cell 85: 733–744.
Galaktionov K, Chen X and Beach D. . 1996 Nature 382: 511–517.
Hateboer G, Hijmans EM, Nooij JB, Schlenker S, Jentsch S and Bernards R. . 1996 J. Biol. Chem. 271: 25906–25911.
Hermeking H, Rago C, Schuhmacher M, Li Q, Barrett JF, Obaya AJ, O'Connell BC, Mateyak MK, Tam W, Kohlhuber F, Dang CV, Sedivy JM, Eick D, Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW. . 2000 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 2229–2234.
Humbert PO, Verona R, Trimarchi JM, Rogers C, Dandapani S and Lees JA. . 2000 Genes Dev. 14: 690–703.
Hurford Jr RK, Cobrinik D, Lee MH and Dyson N. . 1997 Genes Dev. 11: 1447–1463.
Jacobs JJ, Scheijen B, Voncken JW, Kieboom K, Berns A and van Lohuizen M. . 1999 Genes Dev. 13: 2678–2690.
Jansen-Durr P, Meichle A, Steiner P, Pagano M, Finke K, Botz J, Wessbecher J, Draetta G and Eilers M. . 1993 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 3685–3689.
Kanda T, Sullivan KF and Wahl GM. . 1998 Curr. Biol. 8: 377–385.
Land H, Parada LF and Weinberg RA. . 1983 Nature 304: 596–602.
Leone G, DeGregori J, Jakoi L, Cook JG and Nevins JR. . 1999 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96: 6626–6631.
Leone G, DeGregori J, Sears R, Jakoi L and Nevins JR. . 1997 Nature 387: 422–426.
Nesbit CE, Tersak JM and Prochownik EV. . 1999 Oncogene 18: 3004–3016.
Perez-Roger I, Kim SH, Griffiths B, Sewing A and Land H. . 1999 EMBO J. 18: 5310–5320.
Santoni-Rugiu E, Falck J, Mailand N, Bartek J and Lukas J. . 2000 Mol. Cell. Biol. 20: 3497–3509.
Sears R, Ohtani K and Nevins JR. . 1997 Mol. Cell. Biol. 17: 5227–5235.
Steiner P, Philipp A, Lukas J, Godden KD, Pagano M, Mittnacht S, Bartek J and Eilers M. . 1995 EMBO J. 14: 4814–4826.
Vlach J, Hennecke S, Alevizopoulos K, Conti D and Amati B. . 1996 EMBO J. 15: 6595–6604.
Zhu L, Xie E and Chang LS. . 1995 Mol. Cell. Biol. 15: 3552–3562.
Acknowledgements
We thank P Leder and J Roberts for generously supplying the p21 KO and p27 KO mice, respectively. B Scheijen for providing various knockout MEFs, F Michiels (Introgene, Leiden) for providing the Ad-LacZ and Ad-MadMyc adenoviruses, EAJ Reits for optimizing electroporation conditions, AS Pfauth and E Noteboom for their excellent assistance with FACS analyses. This work was funded by the Dutch Cancer Society and a Portuguese grant: PGDBM e praxis XXI to Carla Martins.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berns, K., Martins, C., Dannenberg, JH. et al. p27kip1-independent cell cycle regulation by MYC. Oncogene 19, 4822–4827 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203879
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203879